Abstract
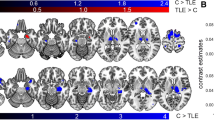
To investigate the influence of epileptogenic cortex (Rolandic areas) with executive functions in Rolandic epilepsy using structural covariance analysis of structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Structural MRI data of drug-naive patients with Rolandic epilepsy (n = 70) and typically developing children as healthy controls (n = 83) were analyzed using voxel-based morphometry. Gray matter volumes in the patients were compared with those of healthy controls, and were further correlated with epilepsy duration and cognitive score of executive function, respectively. By applying Granger causal analysis to the sequenced morphometric data according to disease progression information, causal network of structural covariance was constructed to assess the causal influence of structural changes from Rolandic cortices to the regions engaging executive function in the patients. Compared with healthy controls, epilepsy patients showed increased gray matter volume in the Rolandic regions, and also the regions engaging in executive function. Covariance network analyses showed that along with disease progression, the Rolandic regions imposed positive causal influence on the regions engaging in executive function. In the patients with Rolandic epilepsy, epileptogenic regions have causal influence on the structural changes in the regions of executive function, implicating damaging effects of Rolandic epilepsy on human brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RE:
-
Rolandic epilepsy
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- VBM:
-
Voxel-based morphometry
- GMV:
-
Gray matter volume
- SCN:
-
Structural covariance network
- CaSCN:
-
Causal network of structural covariance
References
Alexander-Bloch, A., Giedd, J. N., & Bullmore, E. (2013). Imaging structural co-variance between human brain regions. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 14, 322–336.
Baptista, H., Mendes, J. M., MacNab, Y. C., Xavier, M., & Caldas-de-Almeida, J. (2016). A Gaussian random field model for similarity-based smoothing in Bayesian disease mapping. Statistical Methods in Medical Research, 25, 1166–1184.
Bernhardt, B. C., Worsley, K. J., Besson, P., Concha, L., Lerch, J. P., Evans, A. C., & Bernasconi, N. (2008). Mapping limbic network organization in temporal lobe epilepsy using morphometric correlations: Insights on the relation between mesiotemporal connectivity and cortical atrophy. NeuroImage, 42, 515–524.
Briellmann, R. S., Wellard, R. M., & Jackson, G. D. (2005). Seizure-associated abnormalities in epilepsy: Evidence from MR imaging. Epilepsia, 46, 760–766.
Ciumas, C., Saignavongs, M., Ilski, F., Herbillon, V., Laurent, A., Lothe, A., Heckemann, R. A., De Bellescize, J., Panagiotakaki, E., & Hannoun, S. (2014). White matter development in children with benign childhood epilepsy with centro-temporal spikes. Brain, 137, 1095–1106.
Filippini, M., Ardu, E., Stefanelli, S., Boni, A., Gobbi, G., & Benso, F. (2016). Neuropsychological profile in new-onset benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS): Focusing on executive functions. Epilepsy & Behavior, 54, 71–79.
Guerrini, R., & Pellacani, S. (2012). Benign childhood focal epilepsies. Epilepsia, 53, 9–18.
Jernigan, T. L., Trauner, D. A., Hesselink, J. R., & Tallal, P. A. (1991). Maturation of human cerebrum observed in vivo during adolescence. Brain, 114, 2037–2049.
Ji, G. J., Liao, W., Chen, F. F., Zhang, L., & Wang, K. (2017). Low-frequency blood oxygen level-dependent fluctuations in the brain white matter: more than just noise. Science Bulletin, S456722799.
Ji, G. J., Yu, Y., Miao, H. H., Wang, Z. J., Tang, Y. L., & Liao, W. (2017b). Decreased network efficiency in benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Radiology, 283, 186–194.
Jiang, Y., Luo, C., Li, X., Duan, M., He, H., Chen, X., Yang, H., Gong, J., Chang, X., & Woelfer, M. (2018). Progressive reduction in gray matter in patients with schizophrenia assessed with MR imaging by using causal network analysis. Radiology, 287, 633–642.
Kim, E., Yum, M., Shim, W., Yoon, H., Lee, Y., & Ko, T. (2015a). Structural abnormalities in benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BCECTS). Seizure, 27, 40–46.
Kim, J., Lee, Y., Han, D., Min, K., Kim, D., & Lee, C. (2015b). The utility of quantitative electroencephalography and integrated visual and auditory continuous performance test as auxiliary tools for the attention deficit hyperactivity disorder diagnosis. Clinical Neurophysiology, 126, 532–540.
Koelewijn, L., Hamandi, K., Brindley, L.M., Brookes, M.J., Routley, B.C., Muthukumaraswamy, S.D., Williams, N., Thomas, M.A., Kirby, A., Te Water Naudé, J. (2015). Resting-state oscillatory dynamics in sensorimotor cortex in benign epilepsy with centro-temporal spikes and typical brain development. Human Brain Mapping, 36, 3935–3949.
Li, J., Biswal, B. B., Wang, P., Duan, X., Cui, Q., Chen, H., & Liao, W. (2019). Exploring the functional connectome in white matter. Human Brain Mapping, 40, 4331–4344.
Lima, E. M., Rzezak, P., Dos, S. B., Gentil, L., Montenegro, M. A., Guerreiro, M. M., & Valente, K. D. (2018). The relevance of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in self-limited childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Epilepsy & Behavior, 82, 164–169.
Lima, E. M., Rzezak, P., Guimarães, C. A., Montenegro, M. A., Guerreiro, M. M., & Valente, K. D. (2017). The executive profile of children with Benign Epilepsy of childhood with centrotemporal spikes and temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior, 72, 173–177.
Lin, J. J., Riley, J. D., Hsu, D. A., Stafstrom, C. E., Dabbs, K., Becker, T., Seidenberg, M., & Hermann, B. P. (2012). Striatal hypertrophy and its cognitive effects in new-onset benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Epilepsia, 53, 677–685.
Lin, J. J., Salamon, N., Lee, A. D., Dutton, R. A., Geaga, J. A., Hayashi, K. M., Luders, E., Toga, A. W., Engel, J. J., & Thompson, P. M. (2007). Reduced neocortical thickness and complexity mapped in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Cerebral Cortex, 17, 2007–2018.
Lindgren, S., Kihlgren, M., Melin, L., Croona, C., Lundberg, S., & Eeg-Olofsson, O. (2004). Development of cognitive functions in children with rolandic epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior, 5, 903–910.
Listed, N. A. (1989). Proposal for revised classification of epilepsies and epileptic syndromes. Commission on classification and terminology of the international league against epilepsy. Epilepsia, 30, 389–399.
Luo, C., Zhang, Y., Cao, W., Huang, Y., Yang, F., Wang, J., Tu, S., Wang, X., & Yao, D. (2015). Altered structural and functional feature of striato-cortical circuit in benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. International Journal of Neural Systems, 25, 1550027.
Montembeault, M., Joubert, S., Doyon, J., Carrier, J., Gagnon, J. F., Monchi, O., Lungu, O., Belleville, S., & Brambati, S. M. (2012). The impact of aging on gray matter structural covariance networks. NeuroImage, 63, 754–759.
Panjwani, N., Wilson, M. D., Addis, L., Crosbie, J., Wirrell, E., Auvin, S., Caraballo, R. H., Kinali, M., McCormick, D., Oren, C., Taylor, J., Trounce, J., Clarke, T., Akman, C. I., Kugler, S. L., Mandelbaum, D. E., McGoldrick, P., Wolf, S. M., Arnold, P., … Strug, L. J. (2016). A microRNA-328 binding site in PAX6 is associated with centrotemporal spikes of rolandic epilepsy. Annals of Clinical Translational Neurology, 3, 512–522.
Pardoe, H. R., Berg, A. T., Archer, J. S., Fulbright, R. K., & Jackson, G. D. (2013). A neurodevelopmental basis for BECTS: Evidence from structural MRI. Epilepsy Research, 105, 133–139.
Piccinelli, P., Borgatti, R., Aldini, A., Bindelli, D., Ferri, M., Perna, S., Pitillo, G., Termine, C., Zambonin, F., & Balottin, U. (2008). Academic performance in children with rolandic epilepsy. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 50, 353–356.
Raznahan, A., Lerch, J. P., Lee, N., Greenstein, D., Wallace, G. L., Stockman, M., Clasen, L., Shaw, P. W., & Giedd, J. N. (2011). Patterns of coordinated anatomical change in human cortical development: A longitudinal neuroimaging study of maturational coupling. Neuron, 72, 873–884.
Riederer, F., Lanzenberger, R., Kaya, M., Prayer, D., Serles, W., & Baumgartner, C. (2008). Network atrophy in temporal lobe epilepsy: A voxel-based morphometry study. Neurology, 71, 419–425.
Shiraseb, F., Siassi, F., Qorbani, M., Sotoudeh, G., Rostami, R., Narmaki, E., Yavari, P., Aghasi, M., & Shaibu, O. M. (2016). Higher dietary diversity is related to better visual and auditory sustained attention. British Journal of Nutrition, 115, 1470–1480.
Strug, L. J., Clarke, T., Chiang, T., Chien, M., Baskurt, Z., Li, W., Dorfman, R., Bali, B., Wirrell, E., Kugler, S. L., Mandelbaum, D. E., Wolf, S. M., McGoldrick, P., Hardison, H., Novotny, E. J., Ju, J., Greenberg, D. A., Russo, J. J., & Pal, D. K. (2009). Centrotemporal sharp wave EEG trait in rolandic epilepsy maps to Elongator Protein Complex 4 (ELP4). European Journal of Human Genetics, 17, 1171–1181.
Tae, W. S., Kim, S. H., Joo, E. Y., Han, S. J., Kim, I. Y., Kim, S. I., Lee, J. M., & Hong, S. B. (2008). Cortical thickness abnormality in juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Journal of Neurology, 255, 561–566.
Tillikainen, L., Salli, E., Korvenoja, A., & Aronen, H. J. (2006). A cluster mass permutation test with contextual enhancement for fMRI activation detection. NeuroImage, 32, 654–664.
Tinius, T. P. (2003). The integrated visual and auditory continuous performance test as a neuropsychological measure. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 18, 439–454.
Wei Liao, Z. Z. D. M. (2013). Relationship between large-scale functional and structural covariance networks in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Brain Connectivity, 3, 240–254.
Wirrell, E. C. (1998). Benign epilepsy of childhood with centrotemporal spikes. Epilepsia, 39, S32–S41.
Xiao, F., An, D., Lei, D., Li, L., Chen, S., Wu, X., Yang, T., Ren, J., Gong, Q., & Zhou, D. (2016). Real-time effects of centrotemporal spikes on cognition in rolandic epilepsy: An EEG-fMRI study. Neurology, 86, 544–551.
Xiao, F., Li, L., An, D., Lei, D., Tang, Y., Yang, T., Ren, J., Chen, S., Huang, X., & Gong, Q. (2015). Altered attention networks in benign childhood epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes (BECTS): A resting-state fMRI study. Epilepsy & Behavior, 45, 234–241.
Yang, B., Wang, X., Shen, L., Ye, X., Yang, G., Fan, J., Hu, P., & Wang, K. (2015). The attentional networks in benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Epilepsy & Behavior, 53, 78–82.
Zang, Z., Yan, C., Dong, Z., Huang, J., & Zang, Y. (2012). Granger causality analysis implementation on MATLAB: A graphic user interface toolkit for fMRI data processing. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 203, 418–426.
Zhang, Z., Liao, W., Xu, Q., Wei, W., Zhou, H. J., Sun, K., Yang, F., Mantini, D., Ji, X., & Lu, G. (2017). Hippocampus-associated causal network of structural covariance measuring structural damage progression in temporal lobe epilepsy. Human Brain Mapping, 38, 753–766.
Zhang, Z., Liao, W., Zuo, X. N., Wang, Z., Yuan, C., Jiao, Q., Chen, H., Biswal, B. B., Lu, G., & Liu, Y. (2011). Resting-state brain organization revealed by functional covariance networks. PLoS ONE, 6, 28817.
Zhu, Y., Yu, Y., Shinkareva, S. V., Ji, G. J., Wang, J., Wang, Z. J., Zang, Y. F., Liao, W., & Tang, Y. L. (2015). Intrinsic brain activity as a diagnostic biomarker in children with benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes. Human Brain Mapping, 36, 3878–3889.
Zielinski, B. A., Gennatas, E. D., Juan, Z., & Seeley, W. W. (2010). Network-level structural covariance in the developing brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 107, 18191–18196.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81871345, 81701680, 81790653, 81422022, 81271553, 81401402, 81471653, 81201078 and 81701678), 863 Project (Grant Nos. 2014BAI04B05 and 2015AA020505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yin Xu, Qiang Xu, Qirui Zhang, Steven M. Stufflebeam, Fang Yang, Yan He, Zheng Hu, Yifei Weng, Junhao Xiao, Guangming Lu, and Zhiqiang Zhang declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All human study procedures were approved by the institutional review boards at Jinling Hospital, Nanjing University School of Medicine.
Informed consent
All patients were informed consent signed by their legal guardians.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Xu, Q., Zhang, Q. et al. Influence of epileptogenic region on brain structural changes in Rolandic epilepsy. Brain Imaging and Behavior 16, 424–434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00517-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00517-5