Abstract
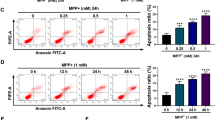
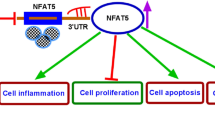
Berberine plays a neuro-protective role in neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease (PD). Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play critical roles in PD pathogenesis. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether LINC00943 was involved in the role of berberine in PD. 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) or 1-methyl-4-phenyl pyridine (MPP+) were used to construct PD mouse and cell models, respectively. Cell proliferation was evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine (Edu) assays. Inflammation and cell apoptosis were assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and flow cytometry, respectively. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was employed to test the expression of LINC00943, microRNA (miR)-142-5p, and karyopherin subunit alpha 4 (KPNA4) mRNA. The protein levels of NF-κB pathway-related markers and KPNA4 were measured by western blot. Oxidative stress level was assessed by corresponding kits. The interaction between miR-142-5p and LINC00943 or KPNA4 was determined via dual-luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assays. Berberine inhibited MPP+-induced injury in SK-N-SH cells by promoting cell proliferation and suppressing inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative injury. LINC00943 and KPNA4 were upregulated and miR-142-5p was downregulated in PD mouse and cell models. LINC00943 (or KPNA4) overexpression or miR-142-5p inhibition abated the neuro-protective role of berberine in PD cell model. Moreover, miR-142-5p was a target of LINC00943, and KPNA4 could specially bind to miR-142-5p. Additionally, berberine inhibited NF-κB pathway by regulating LINC00943/miR-142-5p/KPNA4 axis. Berberine protected SK-N-SH cell from MPP+-induced neuronal damage via regulating LINC00943/miR-142-5p/KPNA4/NF-κB pathway, highlighting novel evidence for the neuro-protective role of berberine in PD.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Lau LM, Breteler MM (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5:525–535
Tysnes OB, Storstein A (2017) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 124:901–905
Michel PP, Hirsch EC, Hunot S (2016) Understanding dopaminergic cell death pathways in Parkinson disease. Neuron 90:675–691
Fan Y, Li J, Yang Q, Gong C, Gao H, Mao Z, Yuan X, Zhu S, Xue Z (2019) Dysregulated long non-coding RNAs in Parkinson’s disease contribute to the apoptosis of human neuroblastoma cells. Front Neurosci 13:1320
Vallée A, Lecarpentier Y, Guillevin R, Vallée JN (2020) Circadian rhythms, neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in the story of Parkinson’s disease. Cells 9:314
Chen D, Zhao J, Cong W (2018) Chinese herbal medicines facilitate the control of chemotherapy-induced side effects in colorectal cancer: progress and perspective. Front Pharmacol 9:1442
Izzo AA, Di Carlo G, Borrelli F, Ernst E (2005) Cardiovascular pharmacotherapy and herbal medicines: the risk of drug interaction. Int J Cardiol 98:1–14
Peng L, Kang S, Yin Z, Jia R, Song X, Li L, Li Z, Zou Y, Liang X, Li L, He C, Ye G, Yin L, Shi F, Lv C, Jing B (2015) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of berberine against Streptococcus agalactiae. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:5217–5223
Habtemariam S (2016) Berberine and inflammatory bowel disease: a concise review. Pharmacol Res 113:592–599
Zou K, Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhang HY, Li B, Zhu WL, Shi JY, Jia Q, Li YM (2017) Advances in the study of berberine and its derivatives: a focus on anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects in the digestive system. Acta Pharmacol Sin 38:157–167
Xia LM, Luo MH (2015) Study progress of berberine for treating cardiovascular disease. Chron Dis Transl Med 1:231–235
Ahmed T, Gilani AU, Abdollahi M, Daglia M, Nabavi SF, Nabavi SM (2015) Berberine and neurodegeneration: a review of literature. Pharmacol Rep 67:970–979
Li J, Xuan Z, Liu C (2013) Long non-coding RNAs and complex human diseases. Int J Mol Sci 14:18790–18808
Gibb EA, Brown CJ, Lam WL (2011) The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol Cancer 10:38
Zhang X, Sun S, Pu JK, Tsang AC, Lee D, Man VO, Lui WM, Wong ST, Leung GK (2012) Long non-coding RNA expression profiles predict clinical phenotypes in glioma. Neurobiol Dis 48:1–8
Zhou Z, Zhu Y, Gao G, Zhang Y (2019) Long noncoding RNA SNHG16 targets miR-146a-5p/CCL5 to regulate LPS-induced WI-38 cell apoptosis and inflammation in acute pneumonia. Life Sci 228:189–197
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Taheri M (2020) Non-coding RNAs are involved in the response to oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother 127:110228
Oe S, Kimura T, Yamada H (2019) Regulatory non-coding RNAs in nervous system development and disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 24:1203–1240
Majidinia M, Mihanfar A, Rahbarghazi R, Nourazarian A, Bagca B, Avci ÇB (2016) The roles of non-coding RNAs in Parkinson’s disease. Mol Biol Rep 43:1193–1204
Meng C, Gao J, Ma Q, Sun Q, Qiao T (2021) LINC00943 knockdown attenuates MPP(+)-induced neuronal damage via miR-15b-5p/RAB3IP axis in SK-N-SH cells. Neurol Res 43:181–190
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146:353–358
Juźwik CA, Drake SS, Zhang Y, Paradis-Isler N, Sylvester A, Amar-Zifkin A, Douglas C, Morquette B, Moore CS, Fournier AE (2019) microRNA dysregulation in neurodegenerative diseases: a systematic review. Prog Neurobiol 182:101664
Chen J, Jiang C, Du J, Xie CL (2020) MiR-142-5p protects against 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cell injury by downregulating BECN1 and autophagy. Dose Response 18:1559325820907016
Xing RX, Li LG, Liu XW, Tian BX, Cheng Y (2020) Down regulation of miR-218, miR-124, and miR-144 relates to Parkinson’s disease via activating NF-κB signaling. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 36:786–792
Zheng Y, Li Y, Liu G, Qi X, Cao X (2018) MicroRNA-24 inhibits the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells in patients with atherosclerosis by targeting importin-α3 and regulating inflammatory responses. Exp Ther Med 15:338–344
Deng C, Zhu J, Yuan J, Xiang Y, Dai L (2020) Pramipexole Inhibits MPP(+)-Induced Neurotoxicity by miR-494-3p/BDNF. Neurochem Res 45:268–277
Jiang W, Li S, Li X (2015) Therapeutic potential of berberine against neurodegenerative diseases. Sci China Life Sci 58:564–569
Zhang N, Gao Y, Yu S, Sun X, Shen K (2020) Berberine attenuates Aβ42-induced neuronal damage through regulating circHDAC9/miR-142–5p axis in human neuronal cells. Life Sci 252:117637
Kim M, Cho KH, Shin MS, Lee JM, Cho HS, Kim CJ, Shin DH, Yang HJ (2014) Berberine prevents nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuronal loss and suppresses hippocampal apoptosis in mice with Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Med 33:870–878
Huang S, Liu H, Lin Y, Liu M, Li Y, Mao H, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Ye P, Ding L, Zhu Z, Yang X, Chen C, Zhu X, Huang X, Guo W, Xu P, Lu L (2020) Berberine protects against NLRP3 inflammasome via ameliorating autophagic impairment in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Front Pharmacol 11:618787
Charles Richard JL, Eichhorn PJA (2018) Platforms for Investigating LncRNA functions. SLAS Technol 23:493–506
Riva P, Ratti A, Venturin M (2016) The long non-coding RNAs in neurodegenerative diseases: novel mechanisms of pathogenesis. Curr Alzheimer Res 13:1219–1231
Cao DW, Liu MM, Duan R, Tao YF, Zhou JS, Fang WR, Zhu JR, Niu L, Sun JG (2020) The lncRNA Malat1 functions as a ceRNA to contribute to berberine-mediated inhibition of HMGB1 by sponging miR-181c-5p in poststroke inflammation. Acta Pharmacol Sin 41:22–33
Dai W, Mu L, Cui Y, Li Y, Chen P, Xie H, Wang X (2019) Berberine promotes apoptosis of colorectal cancer via regulation of the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) cancer susceptibility candidate 2 (CASC2)/AU-binding factor 1 (AUF1)/B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) axis. Med Sci Monit 25:730–738
Zhou Y, Gu C, Li J, Zhu L, Huang G, Dai J, Huang H (2018) Aberrantly expressed long noncoding RNAs and genes in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 14:3219–3229
Sanchez-Mejias A, Tay Y (2015) Competing endogenous RNA networks: tying the essential knots for cancer biology and therapeutics. J Hematol Oncol 8:30
Du L, Pertsemlidis A (2011) Cancer and neurodegenerative disorders: pathogenic convergence through microRNA regulation. J Mol Cell Biol 3:176–180
van den Berg MMJ, Krauskopf J, Ramaekers JG, Kleinjans JCS, Prickaerts J, Briedé JJ (2020) Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Prog Neurobiol 185:101732
Xu R, Bi C, Song J, Wang L, Ge C, Liu X, Zhang M (2015) Upregulation of miR-142-5p in atherosclerotic plaques and regulation of oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis in macrophages. Mol Med Rep 11:3229–3234
Su S, Zhao Q, He C, Huang D, Liu J, Chen F, Chen J, Liao JY, Cui X, Zeng Y, Yao H, Su F, Liu Q, Jiang S, Song E (2015) miR-142-5p and miR-130a-3p are regulated by IL-4 and IL-13 and control profibrogenic macrophage program. Nat Commun 6:8523
Fagerlund R, Kinnunen L, Köhler M, Julkunen I, Melén K (2005) NF-{kappa}B is transported into the nucleus by importin {alpha}3 and importin {alpha}4. J Biol Chem 280:15942–15951
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a001651
Ghosh A, Roy A, Liu X, Kordower JH, Mufson EJ, Hartley DM, Ghosh S, Mosley RL, Gendelman HE, Pahan K (2007) Selective inhibition of NF-kappaB activation prevents dopaminergic neuronal loss in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:18754–18759
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Su, Y., Li, N. et al. Berberine Attenuates MPP+-Induced Neuronal Injury by Regulating LINC00943/miR-142-5p/KPNA4/NF-κB Pathway in SK-N-SH Cells. Neurochem Res 46, 3286–3300 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03431-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03431-w