Abstract
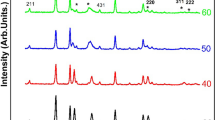
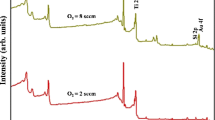
Nickel oxide (NiO) films were deposited on glass and silicon substrates using a Ni target by radio-frequency (RF) sputtering at various working pressure ranging from 5 to 20 mTorr. The films were annealed for 2 h at 400 °C in the air ambient. The effect of working pressure on structural, optical and electrical properties of NiO films was investigated in detail. The deposition rate of the films gradually increased with decreasing working pressure. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) presented that the crystal quality and the average crystallite size of annealed films increased with decreasing working pressure. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) confirmed the presence of Ni2+ and Ni3+ ions along with the main peak and satellite peaks in the NiO films. Raman spectroscopy exhibited the one-phonon and two-phonon vibrations modes corresponding to Ni–O bond. UV–Visible analyses showed that annealed NiO thin films have higher transmittance than deposited ones. The band gap of the films increased from 3.33 to 3.52 eV with decreasing working pressure and further increased after the annealing process. The electrical properties were affected by the varying crystallinity and lattice defects depending on the deposition condition. All annealed NiO films exhibited p-type conductivity. The lowest resistivity (4.2 Ω.cm) was obtained from the annealed film after deposition at 5 mTorr.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The experimental studies were carried out within Eastern Anatolia High Technology Application and Research Center (DAYTAM). The data are available from the author (Fatih Şenaslan; fsenaslan@gumushane.edu.tr) upon reasonable request.
References
R. Sharma, A.D. Acharya, S.B. Shrivastava, T. Shripathi, V. Ganesan, Opt. 125, 6751 (2014)
Z. Xuping, Z. Haokang, L. Qing, L. Hongli, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 21, 215 (2000)
P. Yang, J. Wang, X. Zhao, J. Wang, Z. Hu, Q. Huang, L. Yang, Appl. Phys. A 125, 1 (2019)
B. Varghese, M.V. Reddy, Z. Yanwu, C.S. Lit, T.C. Hoong, G.V. Subba Rao, C.H. Sow, Chem. Mater. 20, 3360 (2008)
Y. Zhang, S. Wang, L. Chen, Y. Fang, H. Shen, Z. Du, Org. Electron. 44, 189 (2017)
S.Y. Tsai, M.H. Hon, Y.M. Lu, Solid-State Electron. 63, 37 (2011)
E. Turgut, Ö. Çoban, S. Sarıtaş, S. Tüzemen, M. Yıldırım, E. Gür, Appl. Surf. Sci. 435, 880 (2018)
D. Du, Z. Hu, Y. Liu, Y. Deng, J. Liu, J. Alloys Compd. 589, 82 (2014)
M. Predanocy, I. Hotový, M. Čaplovičová, Appl. Surf. Sci. 395, 208 (2017)
M.S. Jamal, S.A. Shahahmadi, P. Chelvanathan, H.F. Alharbi, M.R. Karim, M.A. Dar, M. Akhtaruzzaman, Results Phys. 14, 102360 (2008)
T. Maruyama, S. Arai, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 30, 257 (1993)
I. Fasaki, A. Koutoulaki, M. Kompitsas, C. Charitidis, Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 429 (2010)
I. Porqueras, E. Bertran, Thin Solid Films 398, 41 (2001)
S. Pereira, A. Gonçalves, N. Correia, J. Pinto, L. Pereira, R. Martins, E. Fortunato, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells. 120, 109 (2014)
N.R. Aswathy, J. Varghese, R. Vinodkumar, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31, 16634 (2020)
L. Berkat, L. Cattin, A. Reguig, M. Regragui, J.C. Bernede, Mater. Chem. Phys. 89, 11 (2005)
S. Swann, Phys. Technol. 19, 67 (1988)
A.A. Ahmed, N. Afzal, M. Devarajan, S. Subramani, Mater. Res. Express 3, 116405 (2016)
V.R. Buch, A.K. Chawla, S.K. Rawal, Mater. Today: Proc. 3, 1429 (2016)
A.M. Reddy, A.S. Reddy, P.S. Reddy, Vacuum 85, 949 (2011)
G. Atak, Ö.D. Coşkun, Solid State Ionics 305, 43 (2017)
L. Ai, G. Fang, L. Yuan, N. Liu, M. Wang, C. Li, X. Zhao, Appl. Surf. Sci. 254, 2401 (2008)
K. Sato, S. Kim, S. Komuro, X. Zhao, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 55, 06GJ10 (2016)
H.L. Chen, Y.M. Lu, W.S. Hwang, Surf. Coat. Technol. 198, 138 (2005)
S. Wu, H. Chen, X. Du, Z. Liu, Spectrosc. Lett. 49, 514 (2016)
K.Y. Chan, B.S. Teo, J. Mater. Sci. 40, 5971 (2005)
J.L. Yang, Y.S. Lai, J.S. Chen, Thin Solid Films 488, 242 (2005)
Y. Zhang, Y. Shen, X. Xie, W. Du, L. Kang, Y. Wang, B. Wang, Mater. Des. 196, 109111 (2020)
K.S. Usha, R. Sivakumar, C. Sanjeeviraja, V. Sathe, V. Ganesan, T.Y. Wang, RSC Adv. 6, 79668 (2016)
P. Salunkhe, M. A. AV, D. Kekuda, , Mater. Res. Express. 7, 016427 (2020)
T. Potlog, L. Ghimpu, V. Suman, A. Pantazi, M. Enachescu, Mater. Res. Express 6, 096440 (2019)
E. Aytan, B. Debnath, F. Kargar, Y. Barlas, M.M. Lacerda, J.X. Li, A.A. Balandin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 111, 252402 (2017)
G. George, S. Anandhan, RSC Adv. 4, 62009 (2014)
P. Ravikumar, B. Kisan, A. Perumal, AIP Adv. 5, 087116 (2015)
S. Oh, Y.S. Park, P.J. Ko, N.H. Kim, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 18, 6213 (2018)
S.T. Akinkuade, W.E. Meyer, J.M. Nel, Physica B: Condensed Matter. 575, 411694 (2019)
J.D. Hwang, T.H. Ho, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 71, 396 (2017)
Funding
This study was financially supported by Ataturk University, Coordinatorship of Scientific Research Projects (Project Code: FDK-2019–7473).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FŞ: methodology, data analysis, investigation, writing − original draft, visualization. MT: writing—review and editing. AÇ: conceptualization, project administration, writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şenaslan, F., Taşdemir, M. & Çelik, A. Effect of working pressure and post-annealing on structural, optical and electrical properties of p-type NiO thin films produced by RF magnetron sputtering technique. Appl. Phys. A 127, 739 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04901-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04901-2