Abstract
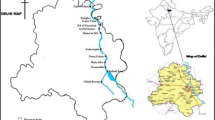
Rosetta Branch (RB) is the Nile western branch, which is considered the main freshwater resource for the western governorates of the Nile Delta, in addition to El-Beheira governorate, Egypt. This work aims to investigate the effectiveness of applying six feasible water quality management scenarios for the RB at Kafr Elzayat (KZ) City, where two major pollution sources (industrial companies and the Tala Drain) are discharging their effluents to the branch. A hydro-ecological model for the branch was developed based on MIKE 11 modeling system (3 modules). The developed model was calibrated using field hydrodynamic and water quality records for the branch during the period from November 2014 to August 2015. The calibrated model results were considered a base case for the simulated management scenarios. According to the study results, diverting the Tala Drain effluents to the nearest main drain will significantly enhance the branch water quality, while diverting of the industrial companies’ effluents to the city sewer system will significantly enhance the water quality conditions downstream of the study. The expected scenario of decreasing the RB discharge, due to future climatic changes and/or construction of the new Ethiopian dams, will significantly affect the RB water quality status in a negative way. Urgent management plans, based on the presented scenarios results (or a combination of them), should be applied to enhance the branch water quality. The Tala Drain should be, at least, provided by a water quality treatment plant, and the branch freshwater discharge should be increased.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data are available from the authors with the permission of Tanta University.
Code availability
MIKE 11 Code (2012) is licensed to the corresponding author by DHI for a single use only.
References
Abdo, M. (2013). Physico-chemeical studies on the pollutants effect in the aquatic environment of rosetta branch river Nile, Egypt. Life Science Journal, 10(4), 493.
Abou El-Anwar, E., Samy, Y., & Salman, S. (2018). Heavy metals hazard in Rosetta Branch sediments Egypt. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 9(7), 2142–2152.
Alawy, A. E., El-Tras, W. F., El Raiy, H. R., & Khater, D. F. (2015). Impact of industrial wastewater on water and fish quality of Nile River in Kafr El-Zayat, Egypt. Benha Veterinary Medical Journal, 28(1), 78–87.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association (APHA).
Assar, W., Ibrahim, M. G., Mahmod, W., & Fujii, M. (2019). Assessing the agricultural drainage water with water quality indices in the El-Salam Canal mega project. Egypt Water Report, 11(5), 1013.
Beilicci, E., & Beilicci, R. (2018). Modelling the evolution of crasna river water quality. Scientific Bulletin of Politehnica University of Timişoara, 63(77) (1), 27–32
Bui, L., & Bui, A. (2019). Application of Mike11 and remote sensing in simulating flood–A case study in Tra Khuc River, Quang Ngai Province, Vietnam. Paper presented at the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.
Chi, J., Sun, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Cao, Y., & Li, L. (2020). MIKE11 model in water quality research of Songhua River in Jiamusi City. Paper presented at the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.
Cole, T. M., & Tillman, D. H. (2001). Water quality modeling of Allatoona and West Point Reservoirs using CE-QUAL-W2. Environmental Laboratory, U.S. Army. Engineer Research and Development Center, vol Report EL SR-01–3, Final report edn.
Daifullah, A., Elewa, A., Shehata, M., & Abdo, M. (2003). Evaluation of some heavy metals in water, sediment and fish samples from Nile River (Kafr El-Zyat City), Egypt: a treatment approach Journal of Environmental Assessment and Management, (6), 16–31
DHI. (2012). MIKE 11 - User guide and technical reference manual. Danish Hydraulic Institute, DHI Water & Environment, Denmark.
Donia, N. (2005). Rosetta branch waste load allocation model. In: 9th International Water Technology Conference, Sharm El-Sheikh. (pp. 7–20).
Donia, N., El-Azizy, I., & Khalifa, A. (2003). Industrial pollution control of Rosetta branch, Nile River, EGYPT. Paper presented at the Seventh International Water Technology Conference Egypt.
Donia, N., El Saadi, A., & K. H. (2017). A decision support tool to reduce pollution along Rosetta Branch. Journal of Environmental Science, 40(2), 63–78.
EEAA. (2008). Egypt state of the environment report 2007. Egyptian Environmental Affairs Agency.
El-Amier, Y. A., Zahran, M. A. E. -K., & Al-Mamory, S. H. (2015). Assessment the physico-chemical characteristics of water and sediment in Rosetta Branch Egypt. Journal of Water Resource Protection, 7(13), 1075.
El-Bahrawy, N., & Abu Elaa, S. (2002). Pollution in the Nile River: Assessment and control case study. Paper presented at the Nile 2002 International Conference on Comprehensive Resources Development in the River Basin, Cairo, Egypt.
El-Bouraie, M. M., Motawea, E. A., Mohamed, G. G., & Yehia, M. M. (2011). Water quality of Rosetta branch in Nile delta. Egypt. Finnish Peatland Society, 62(1), 31–37.
El-Sadek, A., Radwan, M., & Willems, P. (2011). Mathematical modeling of nitrate and salinity along the Rosetta Branch in the Nile Delta. Arab Gulf Journal of Scientific Research, 29(1/2), 1–10.
El Gammal, H. A., & El Shazely, H. S. (2008). Water quality management scenarios in Rosetta River Nile branch, . Paper presented at the Twelfth International Water Technology Conference, IWTC12, Egypt.
El Gohary, R. (2017). Effect of increasing discharge on water quality: A case study. Asian Journal of Natural Applied Sciences, 6(2), 51–62.
El Sayed, S. M., Hegab, M. H., Mola, H. R., Ahmed, N. M., & Goher, M. E. (2020). An integrated water quality assessment of Damietta and Rosetta branches (Nile River, Egypt) using chemical and biological indices. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 192(4), 1–16.
Elhaddad, E., & Al-Zyoud, S. (2017). The quality assessment of pollution of Rosetta branch, Nile River. Egypt. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 10(5), 97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2870-y
Ezzat, S. M., Mahdy, H. M., Abd El Shakour, E. H., & El-Bahnasawy, M. A. (2012). Water quality assessment of river Nile at Rosetta branch: Impact of drains discharge. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 12(4), 413–423.
Gad, M., Elsayed, S., Moghanm, F. S., Almarshadi, M. H., Alshammari, A. S., Khedher, K. M., et al. (2020). Combining water quality indices and multivariate modeling to assess surface water quality in the Northern Nile Delta. Egypt Water Report, 12(8), 21–42.
Girbaciu, A., Girbaciu, C., & Rosu, S. (2016). Water quality modeling of Bega River using MIKE 11. Materiale Plastice, 53(3), 533–536.
Hausler-Cozma, D. P., Beilicci, E., Beilicci, R. (2019). Modeling of water quality evolution with advanced hydroinformatic tool. Study Case: Bega Channel Sector. Paper presented at the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering.
Ibrahim, A., Kamel, S., & OMAR, A., Madkour, H. (2017). Assessment of pollution sources on Rosetta Branch, Egypt. Journal of Natural Sciences, 15(6), 126–144.
Khan, A. A., Abdel-Gawad, S., & Khan, H. (2008). A real time water quality monitoring network and water quality indices for River Nile. In: 13th IWRA world water congress, (pp. 1–4).
Lin, X., Wang, L., Ni, H., Chen, G., Wang, Y., Wang, J., & Liu, S. (2019). Assessment of water quality improvement schemes for a complex river network: A case study of Wenling. CLEAN–Soil, Air, Water, 47(1), 1800008
Mahmoud, A., MH, N., & NAH, E. (2020). Determination of Thermal Pollution Effect on End Part of Stream. International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE), 9(3), 3311–3319.
Mohamed, S. (2013). Surface water quality management case study: Rosetta Branch-River Nile. Ain Shams University.
Mostafa, M. (2014). Modeling of pollutant transport in the Nile Delta Egypt. Department of Civil, Construction, and Environmental Engineering, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, USA,
Mostafa, M., & Peters, R. W. (2016). A comprehensive assessment of water quality at the Rosetta Branch of the Nile River Egypt. Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 10, 513-529. https://doi.org/10.17265/1934-7359/2016.05.001
MWRI. (2002). APRP water policy program. "Survey of Nile System Pollution Sources". Egyptian Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation.
MWRI. (2005). Water for the Future, National Water Resources Plan for Egypt - 2017. Egyptian Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation. Available at: http://extwprlegs1.fao.org/docs/pdf/egy147082.pdf (Accessed on 15th July 2021)
MWRI. (2010). A summary of the Egypt national strategy for the development and management of water resources until 2050 (trans: MWRI_Planning_Sector). Egyptian Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation.
Nada, A., Elshemy, M., Zeidan, B., & Hassan, A. (2016). Water quality assessment of Rosetta Branch, Nile River, at Kafr El-Zayat City, Egypt. Paper presented at the Third International Environmental Forum, Environmental Pollution: Problem & Solution, Tanta , Egypt.
NBI. (2011). Nile Basin national water quality monitoring baseline study report for Egypt. The Nile Transboundary Environmental Action Project (NTEAP). Nile Basin Initiative.
Othman, A. A., Al-Afify, A. D., Abdel-Satar, A. M., & Ramadan, M. F. (2020). Quality assessment of surface water using the Nile Chemical Pollution Index (NCPI) and microbiological pollution of the Rosetta Branch (Nile River, Egypt). African Journal of Aquatic Science, 1–13.
Palmer, M. (2001). Water quality modeling: a guide to effective practice. World Bank Publications. Available at: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/13914/multi0page.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (Accessed on 15th July 2021).
Radwan, M. (2009). Global warming impacts on water quality in the Nile Delta. Egypt. Nile Basin Water Engineering Scientific Magazine, 2, 71–78.
Reda, A., Riad, P., El-Gammal, H., Abd El-Razik, M., Nour El-Een, M., & Khalifa, A. (2015). Water quality management information system upstream Cairo drinking water plants. Journal of Engineering and Applied Science, 14–29.
Teshome, F. T., Bayabil, H. K., Thakural, L., & Welidehanna, F. G. (2020). Verification of the MIKE11-NAM model for simulating streamflow. Journal of Environmental Protection, 11(02), 152.
Waseem, M., Schilling, J., Kachholz, F., & Tränckner, J. (2020). Improved representation of flow and water quality in a North-Eastern German lowland catchment by combining low-frequency monitored data with hydrological modelling. Sustainability, 12(12), 4812.
Willmott, C. J., & Matsuura, K. (2005). Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Climate Research, 30(1), 79–82.
Wongsa, S., Sueathung, S., & Tebakari, T. (2020). Climate change and adaptive water management in Bangpakong River, Thailand. Paper presented at the 22nd IAHR-APD Congress Sapporo, Japan. Available at: https://www.iahr.org/library/download-paper-file?code=0KJurseCLY (Accessed on 15th July 2021).
Acknowledgements
This research was originated as part of a M.Sc. work for the first author at the Faculty of Engineering, Tanta University, Egypt. Providing the field data for this modeling study by the Department of Irrigation and Hydraulics Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tanta University, Egypt, was greatly appreciated. The authors extremely thank the reviewers for their hard work to improve the quality of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nada, A., Zeidan, B., Hassan, A.A. et al. Water quality modeling and management for Rosetta Branch, the Nile River, Egypt. Environ Monit Assess 193, 603 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09357-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09357-8