Abstract
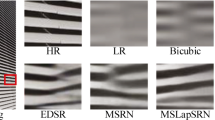
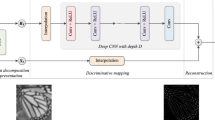
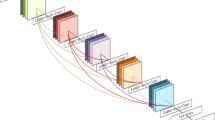
Residual networks (ResNets) have recently achieved great success for single-image super-resolution, but its identity connection leads to accumulation of a mixed levels of feature representations, and it is not conductive to optimize the information flow. To address these issues, a novel Resnet in Resnet architecture (RiRSR) based on generalized residual (GenRes) module is proposed to reconstruct the high-resolution image. Specifically, the network is composed of some Resnet in Resnet blocks containing multiple GenRes sub-blocks for feature extraction, where the GenRes sub-block combines the residual and non-residual streams, which retains the benefits of identity shortcut connections, improving features expressivity. Moreover, both local and global residual learning are integrated to ease the information flow and accelerate convergence. Finally, multi-scale training strategy is utilized to further boost reconstruction performance and reduce the number of model parameters. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed RiRSR can improve the reconstruction performance (more than 0.1 dB than ResNets) with higher accuracy for the integer and non-integer scales, and is competitive in balancing model parameters, reconstruction speed and reconstruction quality.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Hoi, S.C.: Deep learning for image super-resolution: a survey. arXiv:1902.06068 (2019)
Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Cohen, S.; Huang, T.: Coupled dictionary training for image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(8), 3467–3478 (2012)
Zhao, J.; Sun, T.; Cao, F.: Image super-resolution via adaptive sparse representation and self-learning. IET Comput. Vis. 12(5), 753–761 (2018)
Chang, H.; Yeung, D.Y.; Xiong, Y.: Super-resolution through neighbor embedding. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Washington, pp. 275–282 (2004).
Yang, C.Y.; Yang, M.H.: Fast direct super-resolution by simple functions. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 561–568. Australia, Sydney (2013)
Timofte, R.; De Smet, V.; Van Gool, L.: A+: adjusted anchored neighborhood regression for fast super-resolution. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), Singapore, pp. 111–126 (2014)
Huang, J.-J.; Siu, W.-C.; Liu, T.-R.: Fast image interpolation via random forests. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(10), 3232–3245 (2015)
Li, H.; Lam, K.M.; Wang, M.: Image super-resolution via feature-augmented random forest. Signal Process. Image Commun. 72, 25–34 (2019)
Jia, W.; Ling, B.; Chau, K.W.; Heutte, L.: Palmprint identification using restricted fusion. Appl. Math. Comput. 205(2), 927–934 (2008)
Banan, A.; Nasiri, A.; Taheri-Garavand, A.: Deep learning-based appearance features extraction for automated carp species identification. Aquac. Eng. 89, 102053 (2020)
Fan, Y.; Xu, K.; Wu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Tao, B.: Spatiotemporal modeling for nonlinear distributed thermal processes based on KL decomposition. IEEE Access MLP LSTM Netw. 8, 25111–25121 (2020)
Shamshirband, S.; Rabczuk, T.; Chau, K.W.: A survey of deep learning techniques: application in wind and solar energy resources. IEEE Access 7, 164650–164666 (2019)
Huang, Z.K.; Chau, K.W.: A new image thresholding method based on Gaussian mixture model. Appl. Math. Comput. 205(2), 899–907 (2008)
Zhang, J.; Chau, K.W.: Multilayer ensemble pruning via novel multi-sub-swarm particle swarm optimization. J. Univ. Comput. Sci. 15(4), 840–858 (2009)
Bengio, Y.; Simard, P.; Frasconi, P.: Learning long-term dependencies with gradient descent is difficult. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 5(2), 157–166 (1994)
Pang, S.; Chen, Z.; Yin, F.: Convolutional neural network based sub-pixel line-edged angle detection with applications in measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 21(7), 9314–9322 (2021)
Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X.: Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 184–199. Switzerland, Zurich (2014)
Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X.: Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, the Netherlands, pp. 391–407 (2016)
Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszar, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z.: Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1874–1883. Las Vegas (2016)
Kim, J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, K.M.: Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1646–1654. Las Vegas (2016)
Lai, W.S.; Huang, J.B.; Ahuja, N.; Yang, M.H.: Deep Laplacian pyramid networks for fast and accurate super-resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 624–632. Honolulu (2017)
Kim, J.; Kwon Lee, J.; Mu Lee, K.: Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1637–1645. Las Vegas (2016).
Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Lee, K.M.: Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 136–144. Honolulu (2017)
Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.: Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4681–4690. Honolulu (2017)
Bottou, L.; Curtis, F.E.; Nocedal, J.: Optimization methods for large-scale machine learning. SIAM Rev. 60(2), 223–311 (2018)
He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778. Las Vegas (2016)
Targ, S.; Almeida, D.; Lyman, K.: Resnet in resnet: generalizing residual architectures. arXiv:1603.08029 (2016)
Li, J.; Fang, F.; Mei, K.; Zhang, G.: Multi-scale residual network for image super-resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 517–532. Munich (2018)
Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y.: Image super-resolution using very deep residual channel attention networks. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 286–301. Munich (2018)
Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Kong, Y.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y.: Residual dense network for image super-resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2472–2481. Salt Lake City (2018)
Shamsolmoali, P.; Li, X.; Wang, R.: Single image resolution enhancement by efficient dilated densely connected residual network. Signal Process. Image Commun. 79, 13–23 (2019)
Tai, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.: Image super-resolution via deep recursive residual network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3147–3155. Honolulu (2017)
Tai, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, C.: Memnet: A persistent memory network for image restoration. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 4539–4547. Venice (2017)
Liang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, K.; et al.: Single image super-resolution via a lightweight residual convolutional neural network. arXiv:1703.08173 (2017)
Hu, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.: Single image super-resolution via cascaded multi-scale cross network. arXiv:1802.08808 (2018)
Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Jung, C.: DCSR: dilated convolutions for single image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 28(4), 1625–1635 (2019)
Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Yang, Y.: Deep fractal residual network for fast and accurate single image super resolution. Neurocomputing 398, 389–398 (2020)
He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J.: Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1026–1034. Santiago (2015)
Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L.: Learning a single convolutional super-resolution network for multiple degradations. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3262–3271. Salt Lake City (2018)
Sajjadi, M.S.; Scholkopf, B.; Hirsch, M.: Enhancenet: Single image super-resolution through automated texture synthesis. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 4491–4500. Italy (2017)
Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Xue, J.H.; Liao, Q.: Deep learning for single image super-resolution: a brief review. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 21(12), 3106–3121 (2019)
Yang, J.; Wright, J.; Huang, T.S.; Ma, Y.: Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(11), 2861–2873 (2010)
Bevilacqua, M.; Roumy, A.; Guillemot, C.; Alberi-Morel, M.L.: Low-complexity single-image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding. In: the 23rd British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC). Surrey (2012)
Zeyde, R.; Elad, M.; Protter, M.: On single image scale-up using sparse-representations. In: International Conference on Curves and Surfaces, pp. 711–730. Berlin, Heidelberg (2010)
Martin, D.; Fowlkes, C.; Tal, D.; Malik, J.: A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Vancouver (2001)
Huang, J.B.; Singh, A.; AhujaSingle, N.: Image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5197–5206. Boston (2015)
Simmons, C.; Holliday, M.A.: A comparison of two popular machine learning frameworks. J. Comput. Sci. Coll. 35(4), 20–25 (2019)
Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P.: Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86(11), 2278–2324 (1998)
Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C.: Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv:1502.03167 (2015)
Bottou, L.: Stochastic gradient descent tricks. In: Neural networks: tricks of the trade, pp. 421–436. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2012)
Salimans, T.; Kingma, D.P.: Weight normalization: a simple reparameterization to accelerate training of deep neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 901–909 (2016)
Yu, J.; Fan, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.: Wide activation for efficient and accurate image super-resolution. arXiv:1808.08718 (2018).
Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E.: Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In: The 27th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML-10), pp. 807–814. Israel (2010)
Clevert, D.A; Unterthiner, T.; Hochreiter, S.: Fast and accurate deep network learning by exponential linear units (elus). arXiv:1511.07289 (2015)
Zhao, H.; Gallo, O.; Frosio, I.; Kautz, J.: Loss functions for image restoration with neural networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 3(1), 47–57 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundations of China (Nos. 61771091, 61871066), National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program) of China (No. 2015AA016306), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China (No. 20170540159) and Fundamental Research Fund for the Central Universities of China (No. DUT17LAB04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, S., Chen, Z. & Yin, F. Image Super-Resolution Based on Generalized Residual Network. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 1903–1920 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06145-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06145-x