Abstract
Purpose
Pellino3, an ubiquitin E3 ligase, prevents the formation of the death-induced signaling complex in response to TNF-α by targeting receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1), and bioinformatics analysis predicted an interaction between Pellino3 and caspofungin, a common antifungal drug used in clinics. This study aimed to explore the effect of caspofungin on brain injury in ischemic stroke and the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
Ischemic stroke injury was induced in Sprague Dawley rats by occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) for 2 h, followed by 24 h reperfusion. PC12 cells were deprived of both oxygen and glucose for 8 h and then were cultured for 24 h with oxygen and glucose to mimic an ischemic stroke in vitro.
Results
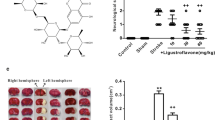
Animal experiments showed brain injury (increase in neurological deficit score and infarct volume) concomitant with a downregulation of Pellino3, a decreased ubiquitination of RIPK1, and an up-regulation of necroptosis-associated proteins [RIPK1, RIPK3, mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL), p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3, and p-MLKL]. Administration of caspofungin (6 mg/kg, i.m.) at 1 h and 6 h after ischemia significantly improved neurological function, reduced infarct volume, up-regulated Pellino3 levels, increased RIPK1 ubiquitination, and down-regulated protein levels of RIPK1, p-RIPK1, p-RIPK3, and p-MLKL. PC12 cells deprived of oxygen/glucose developed signs of cellular injury (LDH release and necroptosis) concomitant with downregulation of Pellino3, decreased ubiquitination of RIPK1, and elevated necroptosis-associated proteins. These changes were reversed by overexpression of Pellino3.
Conclusion
We conclude that Pellino3 has an important role in counteracting necroptosis via ubiquitination of RIPK1 and caspofungin can suppress the brain cell necroptosis in ischemic stroke through upregulation of Pellino3.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data are available upon request.
References
Brewer L, Horgan F, Hickey A, Williams D. Stroke rehabilitation: recent advances and future therapies. QJM-Mon J Assoc Phys. 2013;106:11–25.
Feigin VL, Nguyen G, Cercy K, Johnson CO, Roth GA. Global, regional, and country-specific lifetime risks of stroke, 1990 and 2016. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2429–37.
Wu MY, Yiang GT, Liao WT, Tsai AP, Cheng YL, Cheng PW, et al. Current mechanistic concepts in ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46:1650–67.
Datta A, Sarmah D, Mounica L, Kayr H, Bhattacharya P. Cell death pathways in ischemic stroke and targeted pharmacotherapy. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11:1185–202.
Khan I, Yousif A, Chesnokov M, Hong L, Chefetz I. A decade of cell death studies: breathing new life into necroptosis. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;220(8):107717.
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Chan KM, Kroemer G. Necroptosis: mechanisms and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2017;12:103–30.
Yang S, Wang B, Tang LS, Siednienko J, Callanan JJ, Moynagh PN. Pellino3 targets RIP1 and regulates the pro-apoptotic effects of TNF-α. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2583.
Song JC, Stevens DA. Caspofungin: pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses and treatment outcomes. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42:813–46.
Ren KD, Liu WN, Tian J, Zhang YY, Peng JJ, Zhang D, et al. Mitochondrial E3 ubiquitin ligase 1 promotes brain injury by disturbing mitochondrial dynamics in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;861:172617.
Cui N, Lu H, Li M, Yan Q. PTPN21 protects PC12 cell against oxygen-glucose deprivation by activating cdk5 through ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;814:226–31.
Lu LQ, Tian J, Luo XJ, Peng J. Targeting the pathways of regulated necrosis: a potential strategy for alleviation of cardio-cerebrovascular injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78:63–78.
Kim EH, Wong SW, Martinez J. Programmed necrosis and disease: we interrupt your regular programming to bring you necroinflammation. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26:25–40.
Yuan J, Amin P, Ofengeim D. Necroptosis and RIPK1-mediated neuroinflammation in CNS diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019;20:19–33.
Zhang YY, Liu WN, Li YQ, Zhang XJ, Yang J, Luo XJ, et al. Ligustroflavone reduces necroptosis in rat brain after ischemic stroke through targeting RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL pathway. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol. 2019;392:1085–95.
Naito MG, Xu D, Amin P, Lee J, Wang H, Li W, et al. Sequential activation of necroptosis and apoptosis cooperates to mediate vascular and neural pathology in stroke. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117:4959–70.
Jun-Long H, Yi L, Bao-Lian Z, Jia-Si L, Ning Z, Zhou-Heng Y, et al. Necroptosis signaling pathways in stroke: from mechanisms to therapies. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16:1327–39.
Zhang Y, Li M, Li X, Zhang H, Wang L, Wu X, et al. Catalytically inactive RIP1 and RIP3 deficiency protect against acute ischemic stroke by inhibiting necroptosis and neuroinflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:565.
Yang X, Yi TL, Zhang S, Xu ZW, Yu ZQ, Sun HT, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha is involved in RIP-induced necroptosis caused by in vitro and in vivo ischemic brain injury. Sci Rep. 2017;7:5818.
Deng XX, Li SS, Sun FY. Necrostatin-1 prevents necroptosis in brains after ischemic stroke via inhibition of RIPK1-mediated RIPK3/MLKL signaling. Aging Dis. 2019;10:807–17.
Tian J, Guo S, Chen H, Peng JJ, Jia MM, Li NS, et al. Combination of Emricasan with Ponatinib synergistically reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat brain through simultaneous prevention of apoptosis and necroptosis. Transl Stroke Res. 2018;9:382–92.
Itoh K, Shigemi H, Chihara K, Sada K, Yamauchi T, Iwasaki H. Caspofungin suppresses zymosan-induced cytokine and chemokine release in THP-1 cells: possible involvement of the spleen tyrosine kinase pathway. Transl Res. 2021;227:53–63.
Liang H, Matei N, McBride DW, Xu Y, Zhou Z, Tang J, et al. TGR5 activation attenuates neuroinflammation via Pellino3 inhibition of caspase-8/NLRP3 after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18:40.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82073849 to Xiu-Ju Luo, China, No. 81872873 to Jun Peng, China), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (No. 2020JJ4770 to Jun Peng, China; No. 2020JJ4835 to Zhong-Yang Hu, China), Changsha Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. kq2014145 to Xiu-Ju Luo, China), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (No. 2021zzts0329 to Yi-Yue Zhang, China; No. 1053320184093 to Jing Tian, China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jun Peng, Xiu-Ju Luo, and Xiao-Jie Zhang conceived and designed the study. Yi-Yue Zhang, Jing Tian, Zi-Mei Peng, and Ya-Wei Peng conducted the experiments. Yi-Yue Zhang, Bin Liu, and Zhong-Yang Hu analyzed the data. Yi-Yue Zhang, Xiu-Ju Luo, and Jun Peng wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants.
Consent for Publication
All authors approved its publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 438 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YY., Tian, J., Peng, ZM. et al. Caspofungin Suppresses Brain Cell Necroptosis in Ischemic Stroke Rats via Up-Regulation of Pellino3. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 37, 9–23 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-021-07231-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-021-07231-w