Abstract
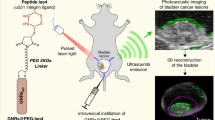
One of the critical problems in bladder cancer (BC) management is the local recurrence of disease. However, achieving the accurate delineation of tumor margins intraoperatively remains extremely difficult due to the lack of effective tumor margin recognition technology. Herein, survivin molecular beacon (MB) and R11 peptide-linked spherical nucleic acids (SNAs) were synthesized as nanoprobes (AuNP-MB@R11) for sensitive detection of BC margins. Physicochemical properties proved that R11 peptides and survivin MB were successfully loaded onto the surface of SNAs. AuNP-MB@R11 had good stability against nuclease activity and high sensitivity and specificity to detect survivin single strand DNA (ssDNA) in vitro. According to cytology, R11 peptides could increase the BC targeting ability and membrane penetrability of SNAs. Notably, R11 peptides significantly promoted the disintegration of lysosomes and the release of SNAs to enhance fluorescence imaging quality. Further RNA sequencing proved that some genes and pathways related to endocytosis and lysosomes were significantly regulated, such as AGPAT5, GPD1L, and GRB2. In orthotopic BC models and a clinical sample from a patient with BC, AuNP-MB@R11 showed a more legible cancerous fluorescence margin and offered remarkably improved detection compared to those achieved by SNAs. R11 peptide-linked SNAs present promising potential to identify BC margin, which may help to improve the R0 resection rate in surgery and improve patients’ quality of life.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoni, S.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Znaor, A.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: A global overview and recent trends. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 96–108.
Kamat, A. M.; Hahn, N. M.; Efstathiou, J. A.; Lerner, S. P.; Malmström, P. U.; Choi, W.; Guo, C. C.; Lotan, Y.; Kassouf, W. Bladder cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 2796–2810.
Cumberbatch, M. G. K.; Foerster, B.; Catto, J. W. F.; Kamat, A. M.; Kassouf, W.; Jübber, I.; Shariat, S. F.; Sylvester, R. J.; Gontero, P. Repeat transurethral resection in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 925–933.
Yossepowitch, O.; Briganti, A.; Eastham, J. A.; Epstein, J.; Graefen, M.; Montironi, R.; Touijer, K. Positive surgical margins after radical prostatectomy: A systematic review and contemporary update. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 303–313.
Kates, M.; Ball, M. W.; Chappidi, M. R.; Baras, A. S.; Gordetsky, J.; Sopko, N. A.; Brant, A.; Pierorazio, P. M.; Epstein, J. I.; Schoenberg, M. P. et al. Accuracy of urethral frozen section during radical cystectomy for bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2016, 34, 532.e1–532.e6.
Lenis, A. T.; Lec, P. M.; Chamie, K.; Mshs, M. D. Bladder cancer: A review. JAMA 2020, 324, 1980–1991.
Davis, R. M.; Kiss, B.; Trivedi, D. R.; Metzner, T. J.; Liao, J. C.; Gambhir, S. S. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanoparticles for multiplexed imaging of bladder cancer tissue permeability and molecular phenotype. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9669–9679.
Liu, J. J.; Droller, M. J.; Liao, J. C. New optical imaging technologies for bladder cancer: Considerations and perspectives. J. Urol. 2012, 188, 361–368.
Park, H.; Saravanakumar, G.; Kim, J.; Lim, J.; Kim, W. J. Tumor microenvironment sensitive nanocarriers for bioimaging and therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2000834.
Chinen, A. B.; Guan, C. M.; Ferrer, J. R.; Barnaby, S. N.; Merkel, T. J.; Mirkin, C. A. Nanoparticle probes for the detection of cancer biomarkers, cells, and tissues by fluorescence. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10530–10574.
Wu, S. Q.; Chi, C. W.; Yang, C. X.; Yan, X. P. Penetrating peptide-bioconjugated persistent nanophosphors for long-term tracking of adipose-derived stem cells with superior signal-to-noise ratio. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4114–4121.
Ren, L. J.; Chen, X. X.; Feng, C.; Ding, L.; Liu, X. M.; Chen, T. S.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. L.; Ma, Z. L.; Tian, B. et al. Visualized and cascade-enhanced gene silencing by smart DNAzyme-graphene nanocomplex. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 2165–2174.
Zhong, L.; Cai, S. X.; Huang, Y. Q.; Yin, L. T.; Yang, Y. L.; Lu, C. H.; Yang, H. H. DNA octahedron-based fluorescence nanoprobe for dual tumor-related mRNAs detection and imaging. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12059–12066.
Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, Y. D.; Zhang, B.; Peng, W. P.; Piao, J.; Zhou, Y. R.; Gao, W. C.; Gong, X. Q.; Chang, J. The construction of a novel nucleic acids detection microplatform based on the NSET for one-step detecting TK1-DNA and microRNA-21. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 26–33.
Xue, J. P.; Shan, L. L.; Chen, H. Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H. Y.; Deng, D. W.; Qian, Z. Y.; Achilefu, S.; Gu, Y. Q. Visual detection of STAT5B gene expression in living cell using the hairpin DNA modified gold nanoparticle beacon. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 71–77.
Li, N.; Chang, C. Y.; Pan, W.; Tang, B. A multicolor nanoprobe for detection and imaging of tumor-related mRNAs in living cells. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7426–7430.
Choi, C. H. J.; Hao, L. L.; Narayan, S. P.; Auyeung, E.; Mirkin, C. A. Mechanism for the endocytosis of spherical nucleic acid nanoparticle conjugates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7625–7630.
Ding, F.; Mou, Q. B.; Ma, Y.; Pan, G. F.; Guo, Y. Y.; Tong, G. S.; Choi, C. H. J.; Zhu, X. Y.; Zhang, C. A crosslinked nucleic acid nanogel for effective siRNA delivery and antitumor therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3064–3068.
He, K.; Zhu, J. Y.; Gong, L. S.; Tan, Y.; Chen, H. R.; Liang, H. R.; Huang, B. H.; Liu, J. B. In situ self-assembly of near-infrared-emitting gold nanoparticles into body-clearable 1D nanostructures with rapid lysosome escape and fast cellular excretion. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 1087–1094.
Guidotti, G.; Brambilla, L.; Rossi, D. Cell-penetrating peptides: From basic research to clinics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 406–424.
Cho, J. H.; Kim, A. R.; Kim, S. H.; Lee, S. J.; Chung, H.; Yoon, M. Y. Development of a novel imaging agent using peptide-coated gold nanoparticles toward brain glioma stem cell marker CD133. Acta Biomater. 2017, 47, 182–192.
Ruoslahti, E. Tumor penetrating peptides for improved drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 110–111, 3–12.
Nitin, N.; Santangelo, P. J.; Kim, G.; Nie, S. M.; Bao, G. Peptide-linked molecular beacons for efficient delivery and rapid mRNA detection in living cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e58.
Yan, J.; Zhu, R. Y.; Wu, F.; Zhao, Z. Y.; Ye, H.; Hou, M. Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L. C. iRGD-reinforced, photo-transformable nanoclusters toward cooperative enhancement of intratumoral penetration and antitumor efficacy. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 2706–2715.
Zhou, J.; Fan, J. H.; Hsieh, J. T. Inhibition of mitogen-elicited signal transduction and growth in prostate cancer with a small peptide derived from the functional domain of DOC-2/DAB2 delivered by a unique vehicle. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8954–8958.
Du, Y. Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, W. Y.; Guo, T.; Zhang, M. Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y. N.; Wu, K. J.; Li, A. X.; Wang, X. Y. et al. Novel application of cell penetrating R11 peptide for diagnosis of bladder cancer. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 161–167.
Zhang, T. T.; Wu, K. J.; Ding, C.; Sun, K. W.; Guan, Z. F.; Wang, X. Y.; Hsieh, J. T.; He, D. L.; Fan, J. H. Inhibiting bladder tumor growth with a cell penetrating R11 peptide derived from the p53 C-terminus. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37782–37791.
Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y. N.; Liu, W. H.; Cui, D. X.; Zhao, X. W.; Song, J.; Guo, T.; Ni, H. B.; Zhang, M. Z.; Zhang, H. B. et al. A molecular beacon based surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanotag for noninvasive diagnosis of bladder cancer. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 1589–1597.
Horstmann, M.; Bontrup, H.; Hennenlotter, J.; Taeger, D.; Weber, A.; Pesch, B.; Feil, G.; Patschan, O.; Johnen, G.; Stenzl, A. et al. Clinical experience with survivin as a biomarker for urothelial bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2010, 28, 399–404.
Lang, J. Y.; Zhao, X.; Qi, Y. Q.; Zhang, Y. L.; Han, X. X.; Ding, Y. P.; Guan, J. J.; Ji, T. J.; Zhao, Y.; Nie, G. J. Reshaping prostate tumor microenvironment to suppress metastasis via cancer-associated fibroblast inactivation with peptide-assembly-based nanosystem. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12357–12371.
Saqafi, B.; Rahbarizadeh, F. Polyethyleneimine-polyethylene glycol copolymer targeted by anti-HER2 nanobody for specific delivery of transcriptionally targeted tBid containing construct. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 501–511.
Wang, Z.; Li, X. H.; Song, Y. C.; Li, L. H.; Shi, W.; Ma, H. M. An upconversion luminescence nanoprobe for the ultrasensitive detection of hyaluronidase. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5816–5823.
Bian, F. K.; Sun, L. Y.; Cai, L. J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. J.; Wang, S. Q.; Zhou, M. T. Molybdenum disulfide-integrated photonic barcodes for tumor markers screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 133, 199–204.
Tao, Y. Y.; Yin, D.; Jin, M. C.; Fang, J.; Dai, T.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. X.; Pu, Q. L.; Xie, G. M. Double-loop hairpin probe and doxorubicin-loaded gold nanoparticles for the ultrasensitive electrochemical sensing of microRNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 99–105.
Azzouzi, S.; Mak, W. C.; Kor, K.; Turner, A. P. F.; Ali, M. B.; Beni, V. An integrated dual functional recognition/amplification bio-label for the one-step impedimetric detection of Micro-RNA-21. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 154–161.
Liu, L.; Lu, H.; Shi, R. X.; Peng, X. X.; Xiang, Q. W.; Wang, B. W.; Wan, Q. Q.; Sun, Y. J.; Yang, F.; Zhang, G. J. Synergy of peptide-nucleic acid and spherical nucleic acid enabled quantitative and specific detection of tumor exosomal MicroRNA. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13198–13205.
Zhang, W. L.; Meckes, B.; Mirkin, C. A. Spherical nucleic acids with tailored and active protein coronae. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 1983–1990.
Lin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Q.; Tian, Y.; Cai, W.; Tang, S. G.; Chu, C. C.; Zhou, J. J.; Mi, P. et al. Metal-organic frameworks nanoswitch: Toward photo-controllable endo/lysosomal rupture and release for enhanced cancer RNA interference. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 238–245.
Liu, J. Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H. L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, P.; Liu, X. M.; Xie, H. Y.; Xiang, W.; Liu, B. et al. Fe-doped chrysotile nanotubes containing siRNAs to silence SPAG5 to treat bladder cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 189.
Andaloussi, S. E. L.; Lehto, T.; Mäger, I.; Rosenthal-Aizman, K.; Oprea, I. I.; Simonson, O. E.; Sork, H.; Ezzat, K.; Copolovici, D. M.; Kurrikoff, K. et al. Design of a peptide-based vector, PepFect6, for efficient delivery of siRNA in cell culture and systemically in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 3972–3987.
Bartz, R.; Fan, H. H; Zhang, J. T.; Innocent, N.; Cherrin, C.; Beck, S. C.; Pei, Y.; Momose, A.; Jadhav, V.; Tellers, D. M. et al. Effective siRNA delivery and target mRNA degradation using an amphipathic peptide to facilitate pH-dependent endosomal escape. Biochem. J. 2011, 435, 475–487.
Lim, C. Y.; Zoncu, R. The lysosome as a command-and-control center for cellular metabolism. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 214, 653–664.
Wang, S. Y.; Tsun, Z. Y.; Wolfson, R. L.; Shen, K.; Wyant, G. A.; Plovanich, M. E.; Yuan, E. D.; Jones, T. D.; Chantranupong, L.; Comb, W. et al. Lysosomal amino acid transporter SLC38A9 signals arginine sufficiency to mTORC1. Science 2015, 347, 188–194.
Liu, Y. J.; Sun, D. D.; Fan, Q.; Ma, Q. L.; Dong, Z. L.; Tao, W. W.; Tao, H. Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C. The enhanced permeability and retention effect based nanomedicine at the site of injury. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 564–569.
Pan, Y.; Chang, T.; Marcq, G.; Liu, C. H.; Kiss, B.; Rouse, R.; Mach, K. E.; Cheng, Z.; Liao, J. C. In vivo biodistribution and toxicity of intravesical administration of quantum dots for optical molecular imaging of bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9309.
Li, S. W.; Tian, C. P.; Liu, Y. X.; Wang, Z. H.; Ma, Y.; Han, Z. H.; Du, J. Y.; Zhang, J. N.; Gu, Y. Q. Mechanism of cellular uptake to optimized AuNP beacon for tracing mRNA changes in living cells. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2018, 35, 1700331.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81901838), Key research and development plan in Shaanxi province (Nos. 2020SF-123 and 2020SF-195), Medical Technology Plan of Zhejiang Province (No. 2021KY042), and Medical research program of department of science and technology of Xi’an, Shaanxi Province (No. 2019115713YX012SF048(4)). The authors thank Dr. Yu Wang at Instrument Analysis Center of Xi’an Jiaotong University for her assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, M., Zhang, P., Liang, X. et al. R11 peptides can promote the molecular imaging of spherical nucleic acids for bladder cancer margin identification. Nano Res. 15, 2278–2287 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3807-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-021-3807-z