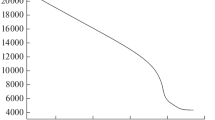
Abstract—
It is believed that microscopic life is possible in the subglacial ocean of Europa, a satellite of Jupiter. However, Jupiter’s radiation belts make it difficult to detect it on the surface or at shallow depths. Using numerical simulations, we investigated the influence of the inclination of the magnetic dipole of Jupiter, the Alfvén wings, and the induced field of Europa on the dynamics of electrons near the satellite of Jupiter, which made it possible to refine the map of radiation doses on Europa’s surface, obtained earlier in the approximation of the guiding center.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bespalov, V.I., Vzaimodeistvie ioniziruyushchikh izluchenii s veshchestvom: uchebnoe posobie (Interaction of Ionizing Radiation with Matter: Handbook), Tomsk: Izd. Tomsk. Politekh. Univ., 2008, 4th ed.
Connerney, J.E.P., Acuña, M.H., Ness, N.F., and Satoh, T., New models of Jupiter’s magnetic field constrained by the Io flux tube footprint, J. Geophys. Res., 1998, vol. 103, no. A6, pp. 11929–11940. https://doi.org/10.1029/97JA03726
Grasset, O., Dougherty, M.K., Coustenis, A., Bunce, E.J., Erd, C., Titov, D., Blanc, M., Coates, A., Drossart, P., Fletcher, L.N., Hussmann, H., Jaumann, R., Krupp, N., Lebreton, J.-P., Prieto-Ballesteros, O., Tortora, P., Tosi, F., and Van Hoolst, T., Jupiter icy moons explorer (JUICE): An ESA mission to orbit Ganymede and to characterise the Jupiter system, Planet. Space Sci., 2013, vol. 78, pp. 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pss.2012.12.002
Jia, X., Kivelson, M.G., Khurana, K.K., and Walker, R.J., Magnetic fields of the satellites of Jupiter and Saturn, Space Sci. Rev., 2010, vol. 152, pp. 271–305.
Kivelson, M.G., Khurana, K.K., Russell, C.T., Volwerk, M., Walker, R.J., and Zimmer, C., Galileo magnetometer measurements: A stronger case for a subsurface ocean at Europa, Science, 2000, vol. 289, pp. 1340–1343. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.289.5483.1340
Neubauer, F.M., Nonlinear standing Alfvén wave current system at Io: Theory, J. Geophys. Res., 1980, vol. 85, no. A3, pp. 1171–1178.
Neubauer, F.M., The sub-Alfvénic interaction of the Galilean satellites with the Jovian magnetosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 1998, vol. 103, no. E9, pp. 19843–19866.
Nordheim, T.A., Hand, K., and Paranicas, C., Preservation of potential biosignatures in the shallow subsurface of Europa, Nat. Astron., 2018, vol. 2, pp. 673–679.
Paranicas, C., McEntire, R.W., Cheng, A.F., Lagg, A., and Williams, D.J., Energetic charged particles near Europa, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys., 2000, vol. 105, no. A7, pp. 16005–16015.
Paranicas, C., Cooper, J.F., Garrett, H.B., Johnson, R.E., and Sturner, S.J., Europa’s radiation environment and its effects on the surface, in Europa, Pappalardo, R.T., McKinnon, W.B., and Khurana, K.K., Eds., Tucson: Univ. of Arizona Press, 2009.
Parkinson, W.D., Introduction to Geomagnetism, Edinburgh: Scottish Acad. Press, 1983.
Podzolko, M.V., Getselev, I.V., Gubar, Y.I., Veselovsky, I.S., and Sukhanov, A.A., Charged particles on the Earth-Jupiter-Europa spacecraft trajectory, Adv. Space Res., 2011, vol. 48, pp. 651–660.
Truscott, P., Heynderickx, D., Sicard-Piet, A., and Bourdarie, S., Simulation of the radiation environment near Europa using the geant4-based planetocosmics-j model, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2011, vol. 58, no. 6, pp. 2776–2784.
Zimmer, C., Khurana, K.K., and Kivelson, M.G., Subsurface oceans on Europa and Callisto: Constraints from Galileo magnetometer observations, Icarus, 2000, vol. 147, no. 2, pp. 329–347.
Funding
The authors are grateful to the Government of the Russian Federation and the Ministry of Higher Education and Science of the Russian Federation for the support of the following works under the grant 075-15-2020-780 (N13.1902.21.0039): 1) building a model of the dynamics of electrons near Europa, 2) calculating radiation doses on the surface of Europa under a layer of water of various thicknesses, 3) building a map of the distribution of radiation doses on the surface of Europa. Research by E.P. Popova was supported by the Russian Science Foundation under the grant 17-11-01052. Within the framework of the Russian Science Foundation grant 17-11-01052, E.P. Popova formulated the problem and magnetic field models were proposed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsareva, O.O., Popova, E.P., Popov, V.Y. et al. Modeling the Dose Distribution of Electron Radiation on the Surface of Jupiter’s Satellite Europa for Different Magnetic Field Models. Sol Syst Res 55, 335–340 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0038094621040109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0038094621040109