Abstract
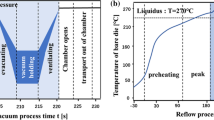
In the actual production process, soldering is a key step in the flip-chip packaging process. The reliability of the interconnection interface of flip-chip LED chips is considered to be one of the most important reliability issues. This paper studies the influence of different soldering temperatures on the microstructure and shear behavior of the Au/Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu/Cu solder joints of flip-chip LED chips. The lead-free solder Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu was selected as the solder. The microstructure of the intermetallic compound (IMC) interface and the inferred surface of the solder joint is observed, and the microstructure evolution of the solder joint is analyzed. The void ratio of the solder joints at 250°C, 260°C, 270°C, 280°C, and 290°C soldering temperature was tested to characterize the influence of the contact area between the chip and the solder joint on the shear stress. In addition, the solder joints were aged for 1000 hours in an environment with a relative humidity of 85°C/85%, and a shear test was performed to evaluate the influence of the interface reaction on the mechanical reliability of the solder joints during the isothermal aging process. The research show that when the soldering temperature is 270°C, the Au on the bottom of the chip, and the solder and Cu on the substrate have fully reacted, and the solder joints have high shear resistance. The shear strength of the aging solder joints increases first and then decreases, because the high temperature repairs the defects in the solder layer caused by the low soldering temperature to a certain extent. With the extension of aging, cracks and voids gradually appear at the fracture interface, and the effective contact area decreases. The shear strength of the solder joint decreases, and the fracture mode becomes brittle.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.H. Lee, and Y.B. Park, J. Electron. Mater. 38, 2194 (2009).
M. Roma, S. Kudtarkar, O. Kierse, D. Sengupta, and J. Cho, J. Electron. Mater. 47, 1 (2018).
L.K. Teh, C.C. Wong, S. Mhaisalkar, K. Ong, P.S. Teo, and E.H. Wong, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 271 (2004).
C.M. Tsai, W.C. Luo, C.W. Chang, Y.C. Shieh, and C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1424 (2004).
J.W. Kim, and S.B. Jung, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 690 (2007).
Z. Huang, P.P. Conway, C. Liu, and R.C. Thomson, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1227 (2004).
W.H. Zhong, Y.C. Chan, M.O. Alam, B.Y. Wu, and J.F. Guan, J. Alloy Compd. 414, 123 (2006).
Y. Kariya, T. Hosoi, S. Terashima, and T.M. Otsuka, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 321 (2004).
W.J. Chen, Y.L. Lee, T.Y. Wu, T.C. Chen, and M.T. Lin, J. Electron. Mater. 47, 1 (2018).
C.E. Ho, Y.W. Lin, S.C. Yang, C.R. Kao, and D.S. Jiang, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1017 (2006).
M.N. Islam, A. Sharif, and Y.C. Chan, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 143 (2005).
C.C. Chang, Y.W. Lin, Y.W. Wang, and C.R. Kao, J. Alloy Compd. 492, 99 (2010).
M.L. Huang, and F. Yang, Sci Rep-uk. 4, 7117 (2014).
Z. Li, G.Y. Li, L.X. Cheng, and Y. Tang, J. Alloy Compd. 685, 983 (2016).
M. Amagai, Microelectron Reliab. 48, 1 (2008).
L. Ping, Y. Pei, and L. Jim, J Alloy Compd. 486, 474 (2009).
Y. Pei, L. Ping, and J. Liu, J. Alloy Compd. 462, 73 (2008).
F. Zhang, M. Li, C.C. Chum, and Z.C. Shao, J. Electron. Mater. 32, 123 (2003).
J. Shen, and Y.C. Chan, J. Alloy Compd. 477, 552 (2009).
S.S. Ha, J.W. Kim, J.W. Yoon, S.O. Ha, and S.B. Jung, J Electron Mater. 38, 70 (2009).
Y.S. Lai, Y.T. Chiu, and J. Chen, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 1624 (2008).
Y.H. Lin, C.M. Tsai, Y.C. Hu, Y.L. Lin, and C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 27 (2005).
C.L. Chuang, J.N. Aoh, Q.A. Liao, C.C. Hsu, S.J. Liao, and G.S. Huang, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 1742 (2008).
S.H. Park, S.H. Lee, Y.H. Kim, Y.W. Kim, and S.W. Ryu, Semicond Sci. Tech. 32, 035022.1 (2017).
C. Guan, J. Zou, H. Liu, Q. Lu, Y. Li, Y. Bobo, and M. Shi, J. Electron. Mater. 50, 1 (2021).
S. Nai, J. Wei, and M. Gupta, J. Alloy Compd. 473, 100 (2009).
Y. Liu, F. Sun, H. Zhang, T. Xin, C.A. Yuan, and G. Zhang, Microelectron. Reliab. 55, 1234 (2015).
Y.J. Chen, C.K. Chung, C.R. Yang, and C.R. Kao, Microelectron Reliab. 53, 47 (2013).
F. Hodaj, O. Liashenko, and Yu, Acta Mater. 99, 106 (2015).
C.H. Chen, S.W. Hsu, and T.H. Chuang, J. Electron. Mater. 50, 1 (2020).
K.Z. Wang, and C.M. Chen, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 1543 (2005).
S.J. Wang, and C.Y. Liu, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 1955 (2006).
K.T. Wu, S.J. Hwang, and H.H. Lee, J. Electron. Mater. 46, 5094 (2017).
D. Li, C. Liu, and P.P. Conway, J. Electron. Mater. 35, 388 (2006).
S.H. Kim, J.Y. Kim, J. Yu, and T.Y. Lee, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 948 (2004).
J. Chengshuo, F. Jiajie, Q. Cheng, Z. Hao, F. Xuejun, G. Weiling, and Z. Guoqi, IEEE T Comp. Pack. Man. 99, 1 (2018).
B. Zhou, T.R. Bieler, T.K. Lee, and K.C. Liu, J. Electron. Mater. 38, 2702 (2009).
H.B. Qin, X.P. Zhang, M.B. Zhou, X.P. Li, and Y.W. Mai, Microelectron. Reliab. 55, 1214 (2015).
C.K. Wong, J.H.L. Pang, J.W. Tew, B.K. Lok, H.J. Lu, F.L. Ng, and Y.F. Sun, Microelectron. Reliab. 48, 611 (2008).
J.W. Yoon, and S.B. Jung, J Alloy Compd. 458, 200 (2008).
T. An, and F. Qin, Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 932 (2014).
F.X. Che, and J. Pang, J. Alloy Compd. 541, 6 (2012).
J.W. Yoon, and S.B. Jung, J. Alloy Compd. 407, 141 (2006).
Y.Y. Shiue, and T.H. Chuang, J. Alloy Compd. 491, 610 (2010).
Q.K. Zhang, and Z.F. Zhang, J. Alloy Compd. 485, 853 (2009).
C. Jie, J. Shen, S. Lai, M. Dong, and X. Wang, J. Alloy Compd. 489, 631 (2010).
S.Y. Chang, Y.C. Huang, and Y.M. Lin, J. Alloy Compd. 490, 508 (2010).
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by the Shanghai Alliance Plan (LM201978), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Zhejiang Province, China (2018C01046), and Enterprise-funded Latitudinal Research Projects (J2016-141), (J2017-171), (J2017-293), and (J2017-243).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, X., Chen, Y., Li, Y. et al. Research on Microstructure and Shear Behavior of Au/Sn-Ag-Cu/Cu Lead-free Solder Joints at Different Soldering Temperatures. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 5965–5980 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09107-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-09107-z