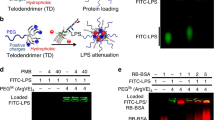
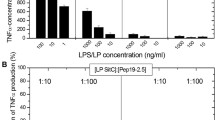
Abstract—
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is commonly used in murine sepsis models, which are largely associated with immunosuppression and collapse of the immune system. After adapting the LPS treatment to the needs of locally bred BALB/c mice, the present study explored the protective role of Micrococcus luteus peptidoglycan (PG)–pre-activated vaccine-on-chip technology in endotoxemia. The established protocol consisted of five daily intraperitoneal injections of 0.2 μg/g LPS, allowing longer survival, necessary for a therapeutic treatment application. A novel immunotherapy technology, the so-called vaccine-on-chip, consists of a 3-dimensional laser micro-textured silicon (Si) scaffold loaded with macrophages and activated in vitro with 1 μg/ml PG, which has been previously shown to exert a mild immunostimulatory activity upon subcutaneous implantation. The LPS treatment significantly decreased CD4 + and CD8 + cells, while increasing CD11b + , Gr1 + , CD25 + , Foxp3 + , and class II + cells. These results were accompanied by increased arginase-1 activity in spleen cell lysates and C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), IL-6, TNF-a, IL-10, and IL-18 in the serum, while acquiring severe sepsis phenotype as defined by the murine sepsis scoring. The in vivo application of PG pre-activated implant significantly increased the percentage of CD4 + and CD8 + cells, while decreasing the percentage of Gr1 + , CD25 + , CD11b + , Foxp3 + cells, and arginase-1 activity in the spleen of LPS-treated animals, as well as all serum markers tested, allowing survival and rescuing the severity of sepsis phenotype. In conclusion, these results reveal a novel immunotherapy technology based on PG pre-activated micro-texture Si scaffolds in LPS endotoxemia, supporting thus its potential use in the treatment of septic patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Bone, Roger C., Robert A. Balk, Frank B. Cerra, Phillip R. Dellinger, Alan M. Fein, William A. Knaus, Ronald M. Schein, and William J. Sibbald. 1992. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis: the ACCP/SCCM consensus conference committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest 101 (6): 1644–1655. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.101.6.1644.
Levy, Mitchell M., Mitchell P. Fink, John C. Marshall, Abraham Edward, Angus Derek, Cook Deborah, Cohen Jonathan, M. Steven, Jean-Louis. Opal, Graham Vincent, and Ramsay. 2003. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Critical Care Medicine 31: 1250–1256. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.CCM.0000050454.01978.3B.
Singer, Mervyn, Clifford S. Deutschman, Christopher W. Seymour, Manu Shankar-Hari, Djillali Annane, Michael Bauer, Rinaldo Bellomo, Gordon R. Bernard, Jean-Daniel. Chiche, Craig M. Coopersmith, Richard S. Hotchkiss, Mitchell M. Levy, John C. Marshall, Greg S. Martin, Steven M. Opal, Gordon D. Rubenfeld, Tom van der Poll, Jean-Louis. Vincent, and Derek C. Angus. 2016. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 315 (8): 801–810. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.0287.
Vincent, Jean-Luis., Rui Moreno, Jukka Takala, Sheila Willatts, Alexandre De Mendonça, C.K. Hajo Bruining, Paolo M. Reinhart, Lambert G. Suter, and Thijs. 1996. Working group on sepsis-related problems of the European society of intensive care medicine: The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Medicine 22 (7): 707–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01709751.
Schulte, Wibke, Jürgen. Bernhagen, and Richard Bucala. 2013. Cytokines in sepsis: Potent immunoregulators and potential therapeutic targets–an updated view. Mediators of Inflammation 2013: 165974. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/165974.
Hotchkiss, Richard S., Guillaume Monneret, and Didier Payen. 2013. Immunosuppression in sepsis: A novel understanding of the disorder and a new therapeutic approach. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 13 (3): 260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70001-X.
De Wilde, Virginie, Nicholas Van Rompaey, Marcelo Hill, et al. 2009. Endotoxin-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells inhibit alloimmune responses via heme oxygenase-1. American Journal of Transplantation 9 (9): 2034–2047. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02757.x.
Popovic, Petar J., Herbert J. Zeh 3rd., and Juan B. Ochoa. 2007. Arginine and immunity. Journal of Nutrition 137 (6 Suppl 2): 1681S-1686S. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/137.6.1681S.
Rodriguez, Paulo C., David G. Quiceno, and Augusto C. Ochoa. 2007. L-Arginine availability regulates T-lymphocyte cell-cycle progression. Blood 109 (4): 1568–1573. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-06-031856.
Meisel, Christian, Joerg C. Schefold, Rene Pschowski, Tycho Baumann, Katrin Hetzger, Jan Gregor, et al. 2009. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to reverse sepsis-associated immunosuppression: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter trial. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 180 (7): 640–648. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200903-0363OC.
Unsinger, Jacqueline, Margaret McGlynn, Kevin R. Kasten, Andrew S. Hoekzema, Eizo Watanabe, Jared T. Muenzer, et al. 2010. IL-7 promotes T cell viability, trafficking, and functionality and improves survival in sepsis. The Journal of Immunology 184 (7): 3768–3779. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0903151.
Topalian, Suzanne L., F. Stephen Hodi, Julie R. Brahmer, Scott N. Gettinger, David C. Smith, et al. 2012. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 366 (26): 2443–2454. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1200690.
Molnár, Zsolt, Axel Nierhaus, and Figen Esen. 2013. Immunoglobulins in sepsis: which patients will benefit the most? In Annual Update in Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine, ed. J.-L. Vincent, 145–152. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Wand, Saskia, Matthias Klages, Christin Kirbach, Joanna Warszawska, Patrick Meybohm, Kai Zacharowski, and Alexander Koch. 2016. IgM-enriched immunoglobulin attenuates systemic endotoxin activity in early severe sepsis: A before-after cohort study. PLoS ONE 11 (8): e0160907. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160907.
Kyvelidou, Christina, Dimitris Sotiriou, Ioanna Zerva, and Irene Athanassakis. 2018. Protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced immunosuppression by IgG and IgM. Shock 49 (4): 474–482. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000937.
Zerva, Ioanna, Vasileia Pateraki, and Irene Athanassakis. 2020. Implantable vaccines: A solution for immune system manipulation to any antigenic stimulus. Journal of Immunological Sciences 4: 5–11.
Zerva, Ioanna, Chara Simitzi, Alexandra Siakouli-Galanopoulou, Anthi Ranella, Emmanuel Stratakis, Costas Fotakis, and Irene Athanassakis. 2015. Implantable vaccines: In vitro antigen presentation enables in vivo immune response. Vaccine 33: 3142–3149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.04.017.
Zerva, Ioanna, Eleni Katsoni, Chara Simitzi, Emmanuel Stratakis, and Irene Athanassakis. 2019. Laser micro-structured Si scaffold implantable vaccines against Salmonella Typhimurium. Vaccine 37: 2249–2257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.02.080.
Shrum, Bradly, Ram V. Anantha, Stacey X. Xu, S.M. Marisa Donnelly, Haeryfar Mansour, John K. McCormick, and Tina Mele. 2014. A robust scoring system to evaluate sepsis severity in an animal model. BMC Research Notes 7: 233–244.
Mytilinaiou, Irene, Kiki Sarganaki, Eirini Sachouli, Sofia Tsagdi, Katerina Vardaki, Anna Vassiliadis, and Irene Athanassakis. 2019. Immune molecules in the female reproductive path and sperm: Relevance to mate choice. Reproduction 158: 159–167. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-19-0084.
Fink, Mitchell P. 2014. Animal models of sepsis. Virulence 5 (1): 143–153. https://doi.org/10.4161/viru.26083.
Thomas, Roisin C., Michael F. Bath, Cordula M. Stover, David G. Lambert, and Jonathan P. Thompson. 2014. Exploring LPS-induced sepsis in rats and mice as a model to study potential protective effects of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ system. Peptides 61: 56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2014.08.009.
Barber, Annabel E., Susette M. Coyle, Eva Fischer, Christopher Smith, Tom van der Poll, et al. 1995. Influence of hypercortisolemia on soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor II and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist responses to endotoxin in human beings. Surgery 118 (2): 401–406. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aew401.
Rossol, Manuela, Holger Heine, Undine Meusch, Dagmar Quandt, Carina Klein, Matthew J. Sweet, and Sunna Hauschildt. 2011. LPS-induced cytokine production in human monocytes and macrophages. Critical Reviews in Immunology 31 (5): 379–446. https://doi.org/10.1615/critrevimmunol.v31.i5.20.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Emmanuel Stratakis, Research Director at the Institute of Electronic Structure and Laser (IESL-FORTH), and Anna Karayiannaki for providing Si scaffolds.
Funding
This work was co-financed by Greece and the European Union (European Social Fund- ESF) through the Operational Programme «Human Resources Development, Education and Lifelong Learning 2014–2020» in the context of the project “Vaccine-on-chip against sepsis” (MIS 5048426).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study. Conceptualization, data analysis, writing, funding acquisition, and supervision were performed by Irene Athanassakis. Material preparation and data collection were performed by Ioanna Zerva and Katerina Bekela (equal contribution). All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The applied protocol was approved by the national Bioethical Committee (Approval # 292314, ADA ΨΗΘ47ΛΚ-Γ5Ψ).
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ioanna, Z., Katerina, B. & Irene, A. Immunotherapy-on-Chip Against an Experimental Sepsis Model. Inflammation 44, 2333–2345 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01506-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01506-y