Abstract—
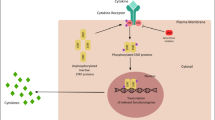
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been demonstrated to play crucial roles in the development and progression of many diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the functions and molecular mechanism of circ_0008360 in RA remain unclear. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was employed to determine the expression of circ_0008360, microRNA-135b-5p (miR-135b-5p), and histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4). Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, wound healing assay, and flow cytometry analysis were performed to assess cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis, respectively. Inflammatory response was evaluated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The interaction between miR-135b-5p and circ_0008360 or HDAC4 was predicted by bioinformatics analysis and verified by dual-luciferase reporter and RNA Immunoprecipitation (RIP) and RNA pull-down assays. Western blot assay was used to detect the protein expression of HDAC4 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). The expression of circ_0008360 was downregulated in RA synovial tissues and RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLSs). Circ_0008360 suppressed the proliferation, migration, and inflammation and promoted apoptosis of RA-FLSs, and circ_0008360 knockdown showed opposite effects. Moreover, miR-135b-5p was a direct target of circ_0008360, and miR-135b-5p could reverse the effects of circ_0008360 on proliferation, migration, inflammation, and apoptosis in RA-FLSs. Furthermore, HDAC4 was a downstream target of miR-135b-5p, and miR-135b-5p accelerated the proliferation, migration, and inflammation and suppressed apoptosis of RA-FLSs by targeting HDAC4. In addition, circ_0008360 positively regulated HDAC4 expression by sponging miR-135b-5p. Circ_0008360 inhibited the proliferation, migration, and inflammation and facilitated apoptosis of RA-FLSs by sponging miR-135b-5p and upregulating HDAC4, providing a potential target for prevention and treatment of RA.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
REFERENCES
Araki, Y., and T. Mimura. 2016. The mechanisms underlying chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of the epigenetic landscape. Journal of Immunology Research 2016: 6290682.
Wang, G., R. Mu, and H. Xu. 2015. Management of rheumatoid arthritis in People’s Republic of China - focus on tocilizumab and patient considerations. International Journal of General Medicine 8: 187–194.
Smolen, J.S., and D. Aletaha. 2015. Rheumatoid arthritis therapy reappraisal: Strategies opportunities and challenges. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 11 (5): 276–289.
Bartok, B., and G.S. Firestein. 2010. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunological Reviews 233 (1): 233–255.
Shang, C.H., Q.Q. Zhang, and J.H. Zhou. 2016. Oridonin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Inflammation 39 (2): 873–880.
You, S., J.H. Koh, L. Leng, W.U. Kim, and R. Bucala. 2018. The tumor-like phenotype of rheumatoid synovium: Molecular profiling and prospects for precision medicine. Arthritis & Rheumatology 70 (5): 637–652.
Memczak, S., M. Jens, A. Elefsinioti, F. Torti, J. Krueger, A. Rybak, L. Maier, S.D. Mackowiak, L.H. Gregersen, M. Munschauer, A. Loewer, U. Ziebold, M. Landthaler, C. Kocks, F. le Noble, and N. Rajewsky. 2013. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495 (7441): 333–338.
Li, Y., Q. Zheng, C. Bao, S. Li, W. Guo, J. Zhao, D. Chen, J. Gu, X. He, and S. Huang. 2015. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Research 25 (8): 981–984.
Chen, Y., C. Li, C. Tan, and X. Liu. 2016. Circular RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human diseases. Journal of Medical Genetics 53 (6): 359–365.
Meng, X., X. Li, P. Zhang, J. Wang, Y. Zhou, and M. Chen. 2017. Circular RNA: An emerging key player in RNA world. Briefings in Bioinformatics 18 (4): 547–557.
Li, B., N. Li, L. Zhang, K. Li, Y. Xie, M. Xue, and Z. Zheng. 2018. Hsa_circ_0001859 Regulates ATF2 expression by functioning as an MiR-204/211 sponge in human rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Immunology Research 2018: 9412387.
Zhong, S., Q. Ouyang, D. Zhu, Q. Huang, J. Zhao, M. Fan, Y. Cai, and M. Yang. 2020. Hsa_circ_0088036 promotes the proliferation and migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes by sponging miR-140-3p and upregulating SIRT 1 expression in rheumatoid arthritis. Molecular Immunology 125: 131–139.
Wen, J., J. Liu, P. Zhang, H. Jiang, L. Xin, L. Wan, Y. Sun, D. Huang, Y. Sun, Y. Long, Y. Zhang, B. Bao, and G. Sun. 2020. RNA-seq reveals the circular RNA and miRNA expression profile of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Bioscience Reports 40(4):BSR20193160.
Hansen, T.B., T.I. Jensen, B.H. Clausen, J.B. Bramsen, B. Finsen, C.K. Damgaard, and J. Kjems. 2013. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495 (7441): 384–388.
Ardekani, A.M., and M.M. Naeini. 2010. The role of microRNAs in human diseases. Avicenna Journal of Medical Biotechnology 2 (4): 161.
Alvarez-Garcia, I., and E.A. Miska. 2005. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development 132 (21): 4653–4662.
Yu, C., W. Chen, and X. Wang. 2011. MicroRNA in osteoarthritis. Journal of International Medical Research 39 (1): 1–9.
Yang, S., and Y. Yang. 2015. Downregulation of microRNA-221 decreases migration and invasion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Molecular Medicine Reports 12 (2): 2395–2401.
Liu, C., A. Pan, X. Chen, J. Tu, X. Xia, and L. Sun. 2019. MiR-5571-3p and miR-135b-5p, derived from analyses of microRNA profile sequencing, correlate with increased disease risk and activity of rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Rheumatology 38 (6): 1753–1765.
Gregoretti, I.V., Y.M. Lee, and H.V. Goodson. 2004. Molecular evolution of the histone deacetylase family: Functional implications of phylogenetic analysis. Journal of Molecular Biology 338 (1): 17–31.
Shao, L., and C. Hou. 2019. miR-138 activates NF-κB signaling and PGRN to promote rheumatoid arthritis via regulating HDAC4. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 519 (1): 166–171.
Zhang, Y., Y.Z. Xu, N. Sun, J.H. Liu, F.F. Chen, X.L. Guan, A. Li, F. Wang, Q.F. Zhao, H.Y. Wang, S.S. Song, W. Yu, J.N. Zhao, and X.J. Li. 2016. Long noncoding RNA expression profile in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 18 (1): 227.
Prelich, G., and B. Stillman. 1988. Coordinated leading and lagging strand synthesis during SV40 DNA replication in vitro requires PCNA. Cell 53 (1): 117–126.
Haque, S., and L.W. Harries. 2017. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) in health and disease. Genes 8 (12): 353.
Bartel, D.P. 2009. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136 (2): 215–233.
Aletaha, D., and J.S. Smolen. 2018. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis: A review. JAMA 320 (13): 1360–1372.
Falconer, J., A.N. Murphy, S.P. Young, A.R. Clark, S. Tiziani, M. Guma, and C.D. Buckley. 2018. Review: Synovial cell metabolism and chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology 70 (7): 984–999.
Chen, L.L., and L. Yang. 2015. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biology 12 (4): 381–388.
Liu, C.X., X. Li, F. Nan, S. Jiang, X. Gao, S.K. Guo, W. Xue, Y. Cui, K. Dong, H. Ding, B. Qu, Z. Zhou, N. Shen, L. Yang, and L.L. Chen. 2019. Structure and degradation of circular RNAs regulate PKR activation in innate immunity. Cell 177 (4): 865-880.e821.
Meng, S., H. Zhou, Z. Feng, Z. Xu, Y. Tang, P. Li, and M. Wu. 2017. CircRNA: Functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Molecular Cancer 16 (1): 94.
Akhter, R. 2018. Circular RNA and Alzheimer’s disease. Circular RNAs 1087: 239–243.
Luo, Q., L. Zhang, X. Li, B. Fu, Z. Deng, C. Qing, R. Su, J. Xu, Y. Guo, Z. Huang, and J. Li. 2018. Identification of circular RNAs hsa_circ_0044235 in peripheral blood as novel biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical & Experimental Immunology 194 (1): 118–124.
Tang, X., J. Wang, X. Xia, J. Tian, K. Rui, H. Xu, and S. Wang. 2019. Elevated expression of ciRS-7 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Diagnostic Pathology 14 (1): 11.
Memczak, S., M. Jens, A. Elefsinioti, F. Torti, J. Krueger, A. Rybak, L. Maier, S.D. Mackowiak, L.H. Gregersen, and M. Munschauer. 2013. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 495 (7441): 333–338.
Du, J., F. Zhang, and J. Guo. 2018. miR-137 decreases proliferation, migration and invasion in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Molecular Medicine Reports 17 (2): 3312–3317.
Wu, J., W. Fan, L. Ma, and X. Geng. 2018. miR-708-5p promotes fibroblast-like synoviocytes’ cell apoptosis and ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by the inhibition of Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway. Drug Design Development and Therapy 12: 3439–3447.
Guo, T., H. Ding, H. Jiang, N. Bao, L. Zhou, and J. Zhao. 2018. miR-338-5p Regulates the viability, proliferation, apoptosis and migration of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting NFAT5. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 49 (3): 899–910.
Wangyang, Y., L. Yi, T. Wang, Y. Feng, G. Liu, D. Li, and X. Zheng. 2018. MiR-199a-3p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes via suppressing retinoblastoma 1. Bioscience Reports 38(6):BSR20180982.
Felekkis, K., E. Touvana, C. Stefanou, and C. Deltas. 2010. microRNAs: A newly described class of encoded molecules that play a role in health and disease. Hippokratia 14 (4): 236.
Marroncelli, N., M. Bianchi, M. Bertin, S. Consalvi, V. Saccone, M. De Bardi, P.L. Puri, D. Palacios, S. Adamo, and V. Moresi. 2018. HDAC4 regulates satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting P21 and Sharp1 genes. Scientific Reports 8 (1): 3448.
Spaety, M.E., A. Gries, A. Badie, A. Venkatasamy, B. Romain, C. Orvain, K. Yanagihara, K. Okamoto, A.C. Jung, G. Mellitzer, S. Pfeffer, and C. Gaiddon. 2019. HDAC4 levels control sensibility toward cisplatin in gastric cancer via the p53–p73/BIK pathway. Cancers (Basel) 11 (11): 1747.
Wang, Z., G. Qin, and T.C. Zhao. 2014. HDAC4: Mechanism of regulation and biological functions. Epigenomics 6 (1): 139–150.
Kawabata, T., K. Nishida, K. Takasugi, H. Ogawa, K. Sada, Y. Kadota, J. Inagaki, S. Hirohata, Y. Ninomiya, and H. Makino. 2010. Increased activity and expression of histone deacetylase 1 in relation to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 12 (4): R133.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jinying Hao designed the study and wrote the manuscript. Yan Chen analyzed the data and performed the experiments. Yunxiang Yu summarized the data. All authors contributed to this study, read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Heping Hospital Affiliated to Changzhi Medical College. Informed consent was obtained.
Consent for Publication
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1. Circ_0008360 was downregulated in RA synovial tissues and RA-FLSs.
2. Circ_0008360 inhibited the proliferation, migration and inflammation and promoted apoptosis of RA-FLSs by sponging miR-135b-5p.
3. MiR-135b-5p promoted the proliferation, migration and inflammation and inhibited apoptosis of RA-FLSs by targeting HDAC4.
4. Circ_0008360 regulated HDAC4 expression by acting as a sponge of miR-135b-5p.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, J., Chen, Y. & Yu, Y. Circular RNA circ_0008360 Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration, and Inflammation and Promotes Apoptosis of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes by Regulating miR-135b-5p/HDAC4 Axis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation 45, 196–211 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01538-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01538-4