Abstract
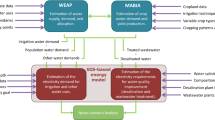
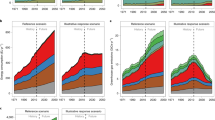
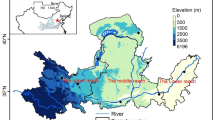
The concept of the water-food-energy nexus has been widely studied in the past decade. In this paper we expand on this concept to include environmental, economic, and social aspects as well as life cycle assessment based thinking. We proposed a set of Environmental Footprint Assessment, Life Cycle Assessment, and Socio-Economic Assessment indicators and calculated them using a developed System Dynamic Model for Water-Land-Food-Energy-Environment-Economic-Social Nexus (SD-WLF3ESN). The developed model was applied to predict the WLF3ESN of the corn crop in the Western Lake Erie Basin (WLEB)-USA for the period 2016-2030. The prediction was based on scenarios for population, land, yield, crop use, and crop production costs and returns at the county level of WLEB. A matrix for WLF3ESN of the corn crop in WLEB was developed. This matrix can help in developing policies and strategies for managing the nexus in the basin.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Most of the data used during the study is illustrated in the submitted article.
Code Availability
Vensim model has been used for this study. All code is illustrated in the submitted article.
References
Al-Ansari T, Korre A, Nie Z, Shah N (2015) Development of a life cycle assessment tool for the assessment of food production systems within the energy, water and food nexus. Sustain Product Consum J 2:52–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2015.07.005
Bare J (2011) TRACI 2.0. The Tool for the Reduction and Assessment of Chemical and other environmental Impacts. clean technologies and environmental policy. Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, 13(5):687-696. https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?Lab=NRMRL&dirEntryId=227747
Barton B, Clark S (2014) Water & Climate Risks Facing U.S. Corn Production, How Companies & Investors Can Cultivate Sustainability. Ceres, New york, USA. https://www.ourenergypolicy.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/ceres-corn.pdf. (Accessed on December 2019).
Bell A, Matthews N, Zhang W (2016) Opportunities for improved promotion of ecosystem services in agriculture under the Water-Energy-Food Nexus. J Environ Stud Sci 6(1):183–191
Boelee E et al (2011a) Ecosystems for water and food security. Nairobi: United Nations Environment Programme, Colombo: International Water Management Institute. http://www.iwmi.org/ecosystems
Boelee E, Chiramba T, Khaka E et al (2011b) An ecosystem services approach to water and food security. Nairobi: United Nations Environment Programme, Colombo: International Water Management Institute
Bonn 2011 Nexus Conference (2011) The water, energy and food security nexus— Solutions for a green economy. http://www.water-energy-food.org/en/whats_the_nexus.html
Chapagain A, Hoekstra A (2004) Water footprints of nations. Value of Water Research Report Series No.16, UNESCO-IHE UNISCO- IHE, Institute for Water Education
Das A, Sahoo B, Panda S (2020) Evaluation of nexus-sustainability and conventional approaches for optimal water-energy-land-crop planning in an irrigated canal command. Water Resour Manag 34:2329–2351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02547-yde
De Vito R, Pagano A, Portoghese I et al (2019) Integrated approach for supporting sustainable water resources management of irrigation based on the WEFN framework. Water Resour Manage 33:1281–1295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-2196-5
El-Gafy I (2017) Water–food–energy nexus index: analysis of water–energy–food nexus of crop’s production system applying the indicators approach. Appl Water Sci 7(6):2857–2868
El-Gafy I, Grigg N, Reagan W (2017b) Water-food-energy nexus index to maximize the economic water and energy productivity in an optimal cropping pattern. Water Int 42(4):495–503
El-Gafy I, Grigg N, Reagan W (2017a) Dynamic behavior of the water-food-energy nexus: focus on crop production and consumption. J Irrig Drain 66:19–33
Field C, Michalak A (2015) Water, Climate, Energy, Food: Inseparable & Indispensable by the American Academy of Arts & Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1162/DAED_a_00337
Franke N, Boyacioglu H, Hoekstra A (2013) Grey water footprint accounting, tier 1 supporting guidelines. Value of water research report series no. 65.UNESCO-IHE Institute for Water Education, the Netherlands
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2014) Walking the nexus talk: assessing the water–energy–food nexus in the context of the sustainable energy for all initiative. Environ Nat Resour Manag Work Pap 58. Rome, Italy
Hoekstra A (2016) A critique on the water-scarcity weighted water footprint in LCA. Ecol Indic 66:564–573
Hoff H (2011) Understanding the nexus. Background paper for the Bonn 2011 Nexus Conference: The Water, Energy and Food Security Nexus Solutions for the Green Economy. Stockholm Environment Institute: Stockholm, Sweden
Huang D, Shen Z, Sun C et al (2021) Shifting from Production-Based to Consumption-Based Nexus Governance: Evidence from an Input-Output Analysis of the Local Water-Energy-Food Nexus. Water Resour Manag 35:1673–1688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02797-4
International Joint Commission (IJC) (2014) A Balanced Diet for Lake Erie: Reducing Phosphorus Loadings and Harmful Algal Blooms. Rep Lake Erie Ecosyst Pri. http://www.utoledo.edu/commissions/water-task-force/reports.html
Institute of Agricultural and Natural Resource (IANR) (2020) Bioenergy corn. University of Nebraska, Lincoln. https://cropwatch.unl.edu/bioenergy/corn. (Accessed November 2020).
Jarvie H, Sharpley A, Flaten D, Kleinman P, Jenkins A, Simmons T (2015) The Pivotal Role of Phosphorus in a Resilient Water–Energy–Food Security Nexus. JEQ. 44(4):1049–1062. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2015.01.0030
Karabulut A, Egoh B, Lanzanova D et al (2015) Mapping water provisioning services to support the ecosystem–water–food–energy nexus in the Danube river basin. Ecosyst Serv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2015.08.002
Karabulut A, Crenna E, Sala S, Udiasb A (2018) A proposal for integration of the ecosystem-water-food-land-energy (EWFLE) nexus concept into life cycle assessment: A synthesis matrix system for food security. J Clean Prod 172(20):3874–3889
Liu Q (2014) Connecting the dots between water, energy, and food, and ecosystem issue for integrated water management in changing climate. Climate Change Program, California Department of Water Resources. Conference: 99th ESA Annual Convention 2014
Liu Q (2016) Interlinking climate change with water-energy-food nexus and related ecosystem processes in California case studies. Ecol Process 5:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-016-0058-0
Marston L, Ao Y, Konar M et al (2018) High-resolution water footprints of production of the United States. Water Resour Res 54:2288–2316. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017WR021923
Ohio Lake Erie Phosphorus Task Force (2010) Lake Erie Phosphorus Task Force I, Final Report. Ohio Environ Protect Agency. https://www.epa.ohio.gov/portals/35/lakeerie/ptaskforce/Task_Force_Final_Report_April_2010.pdf
Ohio Lake Erie Phosphorus Task Force (2013) Lake Erie Phosphorus Task Force II, final report. Ohio Agricultural department, Ohio Department of natural resources, Ohio Environmental Protection Agency, and Lake Erie Commission
Ohio Development Services Agency (ODSA) (2019) 2017 Ohio County Population Estimates. https://www.development.ohio.gov/reports/reports_pop_est.htm.(Accessed June 2019)
Pimentel D (2009) Energy inputs in food crop production in developing and developed nations food. Energies 2:1–24. https://doi.org/10.3390/en20100001
Reddy V, Cunha D, Kurian M (2018) A Water–Energy–Food Nexus Perspective on the Challenge of Eutrophication. Water 10(2):1–26. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020101
Salmoral G, Yan X (2018) Food-energy-water nexus: A life cycle analysis on virtual water and embodied energy in food consumption in the Tamar catchment, UK. Resour Conserv Recycl 133:320–330
Scavia D, Kalcic M, Muenich R et al (2016) Informing Lake Erie agriculture nutrient management via scenario evaluation. Water Center, the University of Michigan Water Center, Final report
Scavia D, Kalcic M, Muenich R et al (2017) Multiple models guide strategies for agricultural nutrient reductions. Front Ecol Environ 15(3):126–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/fee.1472
Schlör H, Hake J, Venghaus S (2018) An integrated assessment model for the German food-energy-water Nexus. JSDEWES 6(1):1–12
Schnoor J (2011) Water-Energy Nexus. https://pubs.acs.org/page/esthag/vi/1. (Accessed May 2021)
Song H (2017) The Water, land, and carbon footprint of different human diet in China.M.Sc. thesis. Faculty of Engineering and Technology. University of Tente, China
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2016) Ohio corn County Estimates 2016. Natl Agric Stat Serv Great Lakes Reg
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2017) Ohio Agricultural Statistics 2016-2017 Annual Bulletin. National Agricultural Statistics Service. https://www.nass.usda.gov/Statistics_by_State/Ohio/Publications/Annual_Statistical_Bulletin/index.php
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2018a) USDA Agricultural Projections to 2027. Long-term Projections Report OCE-2018-1.
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2018b) Fertilizer Use and Price. Econ Res Serv
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2019a) Ohio Agricultural Statistics Annual Bulletin. Natl Agric Stat Serv
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2019b) Historical Costs and Returns: Corn, Economic Research Services
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) (2019c) Daily Ethanol Report Agricultural Marketing Service Livestock, Poultry & Grain Market News
Vanham D, Leip A, Galli A et al (2019) Environmental footprint family to address local to planetary sustainability and deliver on the SDGs. Sci Total Environ 693:133642
Yazdandoost F, Yazdani, A (2019) A New integrated portfolio based water-energy-environment Nexus in wetland catchments. Water Resour Manag 33:2991–3009. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-019-02280-1
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Water Research Center-Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation of Egypt and the University of Toledo-USA, for giving them the chance to cooperate in achieving the current research.
Funding
This study was partially funded by the University of Toledo’s Visiting Faculty Researcher Award (I-127141-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Inas El-Gafy (Corresponding Author): Conceptualization; methodology; review previous research; create the system dynamic model; coding; data collection; validation the system dynamic model; analysis and evaluation of results; writing; review & editing. Defne Apul (Author 2): Conceptualization; LCA data collection, analysis the results; review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Gafy, I., Apul, D. Expanding the Dynamic Modeling of Water-Food-Energy Nexus to Include Environmental, Economic, and Social Aspects Based on Life Cycle Assessment Thinking. Water Resour Manage 35, 4349–4362 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02951-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02951-y