Abstract
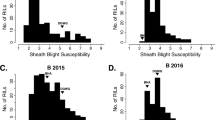
Head smut (HS) is one of the most devastating diseases of maize in spring production regions in China. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) for HS resistance were identified in this study to provide theoretical and applied tools for breeding HS resistance in maize. QTL associated with HS resistance were identified in a F2:3 population derived from a T32 (highly resistant genotype) × HC (highly susceptible genotype) cross. Analysis in each of three environments and a collective analysis across all three environments were used to identify QTL in the F2:3 population. A significant difference in HS resistance was found between the inbred lines, ‘T32’ and ‘HC’. Large genetic variation and transgressive segregation in the F2:3 population were observed between the three different sites, Guian (GA), Huaxi (HX), and Pingba (PB). Two stable and novel QTL for resistance to HS were detected in the different environments that were located within the bnlg1014 to umc2224 (qHS1) interval on chromosome 1 and in the umc1006 to umc1857 (qHS6) interval on chromosome 6. Both QTL can be used for further fine mapping, marker-assisted selection breeding, and theoretical studies on HS resistance in maize.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors described the relevant data sources in the manuscript. The data generated or anzlyzed during this study are included in this manuscript and its supplementary material.
Abbreviations
- HS:
-
Head smut
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- MAS:
-
Marker-assisted selection
- GA:
-
Guian
- HX:
-
Huaxi
- PB:
-
Pingba
- JA:
-
Joint analysis
- cM:
-
Centimorgans
- CIM:
-
Compound intervals mapping
- HS1 :
-
An antidisease position on chromosome 1 in maize
- NILs:
-
Near-isogenic lines
References
Ali A, Baggett JR (1990) Inheritance of resistance to head smut disease in corn. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 115(4):668–672
Bai YF (2009) Application analysis on the genetic regulation of maize head smut resistance. J Maize Sci 17(06):124–126
Bernardo R, Bourrier M, Olivier JL (1992) Generation means analysis of resistance to head smut in maize. Agronomie 12:303–306
Boer MP, Wright D, Feng L, Podlich DW, Luo L, Cooper M, van Eeuwijk FA (2007) A mixed-model quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis for multiple-environment trial data using environmental covariables for QTL-by-environment interactions, with an example in maize. Genetics 177(3):1801–1813
Chen D, Ronald P (1999) A rapid DNA mini-preparation method suitable for AFLP and other PCR applications. Plant Mol Biol Report 17:53–57. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007585532036
Chen YS, Chao Q, Tan GQ, Zhao J, Zhang MJ, Ji Q, Mingliang Xu (2008) Identification and fine-mapping of a major QTL conferring resistance against head smut in maize. Theor Appl Genet 117:1241–1252
Edwards M, Stuber C, Wendel J (1987) Molecular-marker-facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize I. numbers, genomic distribution and types of gene action. Genetics 116:113–125
Gao SR (2005) Inheritance and quantitative trait loci mapping of resistance to head smut caused by sphacelotheca reiliana (kühn) in maize [D]. Jilin University
Gao J, Qi X, Yu RH, Wang YL (2006) Resistance identification of corn germplasm to Sporisorium reilianum. J Jilin Agric Univ 28(2):142–147
Guo MK, Liu YG, Wang XM (2007) Identification and evaluate of maize inbred lines and populations sporisorium holci-sorghi resistance. J Maize Sci 15(5):30–33
Jacobs JME, Van Eck HJ, Arens P, Verkerk-Bakker B, te Lintel Hekkert B, Bastiaanssen HJM, EI-Kharbotly A, Pereira A, Jacobsen E, Stiekema WJ (1995) A genetic map of potato (Solanum tuberosum) integrating molecular markers, including transposons, and classical markers. Theor Appl Genet 91:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00220891
Jian KW (2009) Inclusive composite interval mapping of quantitative trait genes. Acta Agron Sin 35:239–245
Jin QM, Wang XO, Wang ZY, Sha HL, Li H, Song SY (2003) The epidemio logical factors and control tactics of head smut in spring corn area of northeast of China. J Maize Sci 11(1):86–87
Knapp S, Stroup W, Ross W (1985) Exact confidence intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis1. Crop Sci. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci1985.0011183X002500010046x
Li H, Ye G, Wang J (2007) A modified algorithm for the improvement of composite interval mapping. Genetics 175:361–374
Li H, Ribaut J-M, Li Z, Wang J (2008) Inclusive composite interval mapping (ICIM) for digenic epistasis of quantitative traits in biparental populations. Theor Appl Genet 116:243–260
Little CR, Perumal R, Tesso TT, Prom LK, Odvody GN, Magill CW (2012) Sorghum pathology and biotechnology-A fungal disease perspective: part I. Grain mold, head smut, and ergot. Eur J Plant Sci Biotechnol 6:10–30
Liu XH, Tan ZB, Rong TZ (2009) Molecular mapping of a major QTL conferring resistance to SCMV based on immortal RIL population in maize. Euphytica 167:229–235
Lu XW, Brewbaker JL (1999) Molecular mapping of QTLs conferring resistance to sphacelotheca reiliana (kühn) clint. Maize Genet Cooperation News Lett (MNL) 73:36
Lübberstedt XXC, Tan G, Liu X, Melchinger AE (1999) QTL mapping of resistance to Sporisorium reiliana in maize. Theor Appl Genet 99(3–4):593–598
Meng J, Pei EQ, Song YC, Shi YS, Li YX (2015) Resistant identification of stalk rot and head smut for introduced U. S. GEM germplasm in maize. J Plant Genet Resour 16(05):1098–1102
Peng B, Li Y, Wang Y, Liu C, Liu Z, Tan W, Zhang Y, Wang D, Shi Y, Sun B (2011) QTL analysis for yield components and kernel-related traits in maize across multi-environments. Theor Appl Genet 122:1305–1320
Portwood JL, Woodhouse MR, Cannon EK, Gardiner JM, Harper LC, Schaeffer ML, Walsh JR, Sen TZ, Cho KT, Schott DA, Braun BL, Dietze M, Dunfee B, Elsik CG, Manchanda N, Coe E, Sachs M, Stinard P, Tolbert J, Zimmerman S, Andorf CM (2019) Maize GDB 2018: the maize multi-genome genetics and genomics database. Nucl Acids Res 47(D1):D146–D1154. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1046
Potter AA (1914) Head smut of sorghum and maize. Agric Res 2:339–380
Qian HT, Dong H, Cong B (2007) Molecular mark used in the corn breeding. J Maize Sci 15(2):53–57
Ren ZQ, Bu HH, Yang HZ, Xiao JH (2014) Research advance and control on smut disease in maize. An Hui Agric Sci 42(30):10564–10566
Sánchez Pale JR (2011) Modelization of the spatial distribution of corn head smut (Sporisorium reilianum Langdon and Fullerton) in Mexico. Span J Agric Res 9(3):882–893
Shi HL, Jiang YX, Wang ZH, Li XH, Li MS, Zhang SH (2005) QTL identification of resistance to head smut in maize. Acta Agron Sin 31:1449–1454
Shi HL (2009) Developing markers and fine-mapping of genes conferring the resistance to Sphacelotheca reiliana in maize [D]. Sichuan Agricultural University
Shrestha V, Awale M, Karn A (2019) Genome wide association study (GWAS) on disease resistance in maize. In: Wani SH (ed) Disease resistance in crop plants: molecular genetic and genomic perspectives. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 113–130
Song SY, Sun XH, Guo WG, Liu JR (2000) Identification for maize germplasms resources resistant to the head smut caused by Sporisorium reilianum. J Jilin Agric Sci 25(3):32–33
Stuber CW, Edwards M, Wendel J (1987) Molecular marker-facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize II factors influencing yield and its component traits. Crop Sci 27(4):639–648
Tan K, Li CH, Yang M, Shen T, Qiu HB (2019) Identification of head smut resistance and analysis of genetic diversity of 10 commonly used maize inbred lines in Guizhou. J South Agric 50(11):2384–2391
Tuberosa R, Sanguineti M, Landi P, Salvi S, Casarini E, Conti S (1998) RFLP mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling abscisic acid concentration in leaves of drought-stressed maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 97:744–755
Wang LS, Kong LX, Zhao JY, Luo PC (2001) Screening and identification disease resistance of corn to various diseases. J Agric Univ Hebei 24(4):62–67
Wang ZH, Jing YX, Wang LF, Jin Y, Li XH, Shi HL (2002) Research advance on head smut disease in maize. J Maize Sci 04:61–64
Wang ZH, Li XH, Li MH, Li WH, Zhang SH (2004) Inheritance of resistance to sugarcane mosaic virus in maize. Acta Agronomica Sinica 30(2):95–100
Wang ZH, Li XH, EW D YTJ, Zhang L, Dong L, Jiang YX, Jin Y (2004) Germplasm identification and genetics study of resistance to head smut in maize. J Northeast Agric Univ 03:261–267
Yong XL, Xun W, Jennifer J, Zhang D, Cui D, Li C, Hu G, Dong H, Song Y-C, Shi Y-S, Wang T, Li B, Li Y (2015) The Identification of two head smut resistance-related QTL in maize by the joint approach of linkage mapping and association analysis. Plos One 10(12):e0145549
Zhang WZ, Song DZ, Zhao JF, Zhang WY, Li HS, Liu JX, Yang GY (2002) Study on genetics features of maize head smut-resistance. J Maize Sci 04:67–69
Zhang S, Gardiner J, Xiao Y, Zhao J, Wang F, Zheng Y (2013) Floral transition in maize infected with Spor-isorium reilianum disrupts compatibility with this biotrophic fungal pathogen. Planta 237:1251–1266
Zhao XR, Tan GQ, Xing YX, Wei L, Chao Q, Zuo W, Lübberstedt T, Mingliang Xu (2012) Marker-assisted introgression of q HSR1 to improve maize resistance to head smut. Mol Breed 30(2):1077–1088
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Ming liang Zhou for his support with field work in this research.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32060488), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31460384), and Guizhou Province Science & Technology Cooperation Plan [LH (2015)7671].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, H., Tan, K., Li, C. et al. Identification of QTL for resistance to head smut in maize (Zea mays. L). Euphytica 217, 185 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-021-02916-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-021-02916-7