Abstract
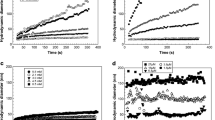
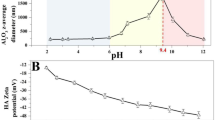
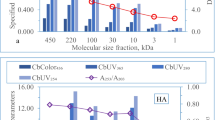
The environmental behavior and ultimate fate of the engineered nanoparticles could inevitably be affected by the widespread dissolved organic matter and sunlight irradiation in the natural environment. In this study, an analysis combined with experimental investigations was used to explore the influence of humic acid (HA) and UV irradiation on the changes in surface charge and aggregation behavior of TiO2 nanoparticles. A prolonged UV irradiation caused the point of zero charge (PZC) of TiO2 nanoparticles shifted to lower values and the aggregate size reached to a maximum value at the PZC. TEM image and FT-IR spectroscopy analysis confirmed the formation of TiO2 cluster aggregates and successive growth of the hydroxyl groups on different sites on TiO2 surface, respectively, although no effect of irradiation on the phase transformation of TiO2 nanoparticles was observed through the use of Raman spectroscopy. The fluorescence spectroscopy analysis illustrated the interactions between the surface hydroxyls formed during UV irradiation on TiO2 surface and functional groups on HA molecules, which accelerated the aggregation process of TiO2 nanoparticles. Widespread HA and UV irradiation in the natural environment significantly altered the surface properties and stability of the nanoparticles in aqueous environments.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chen X, Mao SS (2007) Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: synthesis, properties, modifications, and applications. Chem Rev 107:2891–2959
Tong H, Ouyang S, Bi Y, Umezawa N, Oshikiri M, Ye J (2012) Nano-photocatalytic materials: possibilities and challenges. Adv Mater 24:229–251
Nowack B, Bucheli TD (2007) Occurrence, behavior and effects of nanoparticles in the environment. Environ Pollut 150:5–22
Ohno T, Mitsui T, Matsumura M (2003) TiO2–photocatalyzed oxidation of adamantane in solutions containing oxygen or hydrogen peroxide. J Photochem Photobiol Chem 160:3–9
Zhang Y, Zhu M, Zhang S, Cai Y, Lv Z, Fang M, Tan X, Wang X (2020) Highly efficient removal of U(VI) by the photoreduction of SnO2/CdCO3/CdS nanocomposite under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B 279:119390
Wiesner MR, Lowry GV, Alvarez P, Dionysiou D, Biswas P (2006) Assessing the risks of manufactured nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 40:4336–4345
Dunphy Guzman KA, Finnegan MP, Banfield JF (2006) Influence of surface potential on aggregation and transport of titania nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 40:7688–7693
Daskalaki VM, Antoniadou M, Puma GL, Kondarides DI, Lianos P (2010) Solar light-responsive Pt/Cds/TiO2 photocatalysts for hydrogen production and simultaneous degradation of inorganic or organic sacrificial agents in waste water. Environ Sci Technol 44:7200–7205
Sun J, Guo L, Zhang H, Zhao L (2014) UV irradiation induced transformation of TiO2 nanoparticles in water: aggregation and photoreactivity. Environ Sci Technol 48:11962–11968
Hu G, Cao J, Lu M, Lin ZX (2020) Study on the characteristics of naturally formed TiO2 nanoparticles in various surficial media from China. Chem Geol 550:119703
Priester JH, GeY Chang V, Stoimenov PK, Schimel JP, Stucky GD (2013) Holden P. A. Assessing interactions of hydrophilic nanoscale TiO2 with soil water. J Nanopart Res 15:1899
Battin TI, Kammer FVD, Weilhartner A, Ottofuelling S, Hofmann T (2009) Nanostructured TiO2: transport behavior and effects on aquatic microbial communities under environmental conditions. Environ Sci Technol 43:8098–8104
Wang P, Qi W, Ao Y, Hou J, Wang C, Qian J (2016) Effect of UV irradiation on the aggregation of TiO2 in an aquatic environment: influence of humic acid and pH. Environ Pollut 212:178–187
Thio BJR, Zhou D, Keller AA (2011) Influence of natural organic matter on the aggregation and deposition of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 189:556–553
Hayakawa M, Nonomura H (1987) Humic acid-vitamin agar, a new medium for the selective isolation of soil actinomycetes. J Ferment Technol 65:501–509
Baalousha M (2009) Aggregation and disaggregation of iron oxide nanoparticles: influence of particle concentration, pH and natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 407:2093–2101
Coronado JM, Maira AJ, Conesa JC, Yeung KL, Augugliaro V, Soria J (2001) EPR study of the surface characteristics of nanostructured TiO2 under UV irradiation. Langmuir 17:5368–5374
Domingos RF, Tufenkji N, Wilkinson KJ (2009) Aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: role of a fulvic acid. Environ Sci Technol 43:1282–1286
Zhang H, Sun J, Guo L (2016) UV irradiation mediated aggregation of TiO2 nanoparticles in the simulated aquatic system. NanoImpact 3–4:75–80
Soria J, Sanz J, Sobrados I, Coronado J, Hernández-Alonso M, Fresno F (2010) Water-hydroxyl interactions on small anatase nanoparticles prepared by the hydrothermal route. J Phys Chem C 114:16534–16540
Syafei AD, Lin CF, Wu CH (2008) Removal of natural organic matter by ultrafiltration with TiO2-coated membrane under UV irradiation. J Colloid Interface Sci 323:112–119
Leong S, Low ZX, Liu Q, Hapgood K, Zhang X, Wang H (1988) Preparation of supported photocatalytic membrane from mesoporous titania spheres for humic acid removal from wastewater. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 11:611–619
Degen A, Kosec M (2000) Effect of pH and impurities on the surface charge of zinc oxide in aqueous solution. J Eur Ceram Soc 20:667–673
Hyung H, Fortner JD, Hughes JB, Kim JH (2007) Natural organic matter stabilizes carbon nanotubes in the aqueous phase. Environ Sci Technol 41:179–184
Chen K, Elimelech M (2007) Influence of humic acid on the aggregation kinetics of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles in monovalent and divalent electrolyte solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 309:126–134
Omar FM, Aziz HA (2014) Stoll Serge. Aggregation and disaggregation of ZnO nanoparticles: Influence of pH and adsorption of Suwannee River humic acid. Sci Total Environ 468–469:195–201
Isaacson CW, Bouchard DC (2010) Effects of humic acid and sunlight on the generation and aggregation state of aqu/C60 nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 44:8971–8976
Domingos RF, Peyrot C, Wilkinson KJ (2010) Aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles: role of calcium and phosphate. Environ Chem 7:61–66
Tan L, Tan X, Mei H, Ai Y, Sun L, Zhao G, Hayat T, Alsaedi A, Chen C, Wang X (2018) Coagulation behavior of humic acid in aqueous solutions containing Cs+, Sr2+ and Eu3+: DLS, EEM and MD simulations. Environ Pollut 236:835–843
Zhu M, Wang H, Keller AA, Wang T, Li F (2014) The effect of humic acid on the aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles under different pH and ionic strengths. Sci Total Environ 487:375–380
Zhang L, Li M, Chen J, Li C (2006) UV Raman spectroscopic study on TiO2. I. Phase transformation at the surface and in the bulk. J Phys Chem B 110:927–935
Ivanda M, Musi S, Popovi S, Goti ML (1999) XRD, Raman and FT-IR spectroscopic observations of nanosized TiO2 synthesized by Sol-Gel method based on an esterification reaction. J Mol Struct 480–481:645–649
Kim SY, Duin ACTV, Kubicki JD (2013) Molecular dynamic simulations of the interactions between TiO2 nanoparticles and water with Na+ and Cl-, methanol, and formic acid using a reactive force field. J Mater Res 28:513–520
Wang LF, Wang LL, Ye XD, Li WW, Ren XM, Sheng GP, Yu HQ, Wang XK (2013) Coagulation kinetics of humic aggregates in mono- and di-valent electrolyte solutions. Environ Sci Technol 47:5042–5049
Liu S, Lim M, Fabris R, Chow C, Chiang K, Drikas M, Amal R (2008) Removal of humic acid using TiO2 photocatalytic process-fractionation and molecular weight characterization studies. Chemosphere 72:263–271
Li XZ, Li FB, Fan CM (2002) Photoelectrocatalytic degradation of humic acid in aqueous solution using a Ti/TiO2 mesh photoelectrode. Water Res 36:2215–2224
Yigit Z, Inan H (2009) A study of the photocatalytic oxidation of humic acid on anatase and mixed-phase anatase-rutile TiO2 nanoparticles. Water Air Soil Pollut: Focus 9:237–243
Chen J, LeBoeuf EJ, Dai S, Gu B (2003) Fluorescence spectroscopic studies of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 50:639–647
Mobed JJ, Hemmingsen SL, Autry JL, Mcgown LB (1996) Fluorescence characterization of IHSS humic substances: total luminescence spectra with absorbance correction. Environ Sci Technol 30:3061–3065
Chen W, Qian C, Liu XY, Yu HQ (2014) Two-dimension correlation spectroscopic analysis on the interaction between humic acids and TiO2 nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 48:11119–11126
Birben NC, Uyguner CS, Sen-Kavurmaci S, Gurkan YY, Turkten N, Bekbolet M (2015) Comparative evaluation of anion doped photocatalysts on the mineralization and decolorization of natural organic matter. Catal Today 240:125–131
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully appreciate the technical assistance from Huaiyin Institute of Technology.
Funding
This work is financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the National & Local Joint Engineering Research Center for Mineral Salt Deep Utilization (grant no. SF201905).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.L. and C.Z. conceived the study and performed the measurements. L.T. and Z.L. analyzed the results and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Capsule abstract
The aggregation behaviors of TiO2 nanoparticles in the presence of humic acid and UV irradiation were studied by batch, DLS, EEM, FT-IR, and Raman measurements, and the complexation between HA and TiO2 nanoparticles strongly influenced the physicochemical behavior of TiO2 nanoparticles in the natural environment.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, L., Liu, Z., Zhou, C. et al. Combined factors influencing the surface charge and aggregation behaviors of TiO2 nanoparticles in the presence of humic acid and UV irradiation. J Nanopart Res 23, 191 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05315-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05315-0