Abstract
Background
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is condition characterized by a gradual loss of kidney function, patient with CKD suffering from a variety of immune system defects.
Methods
This study looked at Fas, T cell, BCl2, and P53 activity in people with CKD, end stage renal disease (ESRD), and stable controls.
Results
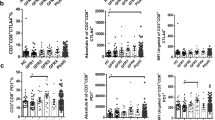
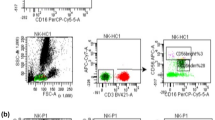
The CD4+ and CD8+ levels in ESRD patients’ peripheral blood were slightly lower than those in CKD patients. The CKD and ESRD groups had slightly higher Fas and FasL mRNA expression and slightly lower BCl2 mRNA gene expression than the normal control group (P < 0.05). P53 mRNA gene expression was shown to be higher in the patients than in the controls (P < 0.01).
Conclusions
ESRD patients have a significantly lower number of T-cell subsets than CKD patients this is related to a higher degree of apoptosis in these cells.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- GFR:
-
Glomerular filtration rate
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
References
Kalkidan A, Misra A, Fedlu A, Getachew A, Mohamed M, Mohamed Y, Habtam H, Tefera B (2021) Consequence of exposure to prenatal famine on estimated glomerular filtration rate and risk of chronic kidney disease among survivors of the great ethiopian famine (1983–85): a historical cohort study. Nutr J. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-021-00675-8
Zhao M, Yu Y, Wang R, Chang M, Ma S, Qu H, Zhang Y (2021) Mechanism in chronic kidney disease. Front Pharmacol 11:619201. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.619201
Elahi W, Syed AZ, Nasim F, Anwar A, Hashmi AA (2020) Hepatitis B and C infections in patients with prolonged hemodialysis secondary to chronic renal failure. Cureus 12(10):10905. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.10905
Hartzell S, Bin S, Cantarelli C, Haverly M, Manrique J, Angeletti A, Manna G, Murphy B, Zhang W, Levitsky J, Gallon L, Yu SM, Cravedi P (2020) Kidney failure associates with Tcell exhaustion and imbalanced follicular helper T cells. Front Immunol 11:583702. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.583702
Jia C, Luan Y, Li X, Zhang X, Li C (2021) Effects of periodontitis on postoperative pneumonia in patients with lung and esophageal cancer. Thorac Cancer 6:768–774. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.13828
Thomas E, Ognian N, Anna W, Karolina K, Peter S, Paul S (2021) Inflammation and oxidative stress in CKD and dialysis patients. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:1089. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2020.8184
Basso PJ, Andrade-Oliveria V, Camara NOS (2021) Targeting immune cell metabolism in kidney diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-021-00413-7
Obeng E (2021) Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and its signals—a review. Braz J Biol 81(4):1133–1143. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.228437
Nazari M, Javandoost E, Talebi M, Movassaghpour A, Soleimani M (2021) Platelet microparticle controversial role in cancer. Adv Pharm Bull 11(1):39–55. https://doi.org/10.34172/apd.2021.005
Schleicher RI, Reichenbach F, Kraft P (2015) Platelets induce apoptosis via membrane-bound FasL. Blood. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-12-544445
Casamayor-Polo L, Lopez-Nevado M, Paz-Artal E, Alberto A, Ferseric RL, Luis A (2020) Immunologic evaluation and genetic defects of apoptosis in patients with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS). Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408363.2020.1855623
Karpuzoglu EM, Kisla Ekinic RM, Balci S, Bisgin A, Yilmaz M (2021) Altered expression of apoptosis related, circulating cell-free miRNAs in children with familial Mediterranean fever: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatol Int 41(1):103–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-020-04541-4
Betjes MG (2020) Uremia-associated ageing of the thymus and adaptive immune responses. Toxins 12:224. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12040224
Lalramenga PC, Gupta S, Naveen P (2019) Study of C-reactive protein significance in chronic kidney disease. Int J Contemp Med Res 6(6):22–25. https://doi.org/10.21276/ijcmr.2019.6.6.48
Abdel-Messeih PL, Alkady MM, Nosseir NM, Tawfik MS (2020) Inflammatory markers in end-stage renal disease patients on haemodialysis. J Med Biochem 39(4):481–487. https://doi.org/10.5937/jomb0-25120
Peters FS, Peeters AMA, Mandaviya PR (2018) Differentially methylated regions in T cells identify kidney transplant patients at risk for de novo skin cancer. Clin Epigenet 10:81. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-018-0519-7
Xiaoyan J, Rongyi C, Xuesen C (2019) The difference of T cell phenotypes in end stage renal disease patients under different dialysis modality. BMC Nehrol 20:301. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-019-1475-y
Akchurin O, Meza K, Biswas S, Greenbaum M, Licona-Freudenstein AP, Goyal P, Choi JJ, Cgoi ME (2021) COVID-19 in patients with CKD in New York City. Kidney 360 2(1):63–70. https://doi.org/10.3406/KID.0004142020
Mohamed AA, Khater SI, Arisha AH, Metwally MM, Hedeab GM, El-Shetry SE (2021) Chitosan-stabilized selenium nanoparticles alleviate cardio-hepatic damage in type 2 diabetes mellitus model via regulation of caspase, Bax/Bcl-2, and Fas/FasL-pathway. Gene 768:145288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2020.145288
Olaposi O, Ukwenya V, Oyekanmi N, Alaba G, Oluwamodupe E, Inyang O (2021) Synergistic erythropoietic mechanisms of Chromolaena odorata and Tithonia diversifolia in the bone marrow of Wistar rats. Comp Clin Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-021-03216-1
Sayequa D (2021) Mechanisms adopted by cancer cells to escape apoptosis—a review. Biocell. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2021.013993
Fairlie WD, Lee EF (2021) Co-operativity between MYC and BCL-2 proteins in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 22:2841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062841
Nourie N, Chamaa MA, Mouawad S (2021) Effective treatment with Tocilizumab in ACOVID-19 patient on maintenance hemodialysis: a case report. CEN Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13730-021-00577-y
Mengwu P, Christine B (2021) Regulation of P53 by E3s. Cancers 13:745. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040745
Xie H, Ma K, Zhang K (2021) Cell-cycle arrest and senescence in TP53-wild type renal Carcinoma by enhancer RNA-P53-bound enhancer regions 2 (p53BER2) in a p53-dependent pathway. Cell Death Dis 12(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03229-8
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MMZ and SAD contributed to conception and design of the study. FME-T and SAD and AES, contributed to acquisition, analysis and interpretation of the data and writing the manuscript. MMZ, AEE-A and FME-T discussed the results and implications and commented on the manuscript at all stages, as well as in the final approval of the version to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies were in accordance with ethics standards of Mansoura University, Faculty of Medicine. We commit to provide Photocopy of consent forms of all subjects involved to the ethical committee when requested before publishing or submitting to refereeing.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakaria, M.M., Derbala, S.A., Salem, A.E. et al. Inflammatory markers in chronic kidney disease and end stage renal disease patients. Mol Biol Rep 48, 6857–6862 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06684-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06684-4