Abstract
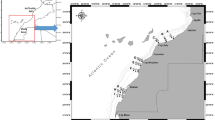
Toxic metal and trace element levels in the ocean are increasing heterogeneously in the world, which is why it is important to assess their concentrations in organisms of fishing interest. The study of metal concentrations in different fishing grounds is of vital importance for nutritional control. In this study, two fishing grounds have been studied, in the Canary Islands and in Portugal, in each area 50 muscle samples have been taken from each of the studied species, Scomber colias, Sardina pilchardus, and Trachurus species from the Canary Islands (T. picturatus) and Portuguese (T. trachurus). The concentrations of Cd, Pb, Cr, Cu, V and Zn have been analyzed in mg / kg. Cd and Pb concentrations are higher in the species from the Canary Islands and may be linked to the African upwelling inputs, which greatly influence the metal concentrations of the species. The species with the highest concentration of metals and trace elements are influenced by the anthropogenic action of coastal pollution and the natural action of African upwelling and Saharan dust. The Cd and Pb concentrations determined in the muscle tissue of S. colias, T. picturatus, T. trachurus and S. pilchardus are below the maximum permitted limits set by the current legislation, and are, therefore, suitable for human consumption. But supporting very little nutritional percentage of the elements studied.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AECOSAN (2006) Spanish diet model for the determination of consumer exposure to chemical substances. Ministry of Health and Consumption, Madrid
Afonso A, Gutiérrez ÁJ, Lozano G, González-Weller D, Lozano-Bilbao E, Rubio C, Caballero JM, Revert C, Hardisson A (2018) Metals in Diplodus sargus cadenati and Sparisoma cretense—a risk assessment for consumers. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0697-4
Afonso A, Gutiérrez AJ, Lozano G, González-weller D, Rubio C, Caballero JM, Hardisson A, Revert C (2017) Determination of toxic metals, trace and essentials, and macronutrients in Sarpa salpa and Chelon labrosus: risk assessment for the consumers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:10557–10569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8741-y
Al-Taani AA, Rashdan M, Khashashneh S (2015) Atmospheric dry deposition of mineral dust to the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea: Rate and trace elements. Mar Pollut Bull 92:252–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.11.047
Ali H, Khan E, Ilahi I (2019) Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J Chem
Anandkumar A, Nagarajan R, Prabakaran K, Rajaram R (2017) Trace metal dynamics and risk assessment in the commercially important marine shrimp species collected from the Miri coast, Sarawak, East Malaysia. Reg Stud Mar Sci 16:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2017.08.007
Anderson M, Braak CT (2003) Permutation tests for multi-factorial analysis of variance. J Stat Comput Simul 73:85–113. https://doi.org/10.1080/00949650215733
Anderson MR (2004) The Resource for the Power Industry Professional. Proc ASME POWER 32
Aral H, Vecchio-Sadus A (2008) Toxicity of lithium to humans and the environment—A literature review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 70:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.02.026
Atici T, Ahiska S, Altinda A (2008) Ecological effects of some heavy metals (Cd, Pb, H, Cr) pollution of phytoplanktonic algae and zooplanktonic organisms in Sarıyar Dam Reservoir in Turkey. 7:1972–1977
Atici T, Obali O, Altindag A, Ahiska S, Aydin D (2010) The accumulation of heavy metals ( Cd, Pb, Hg, Cr ) and their state in phytoplanktonic algae and zooplanktonic organisms in Beysehir Lake and Mogan Lake, Turkey. 9:475–487
Auger PA, Machu E, Gorgues T, Grima N, Waeles M (2015) Comparative study of potential transfer of natural and anthropogenic cadmium to plankton communities in the North-West African upwelling. Sci Total Environ 505:870–888
Barton ED, Arı́stegui J, Tett P, Cantón M, Garcı́a-Braun J, Hernández-León S, Nykjaer L, Almeida C, Almunia J, Ballesteros S, Basterretxea G, Escánez J, Garcı́a-Weill L, Hernández-Guerra A, López-Laatzen F, Molina R, Montero MF, Navarro-Pérez E, Rodrı́guez JM, van Lenning K, Vélez H, Wild K (1998) The transition zone of the Canary Current upwelling region. Prog Oceanogr 41:455–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6611(98)00023-8
Canli M, Atli G (2003) The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ Pollut 121:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00194-X
Christensen V, Coll M, Piroddi C, Steenbeek J, Buszowski J, Pauly D (2014) A century of fish biomass decline in the ocean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 512:155–166
Davenport R, Neuer S, Helmke P, Perez-Marrero J, Llinas O (2002) Primary productivity in the northern Canary Islands region as inferred from SeaWiFS imagery. Deep. Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 49:3481–3496. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-0645(02)00095-4
Dehn LA, Follmann EH, Thomas DL, Sheffield GG, Rosa C, Duffy LK, O’Hara TM (2006) Trophic relationships in an Arctic food web and implications for trace metal transfer. Sci Total Environ 362(1–3):103–123
EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) (2009) Scientific opinion of the panel on contaminants in the food chain. EFSA J 980:1–139
FESNAD (2010) Ingestas Dietéticas de Referencia (IDR) para la Población Española, 2010. Act Diet 14(4):196–197
Fujiwara M (2012) Demographic diversity and sustainable fisheries. PLoS One 7. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034556
Genthe B, Kapwata T, Le Roux W, Chamier J, Wright CY (2018) The reach of human health risks associated with metals/metalloids in water and vegetables along a contaminated river catchment: South Africa and Mozambique. Chemosphere 199:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.01.160
Gilby BL, Olds AD, Hardcastle FE, Henderson CJ, Connolly RM, Martin TS, Schlacher TA (2020) Diverse land uses and high coastal urbanisation do not always result in harmful environmental pollutants in fisheries species. Mar Pollut Bull 159:111487
Gray JS (2002) Biomagnification in marine systems: the perspective of an ecologist. Mar Pollut Bull 45(1–12):46–52
Hathcock JN (1996) Safety limits for nutrients. J Nutr 126(suppl_9):2386S–2389S
Hilborn R, Branch TA, Ernst B, Magnusson A, Minte-Vera CV, Scheuerell MD, Valero JL (2003) State of the world’s fisheries. Annu Rev Environ Resour 28(1):359–399
Islam MS, Tanaka M (2004) Impacts of pollution on coastal and marine ecosystems including coastal and marine fisheries and approach for management: a review and synthesis. Mar Pollut Bull 48(7–8):624–649
Kobayashi N, Okamura H (2005) Effects of heavy metals on sea urchin embryo development. Part 2. Interactive toxic effects of heavy metals in synthetic mine effluents. Chemosphere 61:1198–1203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.071
Lozano-Bilbao E, Alcázar-Treviño J, Fernández JJ (2018a) Determination of δ15N in Anemonia sulcata as a pollution bioindicator. Ecol Indic. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.03.017
Lozano-Bilbao E, Clemente S, Espinosa JM, Jurado-Ruzafa A, Lozano G, Raimundo J, Hardisson A, Rubio C, González-Weller D, Jiménez S, Gutiérrez ÁJ (2019a) Inferring trophic groups of fish in the central-east Atlantic from eco-toxicological characterization. Chemosphere 229:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.218
Lozano-Bilbao E, Díaz Y, Lozano G, Jurado-Ruzafa A, Hardisson A, Rubio C, Jiménez S, González-Weller D, Gutiérrez ÁJ (2019b) Metal Content in Small Pelagic Fish in the North-West Africa. An Int J Mar Sci Thalass. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-019-00141-7
Lozano-Bilbao E, Espinosa JM, Jurado-Ruzafa A, Lozano G, Hardisson A, Rubio C, Weller DG, Gutiérrez ÁJ, González Weller D, Gutiérrez ÁJ (2020a) Inferring Class of organisms in the Central-East Atlantic from eco-toxicological characterization. Reg Stud Mar Sci 35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101190
Lozano-Bilbao E, Espinosa JM, Lozano G, Hardisson A, Rubio C, González-Weller D, Gutiérrez ÁJ (2020b) Determination of metals in Anemonia sulcata (Pennant, 1777) as a pollution bioindicator. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08684-6
Lozano-Bilbao E, Jurado-Ruzafa A, Lozano G, Jiménez S, Hardisson A, Rubio C, Weller DG, Paz S, Gutiérrez ÁJ (2020c) Development stage and season influence in the metal content of small pelagic fish in the North-West Africa. Chemosphere 261:127692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127692
Lozano-Bilbao E, Lozano G, Jiménez S, Jurado-Ruzafa A, Hardisson A, Rubio C, Weller D-G, Paz S, Gutiérrez ÁJ (2020d) Seasonal and ontogenic variations of metal content in the European pilchard (Sardina pilchardus) in northwestern African waters. Environ Pollut 266:115113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115113
Lozano-Bilbao E, Lozano G, Jiménez S, Jurado-Ruzafa A, Hardisson A, Rubio C, Weller DG, Paz S, Gutiérrez ÁJ (2020e) Influence of Biometric and Seasonal Parameters on the Metal Content of Scomber colias in Northwestern African Waters. Biological Trace Element Research. 1–12
Lozano-Bilbao E, Gutiérrez ÁJ, Hardisson A, Rubio C, González-Weller D, Aguilar N, Escánez A, Espinosa JM, Canales P, Lozano G (2018b) Influence of the submarine volcanic eruption off El Hierro (Canary Islands) on the mesopelagic cephalopod’s metal content. Mar Pollut Bull 129:474–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.10.017
Lozano-Bilbao E, Lozano G, Gutiérrez ÁJ, Rubio C, Hardisson A (2018c) Mercury, cadmium, and lead content in demersal sharks from the Macaronesian islands. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:21251–21256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2550-9
Lozano-Bilbao E, Viñé R, Lozano G, Hardisson A, Rubio C, González-Weller D, Matos-Perdomo E, Gutiérrez ÁJ (2019c) Metal content in Mullus surmuletus in the Canary Islands (North-West African Atlantic). Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05365-x
Meyers LD, Hellwig JP, Otten JJ (2006) Dietary reference intakes: the essential guide to nutrient requirements. National Academies Press
Nixon SW (1995) Coastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 41(1):199–219
Ohde T, Siegel H (2010) Biological response to coastal upwelling and dust deposition in the area off Northwest Africa. Cont Shelf Res 30:1108–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2010.02.016
Pérez FF, Mintrop L, Llinas O, Glez-Dávila M, Castro CG, Alvarez M, Rıos AF (2001) Mixing analysis of nutrients, oxygen and inorganic carbon in the Canary Islands region. J Mar Syst 28(3–4):183–201
Plessl C, Otachi EO, Körner W, Avenant-Oldewage A, Jirsa F (2017) Fish as bioindicators for trace element pollution from two contrasting lakes in the Eastern Rift Valley, Kenya: spatial and temporal aspects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19767–19776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9518-z
Raimundo J, Vale C, Caetano M, Giacomello E, Anes B, Menezes GM (2013) Natural trace element enrichment in fishes from a volcanic and tectonically active region (Azores archipelago). Deep Sea Res Part II Top Stud Oceanogr 98:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.02.009
Reglamento (CE) No (1881/2006) DE LA COMISIÓN de 19 de diciembre de 2006 por el que se fija el contenido máximo de determinados contaminantes en los productos alimenticios. Diario Oficial de la Unión Europea. L 364/5 20.12.2006
Reglamento (UE) No (488/2014) DE LA COMISIÓN de 12 de mayo de 2014 que modifica el Reglamento (CE) no 1881/2006 por lo que respecta al contenido máximo de cadmio en los productos alimenticios
Reglamento (UE) (2015/1005) DE LA COMISIÓN de 25 de junio de 2015 que modifica el Reglamento (CE) no 1881/2006 por lo que respecta al contenido máximo de plomo en determinados productos alimenticios
Renwick AG (1991) Safety factors and establishment of acceptable daily intakes. Food Addit Contam 8(2):135–149
Rubio C, Acosta L, Luis-González G, González-Weller D, Revert C, Hardisson A, Gutiérrez Á (2018) A Limited Survey of Metal Content in Blue Jack Mackerel (Trachurus picturatus) Obtained from Markets in the Canary Islands. J Food Prot 81:202–208. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-17-181
Song Q, Li J (2014) A systematic review of the human body burden of e-waste exposure in China. Environ Int 68:82–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.03.018
Steer M, Cole M, Thompson RC, Lindeque PK (2017) Microplastic ingestion in fish larvae in the western English Channel. Environ Pollut 226:250–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.062
Tillitt DE, Gale RW, Meadows JC, Zajicek JL, Peterman PH, Heaton SN (1996) Dietary exposure of mink to carp from Saginaw Bay 3, characterization of dietary exposure to planar halogenated hydrocarbons, dioxin equivalents, and biomagnifications
Topcuo S (2003) Heavy Metal Monitoring of Marine Algae from the Turkish Coast of the Black Sea 1998–2000(52):1683–1688. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00301-1
Tsikliras AC, Froese R (2019) Maximum sustainable yield. Encyclopedia of Ecology 1:108–115
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1995) Great lakes water quality initiative criteria documents for the protection of wildlife. EPA-820\b-95\008, Office of Water, Washington, D.C
Vikas M, Dwarakish GS (2015) Coastal Pollution: a review. Aquatic Procedia 4:381–388
Waeles M, Planquette H, Afandi I, Delebecque N, Bouthir F, Donval A, Tito de Morais L (2016) Cadmium in the waters off South Morocco: Nature of particles hosting Cd and insights into the mechanisms fractionating Cd from phosphate. J Geophys Res: Oceans 121(5):3106–3120
Watson RA, Cheung WWL, Anticamara JA, Sumaila RU, Zeller D, Pauly D (2013) Global marine yield halved as fishing intensity redoubles. Fish Fish 14:493–503. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2979.2012.00483.x
Acknowledgements
Fish acquisition and samplings from Portugal were carried out in the framework of project CEIC—Contaminants in commercially important marine species (CEIC-MAR-01.04.02-FEAMP-0012) funded by program MAR2020. Fish acquisition and samplings from Canary Island were carried out in the framework of the Spanish National Program of collection, management and use of data in the fisheries sector and support for scientific advice regarding the Common Fisheries Policy, partially funded by the European Union through the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund (EMFF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that the use of animals for this research complies with the requirements of European legislation on the use of animals for experimentation. All the fish samples collected were provided by the fishermen in the fish markets, so these fish were not slaughtered by the authors of this manuscript, therefore we faithfully comply with the Code of Practice for Housing and Care of Animals Used in Scientific Procedures.
Credit Author Statement
Introduction: ELB, GL, SJ, AH, CR. Material and Methods: ELB, JR, AJR, AJG, DGW. Results and Discussion: ELB, JR, AJR, GL, SJ, AH, CR, DGW, SP, AJG. Conclusions: ELB, JR, AJR, GL, SJ, AH, CR, DGW, SP, AJG.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lozano-Bilbao, E., Raimundo, J., Jurado-Ruzafa, A. et al. Comparing Element Content in Small Pelagic Fish Species from Different Fishing Grounds in the Central-East Atlantic Ocean. Risk Assessment. Thalassas 37, 861–869 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-021-00340-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-021-00340-1