Abstract
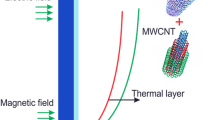
The liquid film flow of a blood-based hybrid nanofluid, comprising carbon nanotubes (CNTs) with variable viscosity, through a stretcshing sheet has been investigated. CNTs have many applications, such as high electrical and thermal conductivity, 18% more elasticity than other commonly used nanoparticles, high tensile strength, low thermal expansion coefficient, and improved electron emission, making the present effort more valuable. In this model, a magnetic field perpendicular to the flow field is used. The governing equations are designed in the form of nonlinear partial differential equations. By using the similarity transformation, the dimensionless ordinary differential equations are depleted. The homotopy analysis method was adjusted to solve this problem. The behavior of the momentum and energy profiles versus several physical constraints was investigated. The results indicated that the use of CNTs in the carrier fluid was more effective due to its C–C bond. CNT nanofluids can be functionalized to achieve the desired properties, which can be utilized for a variety of applications by functionalization of non-covalent and covalent modification.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mukhopadhyay, S.; De, P.R.; Bhattacharyya, K.; Layek, G.C.: Casson fluid flow over an unsteady stretching surface. Ain. Shams. Eng. J. 4, 933–938 (2013)
Sumalatha, C.; Bandari, S.: Effects of radiations and heat source/sink on a Casson fluid flow over nonlinear stretching sheet. WJM 5, 257–265 (2015)
Gbadeyan, J.A.; Titiloye, E.O.; Adeosun, A.T.: Effect of variable thermal conductivity and viscosity on Casson nanofluid flow with convective heating and velocity slip. Heliyon 6, 30–36 (2020)
Bharathi, V.; Vijayaragavan, R.; Prakash, J.: Comparative analysis of Cu/blood and Cu–CuO/blood nanofluids on a peristaltic flow governed by an asymmetric channel. Heat Transf. Eng. 7, 57–65 (2015)
Gul, T.; Akbar, R.; Zaheer, Z.; Amiri, I.S.: The impact of the Marangoni convection and magnetic field versus blood-based carbon nanotube nanofluids. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part N J. Nanomater. Nanoeng. Nanosyst. 23, 37–46 (2020)
Eastman, J.A.; Cho, S.U.S.; Li, S.; Soyez, G.; Thompson, L.J.; Dimelfi, R.J.: Novel thermal properties of nanostructured materials. J. Metastable Nanocrystal. Mater. 2, 629–637 (1999)
Buongiorno, J.; Venerus, D.C.; Prabhat, N., et al.: A benchmark study on the thermal conductivity of nanofluids. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 45–53 (2009)
Khan, U.; Ahmed, N.; Asadullah, M.; Mohyud-Din, S.T.: Effects of viscous dissipation and slip velocity on two-dimensional and axisymmetric squeezing flow of Cu-water and Cu-kerosene nanofluids. Propuls. Power Res. 4, 40–49 (2015)
Akbar, N.S.; Raza, M.; Ellahi, R.: Influence of induced magnetic field and heat flux with the suspension of carbon nano-tubes for the peristaltic flow in a permeable channel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 38, 405–415 (2015)
Ali, A.; Bukhari, Z.; Shahzadi, G.; Abbas, Z.; Umar, M.: Numerical simulation of the thermally developed pulsatile flow of a hybrid nanofluid in a constricted channel. Energies 14(9), 2410 (2021)
Wang, Y.; Meng, F.; Huang, F.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Mei, Y.; Zhou, Z.: Ultrastrong carbon nanotubes/graphene papers via multiple π–π cross-linking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 4, 23–37 (2020)
Tran, H.Q.; Tran, M.T.; Nguyen-Tri, P.: A new four-variable refined plate theory for static analysis of smart laminated functionally graded carbon nanotube reinforced composite plates. Mech. Mater. 14, 82–94 (2020)
Massoudi, M.; Christie, I.: Effects of variable viscosity and viscous dissipation on the flow of a third grade fluid in a pipe. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 9, 687–699 (2020)
Seddeek, M.A.: Effects of radiation and variable viscosity on a MHD free convection flow past a semi-infinite flat plate with an aligned magnetic field in the case of unsteady flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 4, 931–935 (2002)
Makinde, O.D.; Mishra, S.R.: On stagnation point flow of variable viscosity nanofluids past a stretching surface with radiative heat. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 3, 561–578 (2017)
Pantokratoras, A.: Study of MHD boundary layer flow over a heated stretching sheet with variable viscosity: a numerical reinvestigation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 5, 104–110 (2008)
Mukhopadhyay, S.; Layek, G.C.: Effects of thermal radiation and variable fluid viscosity on free convective flow and heat transfer past a porous stretching surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 5, 2167–2178 (2008)
Dada, M.S.; Onwubuoya, C.: Variable viscosity and thermal conductivity effects on Williamson fluid flow over a slendering stretching sheet. World J. Eng. 7, 167–178 (2020)
Hazarika, G.C.; Phukan, B.; Ahmed, S.: Effect of variable viscosity and thermal conductivity on unsteady free convective flow of a micropolar fluid past a vertical cone. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 5, 267–278 (2020)
Tassaddiq, A.: MHD flow of a fractional second grade fluid over an inclined heated plate. Chaos Solitons Fractals 123, 341–346 (2019)
Tassaddiq, A.; Khan, I.; Nisar, K.S.: Heat transfer analysis in sodium alginate based nanofluid using MoS2 nanoparticles: Atangana–Baleanu fractional model. Chaos Soliton Fractals 130, 109445 (2020)
Tassaddiq, A.; Khan, I.; Nisar, K.S.; Singh, J.: MHD flow of a generalized Casson fluid with Newtonian heating: a fractional model with Mittag-Leffler memory. Alex. Eng. J. 59, 3049–3059 (2020)
Tassaddiq, A.; Amin, I.; Shutaywi, M.; Shah, Z.; Ali, F.; Islam, F.S.; Ullah, A.: Thin film flow of couple stress magneto-hydrodynamics nanofluid with convective heat over an inclined exponentially rotating stretched surface. Coatings 10, 338 (2020)
Tassaddiq, A.; Khan, S.; Bilal, M.; Gul, T.; Mukhtar, S.; Shah, Z.; Bonyah, E.: Heat and mass transfer together with hybrid nanofluid flow over a rotating disk. AIP Adv. 10, 55317 (2020)
Tassaddiq, A.: Impact of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model on MHD hybrid nano-micropolar fluid flow and heat transfer with viscous and joule dissipation effects. Sci. Rep. 11, 1–14 (2021)
Ali, A.; Fatima, A.; Bukhari, Z.; Farooq, H.; Abbas, Z.: Numerical investigation of thermally developed MHD flow with pulsation in a channel with multiple constrictions. AIP Adv. 11(5), 055320 (2021)
Ali, A.; Umar, M.; Abbas, Z.; Shahzadi, G.; Bukhari, Z.; Saleem, A.: Numerical investigation of MHD pulsatile flow of micropolar fluid in a channel with symmetrically constricted walls. Mathematics 9, 1000 (2021)
Umar, M.; Ali, A.; Bukhari, Z.; Shahzadi, G.; Saleem, A.: Impact of Lorentz force in thermally developed pulsatile micropolar fluid flow in a constricted channel. Energies 14(8), 2173 (2021)
Hussain, S.; Abbas, Z.; Hasnain, J.; Arslan, M.S.; Ali, A.: Thermally developed unsteady viscous nanofluid flow due to permeable channel with orthogonal motion of walls using Beavers–Joseph slip condition. Alex. Eng. J. 60(2), 2335–2345 (2021)
Abbas, Z.; Altaf, I.; Hasnain, J.; Ali, A.: Theoretical analysis of two-layer fluids with continuity of stresses at interface and slip at the walls of an inclined channel. Ain Shams Eng. J. 12(1), 761–774 (2021)
Ali, A.; Fatima, A.; Bukhari, Z.; Farooq, H.; Abbas, Z.: Non-Newtonian Casson pulsatile fluid flow influenced by Lorentz force in a porous channel with multiple constrictions: a numerical study. Korea Aust. Rheol. J. 33, 79–90 (2021)
Qasim, M.; Khan, Z.H.; Lopez, R.J.; Khan, W.A.: Heat and mass transfer in nanofluid thin film over an unsteady stretching sheet using Buongiornos model. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 3, 216–220 (2016)
Rehman, A.; Zabidin, S.; Gul, T.; Zaheer, Z.: The impact of viscous dissipation on the thin film unsteady flow of GO-EG/GO-W nanofluids. Mathematics 7, 653 (2019)
Makinde, O.D.; Khan, W.A.; Khan, Z.H.: Buoyancy effects on MHD stagnation point flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid past a convectively heated stretching/shrinking sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 62, 526–533 (2013)
Hamad, M.A.A.; Ferdows, M.: Similarity solution of boundary layer stagnation-point flow towards a heated porous stretching sheet saturated with a nanofluid with heat absorption/generation and suction/blowing: a Lie group analysis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17, 132–140 (2012)
Alsagri, A.S.; Nasir, S.; Gul, T.; Islam, S.; Nisar, K.S.; Shah, Z.; Khan, I.: MHD thin film flow and thermal analysis of blood with CNTs nanofluid. Coatings 9(3), 175 (2019)
Narayana, M.; Sibanda, P.: Laminar flow of a nanoliquid film over an unsteady stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55, 7552–7560 (2012)
Xu, H.; Pop, I.; You, X.C.: Flow and heat transfer in a nano-liquid film over an unsteady stretching surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 60, 646–652 (2013)
Liao, S.; Tan, Y.: A general approach to obtain series solutions of nonlinear differential equations. Stud. Appl. Math. 119, 297–354 (2007)
Gul, T.; Kiran, F.: The experimental study to examine the stable dispersion of the graphene nanoparticles and to look at the GO–H2O nanofluid flow between two rotating disks. Appl Nanosci. 8(7), 1711–1727 (2018)
Gul, T.; Noman, W.; Sohail, M.; Khan, M.A.: Impact of the Marangoni and thermal radiation convection on the graphene-oxide-water-based and ethylene-glycol-based nanofluids. Adv. Mech. Eng. 1, 67–78 (2019)
Bilal, M.; Imran, K.; Gul, T.; Tassaddiq, A.; Alghamdi, W.; Mukhtar, S.; Kumam, P.: Darcy-forchheimer hybrid nano fluid flow with mixed convection past an inclined cylinder. CMC Comput. Mater. Continua 66, 2025–2039 (2021)
Acknowledgements
Asifa Tassaddiq would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at Majmaah University for supporting this work under Project No. R-2021-197. The authors are also thankful to the worthy reviewers and editors for their useful and valuable suggestions for the improvement of this paper which led to a better presentation.
Funding
No funding received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No such interest exists.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alhussain, Z.A., Tassaddiq, A. Thin Film Blood Based Casson Hybrid Nanofluid Flow with Variable Viscosity. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 1087–1094 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06067-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06067-8