Abstract
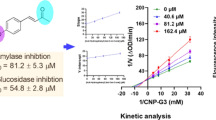
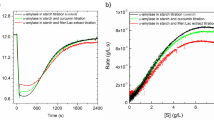
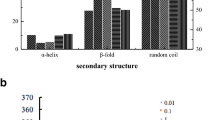
QDs has been deftly explored, studied, and optimized because of its unique optical and physicochemical properties. However, their high production and usage arouses the concern of accidental or unavoidable release in environment which can have toxic impact on animals. It is thus indispensable to comprehend its non-target effect. In the present study, interaction of vital digestive enzyme α-amylase was investigated with water-soluble mercaptopropionic acid (MPA)-capped CdSe QDs of five different sizes (1.9 nm, 2.3 nm, 2.5 nm, 3.3 nm, and 3.9 nm) by various spectroscopic techniques. Distinctive increase in absorption spectra and fluorescence quenching of α-amylase was observed chiefly due to α-amylase-CdSe QDs ground state complex formation. Binding constant (Kb), binding sites (n), and quenching constant (Ksv) were also determined. The results illustrated that binding of α-amylase with CdSe QDs followed 1:1 stoichiometry and induced conformational changes in dose- and size-dependent manner. Effect on α-amylase activity in complex form with size varied CdSe QDs suggested higher inhibition of enzymatic activity by smaller size QDs as compared to larger size. Molecular docking of MPA ligand with α-amylase revealed that interaction was majorly driven by hydrophobic forces. It further suggested that MPA did not interact with active site of α-amylase, thus acting as non-competitive inhibitor. The study thus involved a comprehensive analysis of the structural and functional modulation in α-amylase by interaction with hydrophilic MPA-capped CdSe QDs of different sizes.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardman R (2006) A toxicologic review of quantum dots: toxicity depends on physicochemical and environmental factors. Environ Health Perspect 114:165–172. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8284
Medintz IL, Uyeda HT, Goldman ER, Mattoussi H (2005) Quantum dot bioconjugates for imaging, labelling and sensing. Nature Mater 4:435–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1390
Zayed DG, AbdElhamid AS, Freag MS, Elzoghby AO (2019) Hybrid quantum dot-based theranostic nanomedicines for tumor-targeted drug delivery and cancer imaging. Nanomedicine 14:225–228. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2018-0414
Brazhnik K, Sokolova Z, Baryshnikova M et al (2015) Quantum dot-based lab-on-a-bead system for multiplexed detection of free and total prostate-specific antigens in clinical human serum samples. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology. Biology and Medicine 11:1065–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanumber2015.03.003
Yang Y, Zheng Y, Cao W et al (2015) High-efficiency light-emitting devices based on quantum dots with tailored nanostructures. Nature Photon 9:259–266. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2015.36
Sadeghi S, Mutcu SE, Srivastava SB et al (2018) High quality quantum dots polymeric films as color converters for smart phone display technology. Mater Res Express 6:035015. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aaf3ef
Bawendi MG, Carroll PJ, Wilson WL, Brus LE (1992) Luminescence properties of CdSe quantum crystallites: resonance between interior and surface localized states. J Chem Phys 96:946–954. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.462114
Mir IA, Das K, Rawat K, Bohidar HB (2016) Hot injection versus room temperature synthesis of CdSe quantum dots: a differential spectroscopic and bioanalyte sensing efficacy evaluation. Colloids Surf, A 494:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.01.002
Luan W, Yang H, Wan Z et al (2012) Mercaptopropionic acid capped CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as fluorescence probe for lead (II). J Nanopart Res 14:762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0762-3
Liu Q, Zheng C, Zhao H et al (2019) Tumor cell pH detection based on CdSe quantum dots’ fluorescence characteristics. Technol Health Care 27:239–247. https://doi.org/10.3233/THC-199023
Sadeghi S, Khabbaz Abkenar S, Ow-Yang CW, Nizamoglu S (2019) Efficient white LEDs using liquid-state magic-sized CdSe quantum dots. Sci Rep 9:10061. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46581-2
Masteri-Farahani M, Mollatayefeh N (2019) Chiral colloidal CdSe quantum dots functionalized with cysteine molecules: new optical nanosensor for selective detection and measurement of morphine. Colloids Surf, A 569:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.02.037
Rocha TL, Mestre NC, Sabóia-Morais SMT, Bebianno MJ (2017) Environmental behaviour and ecotoxicity of quantum dots at various trophic levels: a review. Environ Int 98:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.09.021
Ipe BI, Lehnig M, Niemeyer CM (2005) On the generation of free radical species from quantum dots. Small 1:706–709. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200500105
Katsumiti A, Gilliland D, Arostegui I, Cajaraville MP (2014) Cytotoxicity and cellular mechanisms involved in the toxicity of CdS quantum dots in hemocytes and gill cells of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat Toxicol 153:39–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.02.003
Rocha TL, Gomes T, Mestre NC et al (2015) Tissue specific responses to cadmium-based quantum dots in the marine mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Aquat Toxicol 169:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.10.001
Nagy A, Steinbrück A, Gao J et al (2012) Comprehensive analysis of the effects of CdSe quantum dot size, surface charge, and functionalization on primary human lung cells. ACS Nano 6:4748–4762. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn204886b
Sharma VK, McDonald TJ, Sohn M et al (2017) Assessment of toxicity of selenium and cadmium selenium quantum dots: a review. Chemosphere 188:403–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.130
Reyes-Turcu FE, Ventii KH, Wilkinson KD (2009) Regulation and cellular roles of ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinating enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem 78:363–397. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.78.082307.091526
Wang M, Chen L, Xiong Y-Q et al (2017) Iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles combined with actein suppress non-small-cell lung cancer growth in a p53-dependent manner. IJN 12:7627–7651. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S127549
Williams RA, Mamotte CDS, Burnett JR (2008) Phenylketonuria: an inborn error of phenylalanine metabolism. Clin Biochem Rev 29:31–41
DeBerardinis RJ, Thompson CB (2012) Cellular metabolism and disease: what do metabolic outliers Teach Us? Cell 148:1132–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.032
Fraser-Reid BO, Tatsuta K, Thiem J (eds) (2001) Glycoscience: chemistry and chemical biology I - III: with contributions by numerous experts, Softcover reprint of the original 1st edition 2001. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Mandel AL, Breslin PAS (2012) High endogenous salivary amylase activity is associated with improved glycemic homeostasis following starch ingestion in adults. J Nutr 142:853–858. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.111.156984
Vertegel AA, Siegel RW, Dordick JS (2004) Silica nanoparticle size influences the structure and enzymatic activity of adsorbed lysozyme. Langmuir 20:6800–6807. https://doi.org/10.1021/la0497200
Secundo F (2013) Conformational changes of enzymes upon immobilisation. Chem Soc Rev 42:6250. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs35495d
Petkova GA, Záruba К, Žvátora P, Král V (2012) Gold and silver nanoparticles for biomolecule immobilization and enzymatic catalysis. Nanoscale Res Lett 7:287. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-7-287
Zhao L, Guo D, Lin J, Liu R (2019) Responses of catalase and superoxide dismutase to low-dose quantum dots on molecular and cellular levels. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 181:388–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.06.028
Das K, Rawat K, Patel R, Bohidar HB (2016) Size-dependent CdSe quantum dot–lysozyme interaction and effect on enzymatic activity. RSC Adv 6:46744–46754. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA07368A
Wang Y, Mo Y, Zhou L (2011) Synthesis of CdSe quantum dots using selenium dioxide as selenium source and its interaction with pepsin. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 79:1311–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2011.04.061
Deka J, Paul A, Chattopadhyay A (2012) Modulating enzymatic activity in the presence of gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv 2:4736. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra20056b
Saware K, Aurade RM, Kamala Jayanthi PD, Abbaraju V (2015) Modulatory effect of citrate reduced gold and biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on α -Amylase Activity. Journal of Nanoparticles 2015:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/829718
Debnath G, Das P, Saha AK (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using mushroom extract of Pleurotus giganteus: characterization, antimicrobial, and α-amylase inhibitory activity. BioNanoSci 9:611–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-019-00650-y
MacCormack TJ, Clark RJ, Dang MKM et al (2012) Inhibition of enzyme activity by nanomaterials: potential mechanisms and implications for nanotoxicity testing. Nanotoxicology 6:514–525. https://doi.org/10.3109/17435390.2011.587904
Yu WW, Qu L, Guo W, Peng X (2004) Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe and CdS nanocrystals. Chem Mater 16:560–560. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm033007z
Micsonai A, Wien F, Bulyáki É et al (2018) BeStSel: a web server for accurate protein secondary structure prediction and fold recognition from the circular dichroism spectra. Nucleic Acids Res 46:W315–W322. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky497
Xiao Z, Storms R, Tsang A (2006) A quantitative starch–iodine method for measuring alpha-amylase and glucoamylase activities. Anal Biochem 351:146–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2006.01.036
Sun H, Yang B, Cui E, Liu R (2014) Spectroscopic investigations on the effect of N-Acetyl-l-cysteine-capped CdTe quantum dots on catalase. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 132:692–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.04.157
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W et al (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem 30:2785–2791. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21256
Tao P, Li Y, Siegel RW, Schadler LS (2013) Transparent luminescent silicone nanocomposites filled with bimodal PDMS-brush-grafted CdSe quantum dots. J Mater Chem C 1:86–94. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2TC00057A
Wang C, Gao X, Ma Q, Su X (2009) Aqueous synthesis of mercaptopropionic acid capped Mn2+-doped ZnSe quantum dots. J Mater Chem 19:7016. https://doi.org/10.1039/b909546b
Khan MJ, Qayyum S, Alam F, Husain Q (2011) Effect of tin oxide nanoparticle binding on the structure and activity of α-amylase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Nanotechnology 22:455708. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/22/45/455708
Hua F, Zhou P, Wu H-Y et al (2018) Inhibition of α-glucosidase and α-amylase by flavonoid glycosides from Lu’an GuaPian tea: molecular docking and interaction mechanism. Food Funct 9:4173–4183. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FO00562A
Asok A, Ghosh S, More PA et al (2015) Surface defect rich ZnO quantum dots as antioxidants inhibiting α-amylase and α-glucosidase: a potential anti-diabetic nanomedicine. J Mater Chem B 3:4597–4606. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TB00407A
Zhao L, Hu S, Meng Q et al (2018) The binding interaction between cadmium-based, aqueous-phase quantum dots with Candida rugosa lipase. J Mol Recognit 31:e2712. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmr.2712
Alkazaz M, Desseaux V, Marchis-Mouren G et al (1996) The mechanism of porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase. Kinetic evidence for two additional carbohydrate-binding Sites. Eur J Biochem 241:787–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.00787.x
Zheng Y, Yang W, Sun W et al (2020) Inhibition of porcine pancreatic α-amylase activity by chlorogenic acid. Journal of Functional Foods 64:103587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2019.103587
Acknowledgements
Jagriti acknowledge receipt of Junior Research Fellowship from the University Grant Commission (UGC), Government of India. The authors also acknowledge Advanced Research Instrumentation Facility (AIRF) and JNU for characterization assistance. We also thank Dr. Eepsita Priyadarshani for helping in the language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jagriti and Kishan conceived and planned the experiments and synthesized the QDs; Jagriti performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and drafted the manuscript; Paulraj supervised the experiments and helped in manuscript correction. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, J., Das, K. & Rajamani, P. Size-responsive differential modulation in α-amylase by MPA-CdSe QDs: multispectroscopy and molecular docking study. J Nanopart Res 23, 190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05298-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05298-y