Abstract
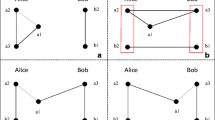
Ma et al. [Int. J. Theor. Phys. (2021): 1328–1338] proposed a multi-party quantum key distribution (MQKD) protocol using Bell states, in which multiple participants can distribute a group key efficiently. However, this study indicates that Ma et al.’s protocol has two security loopholes. First, an attacker can obtain the pre-shared key Ks using an eavesdropping attack. Second, the attacker uses an intercept-and-resend attack to steal the group key shared among the participants without being detected. An improved MQKD protocol is proposed to overcome these loopholes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: "Quantum Cryptography: Public Key Distribution and Coin Tossing," in IEEE International Conference on Computers, pp. 175–179. Systems and Signal Processing, Bangalore (1984)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Mermin, N.D.: Quantum cryptography without Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68(5), 557–559 (1992)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68(21), 3121–3124 (1992)
Ekert, A.K.: Quantum cryptography based on Bell’s theorem. Phys. Rev. Lett. 67(6), 661–663 (1991)
Bruß, D.: Optimal eavesdropping in quantum cryptography with six states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81(14), 3018–3021 (1998)
Scarani, V., Acín, A., Ribordy, G., Gisin, N.: Quantum cryptography protocols robust against photon number splitting attacks for weak laser pulse implementations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(5), 057901 (2004)
Lucamarini, M., Patel, K.A., Dynes, J.F., Fröhlich, B., Sharpe, A.W., Dixon, A.R., Yuan, Z.L., Penty, R.V., Shields, A.J.: Efficient decoy-state quantum key distribution with quantified security. Opt. Express. 21(21), 24550–24565 (2013)
Boyer, M., Kenigsberg, D., Mor, T.: Quantum key distribution with classical bob. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99(14), 140501 (2007)
Boyer, M., Gelles, R., Kenigsberg, D., Mor, T.: Semiquantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A. 79(3), 032341 (2009)
Liu, Z.-R., Hwang, T.: Mediated semi-quantum key distribution without invoking quantum measurement. Ann. Phys. 530(4), 1700206 (2018)
Zou, X., Qiu, D., Li, L., Wu, L., Li, L.: Semiquantum-key distribution using less than four quantum states. Phys. Rev. A. 79(5), 052312 (2009)
Branciard, C., Cavalcanti, E.G., Walborn, S.P., Scarani, V., Wiseman, H.M.: One-sided device-independent quantum key distribution: security, feasibility, and the connection with steering. Phys. Rev. A. 85(1), 010301 (2012)
Cao, W.-F., Zhen, Y.-Z., Zheng, Y.-L., Li, L., Chen, Z.-B., Liu, N.-L., Chen, K.: One-sided measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A. 97(1), 012313 (2018)
Tomamichel, M., Fehr, S., Kaniewski, J., Wehner, S.: One-Sided Device-Independent QKD and Position-Based Cryptography from Monogamy Games, pp. 609–625. Heidelberg, Berlin (2013)
Lo, H.-K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(13), 130503 (2012)
Xu, F., Curty, M., Qi, B., Lo, H.: Measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. IEEE J Sel Top Quant. 21(3), 148–158 (2015)
Phoenix, S.J.D., Barnett, S.M., Townsend, P.D., Blow, K.J.: Multi-user quantum cryptography on optical networks. J Mod Optic. 42(6), 1155–1163 (1995)
Matsumoto, R.: Multiparty quantum-key-distribution protocol without use of entanglement. Phys. Rev. A. 76(6), 062316 (2007)
Hong, C.H., Heo, J.O., Khym, G.L., Lim, J., Hong, S.-K., Yang, H.J.: N quantum channels are sufficient for multi-user quantum key distribution protocol between n users. Opt. Commun. 283(12), 2644–2646 (2010)
Jiang, M., Dong, D.: Multi-party quantum state sharing via various probabilistic channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 237–249 (2013)
Li, L., Li, Z.: A multi-party quantum key distribution protocol based on phase shift operation. Laser Phys. 29(10), 105201 (2019)
Ma, X., Wang, C., Li, Z., Zhu, H.: Multi-party quantum key distribution protocol with new bell states encoding mode. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60(4), 1328–1338 (2021)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Robert, J.M.: Privacy amplification by public discussion. SIAM J. Comput. 17(2), 210–229 (1988)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G., Crepeau, C., Maurer, U.M.: Generalized privacy amplification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 41(6), 1915–1923 (1995)
Carter, J.L., Wegman, M.N.: Universal classes of hash functions. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 18(2), 143–154 (1979)
Abidin, A., "Authentication in Quantum Key Distribution: Security Proof and Universal Hash Functions," Doctoral Thesis, Comprehensive Summary, Linköping Studies in Science and Technology. Dissertations, Linköping University Electronic Press, Linköping, 2013
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their very valuable comments, which greatly enhanced the clarity of this paper. This research was partially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, R.O.C. (Grant Nos. MOST 110-2221-E-039-004, MOST 110-2221-E-143-003, MOST 110-2221-E-259-001, MOST 110-2221-E-143-004, and MOST 110-2218-E-005-008-MBK), and China Medical University, Taiwan (Grant No. CMU109-S-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, CW., Lin, J., Chiu, L. et al. Cryptanalysis and Improvement in Multi-Party Quantum Key Distribution Protocol with New Bell States Encoding Mode. Int J Theor Phys 60, 3599–3608 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04927-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-021-04927-5