Abstract
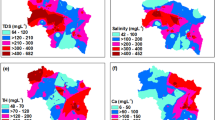
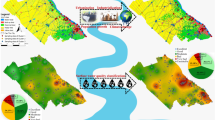
Mathematical statistics, correlation analysis, Piper and Gibbs diagrams, and geographic information system- based multi-criteria decision analysis were used to study the hydrochemical characteristics and identification of hydrochemical ions affected by human activities of the springs in the south of Yanbian City, China. Four criteria were selected: land use/land cover, village density, distance to towns, and distance to main roads. The improved entropy method was used to assign weight to each criterion, followed by evaluating the human activities impact index map, which was used to extract the human activities impact index of springs. The correlation coefficient was calculated to identify the hydrochemical parameters affected by human activities. The results show that the main hydrochemical parameters are Ca2+ among cations and HCO3− among anions. Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3−, Cl−, and total dissolved solids (TDS) have a strong correlation and similar spatial distribution, showing a decreasing trend from northwest to southeast. Most hydrochemical parameters show a similar spatial distribution trend. The hydrochemical types of springs are HCO3-Ca, HCO3-Ca•Mg, HCO3-Na•Ca, and HCO3-Ca. In the study area, Na+, K+, TFe, Mn2+, F−, PO43−, and oxygen consumption are negligibly affected by human activities, Mg2+, HCO3−, and Cl− were slightly affected, and TDS and total hardness (TH) were strongly affected. With a correlation coefficient of 0.913, nitrate exhibited the highest correlation with the human activities impact index; it was significantly affected by human activities. We conclude that nitrate was the most affected by human activities, followed by TH, TDS, and other hydrochemical parameters.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Garni, H. Z., & Awasthi, A. (2017). Solar PV power plant site selection using a GIS-AHP based approach with application in Saudi Arabia. Applied Energy, 206, 1225–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.10.024
Amiri, V., Rezaei, M., & Sohrabi, N. (2014). Groundwater quality assessment using entropy weighted water quality index (EWQI) in Lenjanat. Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 72(9), 3479–3490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3255-0
APHA, 1998. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 20^ Edition Washington D.c
Arabameri, A., Pradhan, B., Rezaei, K., & Conoscenti, C. (2019a). Gully erosion susceptibility mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis techniques. CATENA, 180, 282–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.04.032
Arabameri, A., Rezaei, K., Cerda, A., Conoscenti, C., & Kalantari, Z. (2019b). A comparison of statistical methods and multi-criteria decision making to map flood hazard susceptibility in Northern Iran. The Science of the Total Environment, 660, 443–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.021
Atici, K. B., Simsek, A. B., Ulucan, A., & Tosun, M. U. (2015). A GIS-based Multiple criteria decision analysis approach for wind power plant site selection. Utilities Policy, 37, 86–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jup.2015.06.001
Barzegar, R., et al. (2020). Exploring the hydrogeochemical evolution of cold and thermal waters in the Sarein-Nir area, Iran using stable isotopes (δ18O and δD), geothermometry and multivariate statistical approaches. Geothermics, 85, 101815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2020.101815
Bulia, I. L., & Enzweiler, J. (2018). The hydrogeochemistry of bottled mineral water in São Paulo state, Brazil. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 188, 43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.01.007
Burri, N. M., Weatherl, R., Moeck, C., & Schirmer, M. (2019). A review of threats to groundwater quality in the anthropocene. The Science of the Total Environment, 684, 136–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.236
Çetinkaya, C., Kabak, M., Erbaş, M., & Özceylan, E. (2018). Evaluation of ecotourism sites: A GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis. Kybernetes, 47(8), 1664–1686. https://doi.org/10.1108/k-10-2017-0392
Chatterjee, K.K., 2015. Macro-Economics of Mineral and Water Resources. Springer International Publishing.
Chen, J., Zhang, Y., Chen, Z., & Nie, Z. (2014). Improving assessment of groundwater sustainability with analytic hierarchy process and information entropy method: A case study of the Hohhot Plain. China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(5), 2353–2363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3583-0
Chen, W., et al. (2020). Evaluating the usage of tree-based ensemble methods in groundwater spring potential mapping. Journal of Hydrology, 583, 124602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124602
Díaz-Alcaide, S., & Martínez-Santos, P. (2019). Mapping fecal pollution in rural groundwater supplies by means of artificial intelligence classifiers. Journal of Hydrology, 577, 124006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124006
Du, Y., Zheng, Y., Wu, G., & Tang, Y. (2020). Decision-making method of heavy-duty machine tool remanufacturing based on AHP-entropy weight and extension theory. Journal of Cleaner Production, 252, 119607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119607
Dube, T., et al. (2020). Spatial modelling of groundwater quality across a land use and land cover gradient in Limpopo Province, South Africa. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c, 115, 102820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2019.102820
Dupont, C., et al. (2019). Time to treatment response of a magnesium- and sulphate-rich natural mineral water in functional constipation. Nutrition, 65, 167–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.018
Ferreira Marmontel, C. V., Lucas-Borja, M. E., Rodrigues, V. A., & Zema, D. A. (2018). Effects of land use and sampling distance on water quality in tropical headwater springs (Pimenta creek, Sao Paulo State, Brazil). The Science of the Total Environment, 622–623, 690–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.011
Gao, Y., et al. (2020). Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater based on integrated-weight water quality index in a concentrated urban area. Journal of Cleaner Production, 260, 121006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121006
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science, 170(3962), 1088–1090.
Gorgij, A. D., Wu, J., & Moghadam, A. A. (2019). Groundwater quality ranking using the improved entropy TOPSIS method: A case study in Azarshahr plain aquifer, east Azerbaijan. Iran. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 25(1–2), 176–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1564235
Greene, R., Luther, J. E., Devillers, R., & Eddy, B. (2010). An approach to GIS-based multiple criteria decision analysis that integrates exploration and evaluation phases: Case study in a forest-dominated landscape. Forest Ecology and Management, 260(12), 2102–2114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2010.08.052
Guadayol, M., Cortina, M., Guadayol, J. M., & Caixach, J. (2016). Determination of dimethyl selenide and dimethyl sulphide compounds causing off-flavours in bottled mineral waters. Water Research, 92, 149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.016
Hariz, H. A., Dönmez, C. Ç., & Sennaroglu, B. (2017). Siting of a central healthcare waste incinerator using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 166, 1031–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.08.091
Hasan, M. S. U., & Rai, A. K. (2020). Groundwater quality assessment in the Lower Ganga Basin using entropy information theory and GIS. Journal of Cleaner Production, 274, 123077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123077
Huang, Y., et al. (2018). Low-mineral direct drinking water in school may retard height growth and increase dental caries in schoolchildren in China. Environment International, 115, 104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.02.021
Jenifer, M. A., & Jha, M. K. (2017). Comparison of Analytic Hierarchy Process, Catastrophe and Entropy techniques for evaluating groundwater prospect of hard-rock aquifer systems. Journal of Hydrology, 548, 605–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.03.023
Jiang, L., Yao, Z., Liu, Z., Wang, R., & Wu, S. (2015). Hydrochemistry and its controlling factors of rivers in the source region of the Yangtze River on the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 155, 76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.04.009
Kaur, L., Rishi, M. S., Singh, G., & Nath Thakur, S. (2020). Groundwater potential assessment of an alluvial aquifer in Yamuna sub-basin (Panipat region) using remote sensing and GIS techniques in conjunction with analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and catastrophe theory (CT). Ecological Indicators, 110, 105850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105850
Kittipongvises, S., et al. (2020). AHP-GIS analysis for flood hazard assessment of the communities nearby the world heritage site on Ayutthaya Island, Thailand. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 48, 101612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101612
Lu, S. et al., 2020. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of karst groundwater in Jinci spring area, north China. Carbonates and Evaporites, 35 (3) https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00602-8.
Ma, X.-Y., Sun, Y.-Z., Fang, H.-L., & Tian, Y. (2013). Scenario-Based Multiobjective decision-making of optimal access point for wind power transmission corridor in the load centers. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 4(1), 229–239. https://doi.org/10.1109/TSTE.2012.2214791
Matiatos, I. (2016). Nitrate source identification in groundwater of multiple land-use areas by combining isotopes and multivariate statistical analysis: A case study of Asopos basin (Central Greece). The Science of the Total Environment, 541, 802–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.134
Mencio, A., et al. (2016). Nitrate pollution of groundwater; all right..., but nothing else? The Science of the Total Environment, 539, 241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.151
Merk, M., Goeppert, N., & Goldscheider, N. (2020). Processes controlling spatial and temporal dynamics of spring water chemistry in the Black Forest National Park. The Science of the Total Environment, 723, 137742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137742
Monnard, C. R., Montani, J.-P., & Grasser, E. K. (2020). Short-term cardiovascular responses to ingestion of mineral water in healthy non-obese adults: Impact of mineral components. Journal of Functional Foods, 71, 104017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2020.104017
Pacheco, M. H. S., et al. (2018). Exploration of gender differences in bottled mineral water consumption: A projective study of consumer’s perception in Brazil. Journal of Sensory Studies, 33(4), e12434. https://doi.org/10.1111/joss.12434
Page, R. M., et al. (2017). Online analysis: Deeper insights into water quality dynamics in spring water. The Science of the Total Environment, 599–600, 227–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.204
Petraccia, L., Liberati, G., Masciullo, S. G., Grassi, M., & Fraioli, A. (2006). Water, mineral waters and health. Clinical Nutrition, 25(3), 377–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2005.10.002
Ren, K., Pan, X., Zeng, J., & Yuan, D. (2019). Contaminant sources and processes affecting spring water quality in a typical karst basin (Hongjiadu Basin, SW China): Insights provided by hydrochemical and isotopic data. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 26(30), 31354–31367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06272-x
Ruiz-Pico, Á., et al. (2019). Hydrochemical characterization of groundwater in the Loja Basin (Ecuador). Applied Geochemistry, 104, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.02.008
Saaty, T.L., 1995. Decision Making for Leaders. Systems Man & Cybernetics IEEE Transactions on, smc-15(3). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1985.6313384
Saaty, T. L. (2008). Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. International Journal of Services Sciences, 1(1), 83–98. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSSCI.2008.017590
Shannon, C. E. (1948). A mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Tech J. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb00917.x
Tijani, M.N., Onodera, S.I., 2007. Surface and Groundwater Qualities In an Urbanized Catchment: Scenario from a Developing Country.
Tinti, F., Kasmaee, S., Elkarmoty, M., Bonduà, S., & Bortolotti, V. (2018). Suitability Evaluation of Specific Shallow Geothermal Technologies Using a GIS-Based Multi Criteria Decision Analysis Implementing the Analytic Hierarchic Process. Energies, 11(2), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11020457
Veronesi, F., Schito, J., Grassi, S., & Raubal, M. (2017). Automatic selection of weights for GIS-based multicriteria decision analysis: Site selection of transmission towers as a case study. Applied Geography, 83, 78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2017.04.001
Zhang, J.-L., Ren, J., 2011. The Deficiencies and Amendments of the Calculation Formulate of Entropy and Entropy Weight in the Theory of Entropy. Statistics & Information Forum.(in Chinese)
Zhang, F., et al. (2019). Groundwater quality in the Pearl River Delta after the rapid expansion of industrialization and urbanization: Distributions, main impact indicators, and driving forces. Journal of Hydrology, 577, 124004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124004
Zhang, X., Wang, C., Li, E., & Xu, C. (2014). Assessment model of ecoenvironmental vulnerability based on improved entropy weight method. The Scientific World Journal, 2014, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/797814
Zhao, H., Yao, L., Mei, G., Liu, T., & Ning, Y. (2017). A Fuzzy Comprehensive evaluation method based on ahp and entropy for a landslide susceptibility map. Entropy, 19(8), 396. https://doi.org/10.3390/e19080396
Zheng, P., Wang, N., Wang, J., Mao, X., & Luo, Y. (2019). Classification of bottled mineral waters using solution cathode glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy and chemometrics methods. Microchemical Journal, 151, 104216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104216
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support received as well as the editors and reviewers for their feedback and suggestions.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41572216); Project of Provincial-School Co-construction Plan: Frontier Science and Technology Guidance Class (No. SXGJQY2017-6); Key Projects of Geological Exploration Fund of Jilin Province (No. 2018–13, No. 2018–11); Project of China Geological Survey, Regional Water Resource Investigation Method and Groundwater Ecological Threshold Investigation (No. DD20190340-W09); Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province, Construction of Big Data Platform for Geotechnical Engineering (No. 2017ZDCXL-SF-03–01-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fanao Meng was involved in the investigation, conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. Xiujuan Liang contributed to the writing—original draft, investigation, and project administration. Changlai Xiao was involved in the project administration, supervision, and funding acquisition. Wang Ge contributed to the investigation, software, data curation, and writing—original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, F., Liang, X., Xiao, C. et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and identification of pollution ions of the springs in the south of Yanbian City, China. Environ Geochem Health 44, 2215–2233 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01070-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01070-2