Abstract
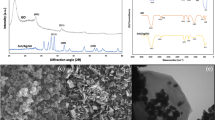
The drinking water shortage is globe concern currently, thus, developing an economical, green, antibacterial composites is urgent. Here, we report a simple and scalable strategy to synthesize zeolite-cellulose composites by the filter paper immersed in the precursor solution of synthetic zeolite. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray fluorescence spectrophotometer (XRF), infrared spectra (IR), and thermogravimetry analyzer (TGA). It was confirmed that the sub-micron zeolite was successfully embedded into cellulose. Zn2+ and Cu2+ are induced into the composites by ion exchange, the composites were able to able to kill nearly all viable bacteria of 1 L of the natural water sample via gravity driving, demonstrating high suitability for practical water disinfection. Furthermore, after the dynamic test of deionized water, the contents of Zn2+ and Cu2+ ions exuded are far below the standard of drinking water, indicating that the materials are safe and have a long-term antibacterial property.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Joseph, Cotruvo, 2017 WHO Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality: First Addendum to the Fourth Edition. J AWWA 109(7), 44–51 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5942/jawwa.2017.109.0087
C.K. Pooi, H.Y. Ng, Review of low-cost point-of-use water treatment systems for developing communities. Npj Clean Water 1, 11–18 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-018-0011-0
N. Phaswana-Mafuya, An investigation into the perceived sanitation challenges in the Eastern Cape rural communities:research. Health SA Gesondheid(Online) 11(1), 18–30 (2006). https://hdl.handle.net/10520/EJC34987
J. Lin, A. Ganesh, Waterborne human pathogenic viruses of public health concern. Int. J. Environ. Heal R. 23(6), 544–564 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2013.769205
M. Dudziak, J. Wyczarska-Kokot, E. Laskawiec, A. Stolarczyk, Application of ultrafiltration in a swimming pool water treatment system. Membranes 9(3), 44–54 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9030044
D. Yu, X. Yu, C. Wang, X. Liu, Y. Xing, Synthesis of natural cellulose-templated TiO2/Ag nanosponge composites and photocatalytic properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 4(5), 2781–2787 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/am3004363
N. Keshavarzi, F. Mashayekhy Rad, A. Mace, F. Ansari, F. Akhtar, U. Nilsson, L. Berglund, L. Bergström, Nanocellulose-Zeolite composite films for odor elimination. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 7(26), 14254–14262 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02252
J.A. Sanchez-Marquez, R. Fuentes-Ramírez, I. Cano-Rodriguez, Z. Gamino-Arroyo, E. Rubio-Rosas, J.M. Kenny, N. Rescignano, Membrane made of cellulose acetate with polyacrylic acid reinforced with carbon nanotubes and its applicability for chromium removal. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 1–12 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/320631
G. Liu, J. Jiang, R. Yu, H. Yan, R. Liang, Silver nanoparticle-incorporated porous renewable film as low-cost bactericidal and antifouling filter for point-of-use water disinfection. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59(23), 10857–10867 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c00157
A. Simon, J.A. McDonald, S.J. Khan, W.E. Price, L.D. Nghiem, Effects of caustic cleaning on pore size of nanofiltration membranes and their rejection of trace organic chemicals. J. Membrane Sci. 447, 153–162 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.07.013
Y. Zheng, U. Ash, R.P. Pandey, A.G. Ozioko, J. Ponce-Gonzalez, M. Handl, T. Weissbach, J.R. Varcoe, S. Holdcroft, M.W. Liberatore, R. Hiesgen, D.R. Dekel, Water uptake study of anion exchange membranes. Macromolecules 51(9), 3264–3278 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.8b00034
J. Garcia-Ivars, J. Dura-Maria, C. Moscardo-Carreno, C. Carbonell-Alcaina, M. Alcaina-Miranda, M. Iborra-Clar, Rejection of trace pharmaceutically active compounds present in municipal wastewaters using ceramic fine ultrafiltration membranes: effect of feed solution pH and fouling phenomena. Sep. Purif. Technol. 175, 58–71 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.11.027
T. Clasen, W. Schmidt, T. Rabie, I. Roberts, S. Cairncross, Interventions to improve water quality for preventing diarrhoea: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 334(7597), 782–785 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39118.489931.BE
J. Zhu, J. Hou, Y. Zhang, M. Tian, T. He, J. Liu, V. Chen, Polymeric antimicrobial membranes enabled by nanomaterials for water treatment. J Membrane Sci 550, 173–197 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.12.071
S. Li, J. Huang, Cellulose-Rich Nanofiber-Based functional nanoarchitectures. Adv Mater 28(6), 1143–1158 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501878
S. Chen, J. Popovich, N. Iannuzo, S.E. Haydel, D. Seo, Silver-Ion-exchanged nanostructured Zeolite X as antibacterial agent with superior ion release kinetics and efficacy against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 9(45), 39271–39282 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b15001
J. Cui, R. Yeasmin, Y. Shao, H. Zhang, H. Zhang, J. Zhu, Fabrication of Ag+, Cu2+, and Zn2+ ternary ion-exchanged Zeolite as an antimicrobial agent in powder coating. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59(2), 751–762 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b05338
R.E. Hall, G. Bender, R.E. Marquis, Inhibitory and cidal antimicrobial actions of electrically generated silver ions. J. Oral. Maxil. Surg. 45(9), 779–784 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-2391(87)90202-3
E. Krol, M. Jeszka-Skowron, Z. Krejpcio, E. Flaczyk, R.W. Wojciak, The effects of supplementary mulberry leaf (Morus alba) extracts on the trace element status (Fe, Zn and Cu) in relation to diabetes management and antioxidant indices in diabetic rats. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 174(1), 158–165 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0696-1
J. Pasquet, Y. Chevalier, J. Pelletier, E. Couval, D. Bouvier, M. Bolzinger, The contribution of zinc ions to the antimicrobial activity of zinc oxide. Colloid Surf. A 457, 263–274 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.05.057
V.B.P. Sudha, K.O. Singh, S.R. Prasad, P. Venkatasubramanian, Killing of enteric bacteria in drinking water by a copper device for use in the home: laboratory evidence. T. Roy Soc. Trop. Med. H. 103(8), 819–822 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2009.01.019
C. Ning, X. Wang, L. Li, Y. Zhu, M. Li, P. Yu, L. Zhou, Z. Zhou, J. Chen, G. Tan, Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, C. Mao, Concentration ranges of antibacterial cations for showing the highest antibacterial efficacy but the least cytotoxicity against mammalian cells: Implications for a new antibacterial mechanism. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 28(9), 1815–1822 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00258
H. Sanaeepur, A. Kargari, B. Nasernejad, A. Ebadi Amooghin, M. Omidkhah, A novel Co2+ exchanged zeolite Y/cellulose acetate mixed matrix membrane for CO2/N2 separation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 60, 403–413 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.10.042
F. Ji, C. Li, B. Tang, J. Xu, G. Lu, P. Liu, Preparation of cellulose acetate/zeolite composite fiber and its adsorption behavior for heavy metal ions in aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 209, 325–333 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.014
K. Baghdad, A.M. Hasnaoui, Zeolite-cellulose composite membranes: synthesis and applications in metals and bacteria removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8(4), 104047–104070 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104047
L. Yu, X. Shang, H. Chen, L. Xiao, Y. Zhu, J. Fan, A tightly-bonded and flexible mesoporous zeolite-cotton hybrid hemostat. Nat. Commun. 10, 1932–1940 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09849-9
K.K. Han, L. Ma, H.M. Zhao, X. Li, Y. Chun, J.H. Zhu, In situ synthesis of SBA-3/cotton fiber composite materials: a hybrid device for CO2 capture. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 151, 157–162 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.10.043
N. Keshavarzi, F. Mashayekhy Rad, A. Mace, F. Ansari, F. Akhtar, U. Nilsson, L. Berglund, L. Bergström, Nanocellulose-zeolite composite coatings and films for odor elimination. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 7(26), 14254–14262 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b02252
D. Klemm, B. Heublein, H.P. Fink, A. Bohn, Cellulose: Fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 44(22), 3358–3393 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200460587
B. Medronho, B. Lindman, Brief overview on cellulose dissolution/regeneration interactions and mechanisms. Adv Colloid Interfac 222, 502–508 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2014.05.004
I. Schmidt, C. Madsen, C.J.H. Jacobsen, Confined space synthesis. A novel route to nanosized zeolites. Inorg. Chem. 39(11), 2279–2283 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1021/ic991280q
I. Schmidt, A. Boisen, E. Gustavsson, K. Stahl, S. Pehrson, S. Dahl, A. Carlsson, C.J.H. Jacobsen, Carbon nanotube templated growth of mesoporous zeolite single crystals. Chem. Mater. 13(12), 4416–4418 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm011206h
S. Chu, Y. Miao, Y. Qian, F. Ke, P. Chen, C. Jiang, X. Chen, Synthesis of uniform layer of TiO2 nanoparticles coated on natural cellulose micrometer-sized fibers through a facile one-step solvothermal method. Cellulose 26(8), 4757–4765 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02425-w
I.M. Gerzeliev, V.A. Ostroumova, M.N. Baskhanova, Enhancement of ion exchange in a FAU type zeolite during the synthesis of an active and selective catalyst for isobutane alkylation with Butylenes. Petrol Chem. 58(8), 676–680 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0965544118080066
W. Maria, S. Aneela, S. Muhammad, I. Atif, J. Tahir, Preparation and characterization of composite membrane via layer by layer assembly for desalination. Appl. Surf. Sci. 396, 259–268 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.10.098
S.B. Ma, Infrared spectrum test and analysis of regenerated cellulose fibers. Adv. Mat. Res. 671–674, 1954–1957 (2013).
H. Dai, Y. Shen, T. Yang, C. Lee, D. Fu, A. Agarwal, T.T. Le, M. Tsapatsis, J.C. Palmer, B.M. Weckhuysen, P.J. Dauenhauer, X. Zou, J.D. Rimer, Finned zeolite catalysts. Nat. Mater. 19, 1074–1080 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-020-0753-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Wang, G. & Xu, X. Preparation of zeolite-cellulose composites for water disinfection. J Porous Mater 28, 1459–1468 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-021-01096-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-021-01096-y