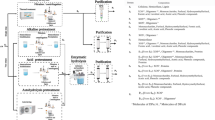
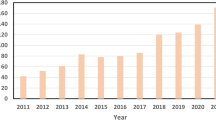
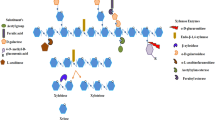
Abstract
The majority of lignocellulosic biomass on the planet originates from plant cell walls, which are complex structures build up mainly by cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. The largest part of hemicellulose, xylan, is a polymer with a β-(1→4)-linked xylose residues backbone decorated with α-D-glucopyranosyl uronic acids and/or L-arabinofuranose residues. Xylan is the second most abundant biopolymer in nature, which can be sustainably and efficiently degraded into decorated and undecorated xylooligosaccharides (XOS) using combinations of thermochemical pretreatments and enzymatic hydrolyses, that have broad applications in the food, feed, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. Endo-xylanases from different complex carbohydrate-active enzyme (CAZyme) families can be used to cleave the backbone of arabino(glucurono)xylans and xylooligosaccharides and degrade them into short XOS. It has been shown that XOS with a low degree of polymerization have enhanced prebiotic effects conferring health benefits to humans and animals. In this review we describe recent advances in the enzymatic production of XOS from lignocellulosic biomass arabino- and glucuronoxylans and their applications as food and feed additives and health-promoting ingredients. Comparative advantages of xylanases from different CAZy families in XOS production are discussed and potential health benefits of different XOS are presented.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aachary AA, Prapulla SG (2011) Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) as an Emerging Prebiotic: Microbial Synthesis, Utilization, Structural Characterization, Bioactive Properties, and Applications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 10:2–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2010.00135.x
Agrawal R, Verma A, Singhania RR et al (2021) Current understanding of the inhibition factors and their mechanism of action for the lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 332:125042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125042
Amorim C, Silvério SC, Cardoso BB et al (2020) In vitro assessment of prebiotic properties of xylooligosaccharides produced by Bacillus subtilis 3610. Carbohydr Polym 229:115460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115460
Amorim C, Silvério SC, Prather KLJ, Rodrigues LR (2019) From lignocellulosic residues to market: production and commercial potential of xylooligosaccharides. Biotechnol Adv 37:107397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.05.003
Aronsson A, Güler F, Petoukhov MV et al (2018) Structural insights of RmXyn10A—a prebiotic-producing GH10 xylanase with a non-conserved aglycone binding region. Biochim Biophys Acta 1866:292–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2017.11.006
Aspeborg H, Coutinho PM, Wang Y et al (2012) Evolution, substrate specificity and subfamily classification of glycoside hydrolase family 5 (GH5). BMC Evol Biol 12:186. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-12-186
Associação Brasileira da Indústria de Higiene Pessoal Perfumaria e Cosméticos, and Serviço Brasileiro de Apoio às Micro e Pequenas Empresas. 2018. Caderno de Tendências 2019–2020. Accessed https://abihpec.org.br/publicacao/caderno-de-tendencias-2019-2020/
Berg G, Rybakova D, Fischer D et al (2020) Microbiome definition re-visited: old concepts and new challenges. Microbiome 8:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-020-00875-0
Biely P, Singh S, Puchart V (2016) Towards enzymatic breakdown of complex plant xylan structures: State of the art. Biotechnol Adv 34:1260–1274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.09.001
Brandt A, Gräsvik J, Hallett JP, Welton T (2013) Deconstruction of lignocellulosic biomass with ionic liquids. Green Chem 15:550–848. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2gc36364j
Brienzo M, Flavia A, Carvalho A et al (2016) Sugarcane bagasse hemicellulose properties, extraction technologies and xylooligosaccharide production. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppage
Briganti L, Capetti C, Pellegrini VOA et al (2021) Structural and molecular dynamics investigations of ligand stabilization via secondary binding site interactions in Paenibacillus xylanivorans GH11 xylanase. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19:1557–1566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2021.03.002
Broekaert WF, Courtin CM, Verbeke K et al (2011) Prebiotic and Other Health-Related Effects of Cereal-Derived Arabinoxylans, Arabinoxylan-Oligosaccharides, and Xylooligosaccharides. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 51:178–194. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390903044768
Bustamante M, Oomah BD, Oliveira WP et al (2020) Probiotics and prebiotics potential for the care of skin, female urogenital tract, and respiratory tract. Folia Microbiol 65:245–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00759-3
Byrd AL, Belkaid Y, Segre JA (2018) The human skin microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:143–155. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.157
Carvalho AFA, Neto P, de O, da Silva DF, Pastore GM (2013) Xylo-oligosaccharides from lignocellulosic materials: Chemical structure, health benefits and production by chemical and enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Res Int 51:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2012.11.021
Chanda SK, Hirst EL, Jones JKN, Percival EGV (1950) The constitution of xylan from esparto grass (Stipa tenacissima L.). J Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1039/jr9500001289
Chu Y, Hao Z, Wang K et al (2019) The GH10 and GH48 dual-functional catalytic domains from a multimodular glycoside hydrolase synergize in hydrolyzing both cellulose and xylan. Biotechnol Biofuels 121:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13068-019-1617-2
Correia MAS, Mazumder K, Brás JLA et al (2011) Structure and Function of an Arabinoxylan-specific Xylanase. J Biol Chem 286:22510–22520. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.217315
de Freitas C, Carmona E, Brienzo M (2019) Xylooligosaccharides production process from lignocellulosic biomass and bioactive effects. Bioact Carbohydrates Diet Fibre 18:100184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcdf.2019.100184
de Souza AP, Kamei CLA, Torres AF et al (2015) How cell wall complexity influences saccharification efficiency in Miscanthus sinensis. J Exp Bot 66:4351–4365. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv183
Ding XM, Li DD, Bai SP et al (2018) Effect of dietary xylooligosaccharides on intestinal characteristics, gut microbiota, cecal short-chain fatty acids, and plasma immune parameters of laying hens. Poult Sci 97:874–881. https://doi.org/10.3382/ps/pex372
Espirito Santo M, Rezende CA, Bernardinelli OD et al (2018) Structural and compositional changes in sugarcane bagasse subjected to hydrothermal and organosolv pretreatments and their impacts on enzymatic hydrolysis. Ind Crops Prod 113:64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.01.014
Evangelista DE, de Oliveira Arnoldi Pellegrini V, Santo ME et al (2019) Biochemical characterization and low-resolution SAXS shape of a novel GH11 exo-1,4-β-xylanase identified in a microbial consortium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:8035–8049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10033-8
Falck P, Aronsson A, Grey C et al (2014) Production of arabinoxylan-oligosaccharide mixtures of varying composition from rye bran by a combination of process conditions and type of xylanase. Bioresour Technol 174:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.139
Falck P, Linares-Pastén JA, Karlsson EN, Adlercreutz P (2018) Arabinoxylanase from glycoside hydrolase family 5 is a selective enzyme for production of specific arabinoxylooligosaccharides. Food Chem 242:579–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.048
Fehlbaum S, Prudence K, Kieboom J et al (2018) In Vitro Fermentation of Selected Prebiotics and Their Effects on the Composition and Activity of the Adult Gut Microbiota. Int J Mol Sci 19:3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103097
Fei Y, Wang Y, Pang Y et al (2020) Xylooligosaccharide Modulates Gut Microbiota and Alleviates Colonic Inflammation Caused by High Fat Diet Induced Obesity. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01601
FDA (2010) U.S. Food and Drug Administration GRAS Not., 343. https://www.cfsanappsexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=GRASNotices&id=343. Accessed 17 Apr 2021
FDA (2013) U.S. Food and Drug Administration GRAS Not., 458. https://www.cfsanappsexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=GRASNotices&id=458. Accessed 17 Apr 2021
FDA (2019) U.S. Food and Drug Administration GRAS Not., 816. https://www.cfsanappsexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=GRASNotices&id=816. Accessed 17 Apr 2021
Fundador NGV, Enomoto-Rogers Y, Takemura A, Iwata T (2012) Acetylation and characterization of xylan from hardwood kraft pulp. Carbohydr Polym 87:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.07.034
Garrote G, Domínguez H, Parajó JC (1999) Mild autohydrolysis: An environmentally friendly technology for xylooligosaccharide production from wood. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 74:1101–1109
Ghio S, Ontañon O, Piccinni FE et al (2018) Paenibacillus sp. A59 GH10 and GH11 Extracellular Endoxylanases: Application in Biomass Bioconversion. Bioenergy Res 11:174–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-017-9887-7
Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ME et al (2017) Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:491–502. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2017.75
Gilmore SP, Lillington SP, Haitjema CH et al (2020) Designing chimeric enzymes inspired by fungal cellulosomes. Synth Syst Biotechnol 5:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2020.01.003
Global Xylooligosaccharide (Xylo-Oligosaccharide, XOS) Market outlook 2019-202 (2019). Available at https://www.asdreports.com/market-research-report-485534/global-xylooligosaccharide-xylo-oligosaccharide-xos-market-outlook
Gowdhaman D, Ponnusami V (2015) Production and optimization of xylooligosaccharides from corncob by Bacillus aerophilus KGJ2 xylanase and its antioxidant potential. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.05.046
Grice EA, Segre JA (2011) The skin microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:244–253. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2537
Grootaert C, Verstraete W, Van de Wiele T (2007) Microbial metabolism and prebiotic potency of arabinoxylan oligosaccharides in the human intestine. Trends Food Sci Technol 18:64–71
Hansen CHF, Frøkiær H, Christensen AG et al (2013) Dietary Xylooligosaccharide Downregulates IFN-γ and the Low-Grade Inflammatory Cytokine IL-1β Systemically in Mice. J Nutr 143:533–540. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.112.172361
Jones DR, Thomas D, Alger N et al (2018) SACCHARIS: An automated pipeline to streamline discovery of carbohydrate active enzyme activities within polyspecific families and de novo sequence datasets. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1027-x
Klein-Marcuschamer D, Oleskowicz-Popiel P, Simmons BA, Blanch HW (2012) The challenge of enzyme cost in the production of lignocellulosic biofuels. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:1083–1087. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24370
Krishna G, Divyashri G, Prapulla SG, Muralidhara (2015) A Combination Supplement of Fructo- and Xylo-Oligosaccharides Significantly Abrogates Oxidative Impairments and Neurotoxicity in Maternal/Fetal Milieu Following Gestational Exposure to Acrylamide in Rat. Neurochem Res 40:1904–1918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1687-x
Labourel A, Crouch LI, Brás JLA et al (2016) The Mechanism by Which Arabinoxylanases Can Recognize Highly Decorated Xylans. J Biol Chem 291:22149–22159. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.743948
Li Z, Li X, Liu T et al (2019) The critical roles of exposed surface residues for the thermostability and halotolerance of a novel GH11 xylanase from the metagenomic library of a saline-alkaline soil. Int J Biol Macromol 133:316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.090
Lin S-H, Chou L-M, Chien Y-W et al (2016) Prebiotic Effects of Xylooligosaccharides on the Improvement of Microbiota Balance in Human Subjects. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2016:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5789232
Linares-Pasten JA, Aronsson A, Karlsson EN (2016) Structural Considerations on the Use of Endo-Xylanases for the Production of prebiotic Xylooligosaccharides from Biomass. Curr Protein Pept Sci 19:48–67. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203717666160923155209
Maeda R, Ida T, Ihara H, Sakamoto T (2012) Induction of Apoptosis in MCF-7 Cells by β-1,3-Xylooligosaccharides Prepared from Caulerpa lentillifera. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76:1032–1034. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.120016
Markets and Markets (2018) Prebiotic ingredients market by type (oligosaccharides, inulin, and polydextrose), application (food & beverages, dietary supplements, and animal feed), source (roots, grains, and vegetables), and region-global forecast to 2023. https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/prebiotics-ingredients-market-219677001.html. Accessed 17 Apr 2021
Mello BL, Alessi AM, Riaño-Pachón DM et al (2017) Targeted metatranscriptomics of compost-derived consortia reveals a GH11 exerting an unusual exo-1,4-β-xylanase activity. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:254. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0944-4
Montanier CY, Correia MAS, Flint JE et al (2011) A Novel, Noncatalytic Carbohydrate-binding Module Displays Specificity for Galactose-containing Polysaccharides through Calcium-mediated Oligomerization. J Biol Chem 286:22499–22509. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.217372
Morgan NK, Wallace A, Bedford MR, Choct M (2017) Efficiency of xylanases from families 10 and 11 in production of xylo-oligosaccharides from wheat arabinoxylans. Carbohydr Polym 167:290–296
Morrison DJ, Preston T (2016) Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 7:189–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2015.1134082
Naidu DS, Hlangothi SP, John MJ (2018) Bio-based products from xylan: A review. Carbohydr Polym 179:28–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.09.064
Nieto-Domínguez M, de Eugenio LI, York-Durán MJ et al (2017a) Prebiotic effect of xylooligosaccharides produced from birchwood xylan by a novel fungal GH11 xylanase. Food Chem 232:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.03.149
Nordberg Karlsson E, Schmitz E, Linares-Pastén JA, Adlercreutz P (2018) Endo-xylanases as tools for production of substituted xylooligosaccharides with prebiotic properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:9081–9088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9343-4
Paës G, Berrin JG, Beaugrand J (2012) GH11 xylanases: Structure/function/properties relationships and applications. Biotechnol Adv 30:564–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.10.003
Pinales-Márquez CD, Rodríguez-Jasso RM, Araújo RG et al (2021) Circular bioeconomy and integrated biorefinery in the production of xylooligosaccharides from lignocellulosic biomass: A review. Ind Crops Prod 162:113274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113274
Puchart V, Šuchová K, Biely P (2021) Xylanases of glycoside hydrolase family 30—An overview. Biotechnol Adv 47:107704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107704
Rezende C, de Lima M, Maziero P et al (2011) Chemical and morphological characterization of sugarcane bagasse submitted to a delignification process for enhanced enzymatic digestibility. Biotechnol Biofuels 4:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-4-54
Saleh SAA, Abdel Wahab WA, El-Dein AN et al (2021) Characterization of Aspergillus niger MK981235 xylanase with extraction of anti-hepatotoxic, antioxidant, hypocholesterolemic and prebiotic Corchorus olitorius stems xylooligosaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol 166:677–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.225
Santibáñez L, Henríquez C, Corro-Tejeda R et al (2021) Xylooligosaccharides from lignocellulosic biomass: A comprehensive review. Carbohydr Polym 251:117118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117118
Senatore A, Corrente GA, Verteramo F, Dalena F (2021) An overview on pretreatment processes for an effective conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into bioethanol. Advances in bioenergy and microfluidic applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 41–68
Sepulchro AGV, Pellegrini VOA, Briganti L et al (2020) Transformation of xylan into value-added biocommodities using Thermobacillus composti GH10 xylanase. Carbohydr Polym 247:116714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116714
St John FJ, Dietrich D, Crooks C et al (2014) A novel member of glycoside hydrolase family 30 subfamily 8 with altered substrate specificity. Acta Crystallogr Sect D 70:2950–2958. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714019531
St John FJ, González JM, Pozharski E (2010) Consolidation of glycosyl hydrolase family 30: A dual domain 4/7 hydrolase family consisting of two structurally distinct groups. FEBS Lett 584:4435–4441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2010.09.051
St John FJ, Hurlbert JC, Rice JD et al (2011) Ligand Bound Structures of a Glycosyl Hydrolase Family 30 Glucuronoxylan Xylanohydrolase. J Mol Biol 407:92–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2011.01.010
Talens-Perales D, Jiménez-Ortega E, Sánchez-Torres P et al (2021) Phylogenetic, functional and structural characterization of a GH10 xylanase active at extreme conditions of temperature and alkalinity. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19:2676–2686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2021.05.004
Talens-Perales D, Sánchez-Torres P, Marín-Navarro J, Polaina J (2020) In silico screening and experimental analysis of family GH11 xylanases for applications under conditions of alkaline pH and high temperature. Biotechnol Biofuels 13:198. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-020-01842-5
The Market Reports (2021) Global Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) Market Research Report 2021. https://www.themarketreports.com/report/global-xylooligosaccharides-xos-market-research-report. Accessed 17 Apr 2021
Törrönen A, Harkki A, Rouvinen J (1994) Three-dimensional structure of endo-1,4-β-xylanase II from Trichoderma reesei: Two conformational states in the active site. EMBO J 13:2493–2501. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06536.x
Urbániková Ľ, Vršanská M, Mørkeberg Krogh KBR et al (2011) Structural basis for substrate recognition by Erwinia chrysanthemi GH30 glucuronoxylanase. FEBS J 278:2105–2116. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08127.x
Vacilotto MM, Sepulchro AGV, Pellegrini VOA, Polikarpov I (2021) Production of prebiotic xylooligosaccharides from arabino- and glucuronoxylan using a two-domain Jonesia denitrificans xylanase from GH10 family. Enzyme Microb Technol 144:109743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2021.109743
Valls C, Pastor FIJ, Vidal T et al (2018) Antioxidant activity of xylooligosaccharides produced from glucuronoxylan by Xyn10A and Xyn30D xylanases and eucalyptus autohydrolysates. Carbohydr Polym 194:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.028
Varki A, Cummings RD, Aebi M et al (2015) Symbol Nomenclature for Graphical Representations of Glycans. Glycobiology 25:1323–1324. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwv091
Vieira TF, Corrêa RCG, Peralta RA et al (2020) An Overview of Structural Aspects and Health Beneficial Effects of Antioxidant Oligosaccharides. Curr Pharm Des 26:1759–1777. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612824666180517120642
Vršanská M, Kolenová K, Puchart V, Biely P (2007) Mode of action of glycoside hydrolase family 5 glucuronoxylan xylanohydrolase from Erwinia chrysanthemi. FEBS J 274:1666–1677. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05710.x
Wang L, Jing N, Liu X et al (2020) Nurturing and modulating gut microbiota with jujube powder to enhance anti-PD-L1 efficiency against murine colon cancer. J Funct Foods 64:103647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.103647
Yang J, Summanen PH, Henning SM et al (2015) Xylooligosaccharide supplementation alters gut bacteria in both healthy and prediabetic adults: a pilot study. Front Physiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00216
Yoshino K, Higashi N, Koga K (2006) Inhibitory effects of acidic xylooligosaccharide on stress-induced gastric inflammation in mice. J Food Hyg Soc Jpn 47:284–287. https://doi.org/10.3358/shokueishi.47.284
Yu X, Yin J, Li L et al (2015) Prebiotic Potential of Xylooligosaccharides Derived from Corn Cobs and Their In Vitro Antioxidant Activity When Combined with Lactobacillus. J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1084–1092. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1501.01022
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) via Grant #15/13684-0, the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) via Grant #303988/2016-9 and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) via Grant #88887.601517/2021-00.
Funding
Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo—FAPESP (15/13684-0), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—CNPq (303988/2016-9) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—CAPES (88887.601517/2021-00).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capetti, C.C., Vacilotto, M.M., Dabul, A.N.G. et al. Recent advances in the enzymatic production and applications of xylooligosaccharides. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 37, 169 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03139-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-03139-7