Abstract
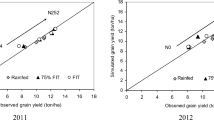
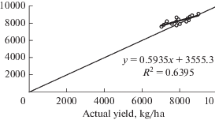
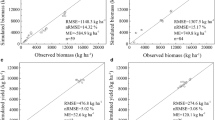
Sensitivity analysis (SA) can identify the most critical parameters for crop growth model output, thus helping to improve model calibration efficiency. However, when combined with different production conditions, especially adverse conditions such as water stress and fertilizer stress, parameter sensitivity remains unclear. This study (i) assessed the sensitivity of the output response of the CERES-Maize model to the input parameters, particularly the effect of water and fertilizer stress on the SA results and (ii) evaluated the model performance based on the SA results. The results indicated that water stress had a considerable effect on SA, whereas nitrogen stress had little effect on SA. P5, G3, and P2 had significant effects on yield, maximum aboveground biomass (AGB), daily AGB, daily leaf area index (LAI), and daily actual evapotranspiration (ETc). Under water stress, soil drainage rate, soil runoff curve number, and photosynthesis factor greatly affected the output response of CERES-Maize. Compared with the calibration of maize cultivar coefficients, CERES-Maize with additional consideration of soil parameter calibration was more accurate. The model evaluation results revealed that the simulated LAI, yield, and soil water content were consistent with the actual measured values. These findings can provide a reference for the calibration of CERES-Maize model parameters under water and fertilizer stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attia, A., El-Hendawy, S., Al-Suhaibani, N., Tahir, M. U., Mubushar, M., dos Santos Vianna, M., Ullah, H., Mansour, E., & Datta, A. (2021). Sensitivity of the DSSAT model in simulating maize yield and soil carbon dynamics in arid Mediterranean climate: effect of soil, genotype and crop management. Field Crops Research, 260, 107981.
Corbeels, M., Chirat, G., Messad, S., & Thierfelder, C. (2016). Performance and sensitivity of the DSSAT crop growth model in simulating maize yield under conservation agriculture. European Journal of Agronomy, 76, 41–53.
Deihimfard, R., Eyni-Nargeseh, H., & Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A. (2018). Effect of future climate change on wheat yield and water use efficiency under semi-arid conditions as predicted by APSIM-wheat model. International Journal of Plant Production, 12, 115–125.
DeJonge, K. C., Ascough, J. C., II., Ahmadi, M., Andales, A. A., & Arabi, M. (2012). Global sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of a dynamic agroecosystem model under different irrigation treatments. Ecological Modelling, 231, 113–125.
Fu, C., Wang, J., Gong, S., Zhang, Y., Wang, C., & Mo, Y. (2020). Optimization of irrigation and fertilization of drip-irrigated corn in the chernozem area of north-east China based on the CERES-Maize model. Irrigation and Drainage., 69, 714–731.
Gilardelli, C., Confalonieri, R., Cappelli, G. A., & Bellocchi, G. (2018). Sensitivity of WOFOST-based modelling solutions to crop parameters under climate change. Ecological Modelling, 368, 1–14.
Guo, D., Olesen, J. E., Manevski, K., & Ma, X. (2021). Optimizing irrigation schedule in a large agricultural region under different hydrologic scenarios. Agricultural Water Management, 245, 106575.
Guo, D., Zhao, R., Xing, X., & Ma, X. (2020). Global sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of the AquaCrop model for maize under different irrigation and fertilizer management conditions. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 66, 1115–1133.
He, J., Dukes, M. D., Hochmuth, G. J., Jones, J. W., & Graham, W. D. (2012). Identifying irrigation and nitrogen best management practices for sweet corn production on sandy soils using CERES-Maize model. Agricultural Water Management, 109, 61–70.
He, J., Dukes, M., Jones, J., Graham, W., & Judge, J. (2009). Applying GLUE for estimating CERES-Maize genetic and soil parameters for sweet corn production. Transactions of the ASABE, 52, 1907–1921.
Hoogenboom, G., Jones, J., Wilkens, P., Porter, C., Boote, K., Hunt, L., Singh, U., Lizaso, J., White, J., & Uryasev, O. (2010). Decision support system for agrotechnology transfer (DSSAT) Version 4.5 [CD-ROM]. University of Hawaii.
Iooss, B., & Lemaître, P. (2015). A review on global sensitivity analysis methods (pp. 101–122). Uncertainty management in simulation-optimization of complex systems. Springer.
Jin, X., Li, Z., Nie, C., Xu, X., Feng, H., Guo, W., & Wang, J. (2018). Parameter sensitivity analysis of the AquaCrop model based on extended Fourier amplitude sensitivity under different agro-meteorological conditions and application. Field Crops Research, 226, 1–15.
Jones, C., & Kiniry, J. (1986). A simulation model of maize growth and development. Texas A&M University Press.
Jones, J. W., Naab, J., Fatondji, D., Dzotsi, K., Adiku, S., & He, J. (2012). Uncertainties in simulating crop performance in degraded soils and low input production systems, improving soil fertility recommendations in Africa using the Decision Support System for Agrotechnology Transfer (DSSAT) (pp. 43–59). Springer.
Jones, J. W., Hoogenboom, G., Porter, C. H., Boote, K. J., Batchelor, W. D., Hunt, L., Wilkens, P. W., Singh, U., Gijsman, A. J., & Ritchie, J. T. (2003). The DSSAT cropping system model. European Journal of Agronomy, 18, 235–265.
Li, Z.-H., Jin, X.-L., Liu, H.-L., Xu, X.-G., & Wang, J.-H. (2019). Global sensitivity analysis of wheat grain yield and quality and the related process variables from the DSSAT-CERES model based on the extended Fourier Amplitude Sensitivity Test method. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 18, 1547–1561.
Liang, H., Qi, Z., DeJonge, K. C., Hu, K., & Li, B. (2017). Global sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of nitrate leaching and crop yield simulation under different water and nitrogen management practices. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 142, 201–210.
Lindquist, J. L., Arkebauer, T. J., Walters, D. T., Cassman, K. G., & Dobermann, A. (2005). Maize radiation use efficiency under optimal growth conditions. Agronomy Journal, 97, 72–78.
Ma, L., Ahuja, L., Saseendran, S., Malone, R., Green, T., Nolan, B., Bartling, P., Flerchinger, G., Boote, K., & Hoogenboom, G. (2011). A protocol for parameterization and calibration of RZWQM2 in field research. Methods of Introducing System Models into Agricultural Research, 2, 1–64.
MacCarthy, D. S., Adiku, S. G., Freduah, B. S., & Gbefo, F. (2017). Using CERES-Maize and ENSO as decision support tools to evaluate climate-sensitive farm management practices for maize production in the northern regions of Ghana. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 31.
Malik, W., Isla, R., & Dechmi, F. (2019). DSSAT-CERES-maize modelling to improve irrigation and nitrogen management practices under Mediterranean conditions. Agricultural Water Management, 213, 298–308.
Mirjalili, S. (2019). Genetic algorithm, evolutionary algorithms and neural networks (pp. 43–55). Springer.
Monod, H., Naud, C., & Makowski, D. (2006). Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis for crop models. Working with Dynamic Crop Models: Evaluation, Analysis, Parameterization, and Applications, 4, 55–100.
Naves, J., Rieckermann, J., Cea, L., Puertas, J., & Anta, J. (2020). Global and local sensitivity analysis to improve the understanding of physically-based urban wash-off models from high-resolution laboratory experiments. Science of the Total Environment, 709, 136152.
Qi, D., Hu, T., & Niu, X. (2017). Responses of root growth and distribution of maize to nitrogen application patterns under partial root-zone irrigation. International Journal of Plant Production, 11, 209–224.
Saltelli, A., Ratto, M., Andres, T., Campolongo, F., Cariboni, J., Gatelli, D., Saisana, M., & Tarantola, S. (2008). Global sensitivity analysis: The primer. Wiley.
Saltelli, A., Tarantola, S., & Chan, K.-S. (1999). A quantitative model-independent method for global sensitivity analysis of model output. Technometrics, 41, 39–56.
Schwab, G. O., Frevert, R. K., Edminster, T. W., & Barnes, K. K. (1982). Soil and water conservation engineering. Soil Science, 134, 146.
Shen, H., Xu, F., Zhao, R., & Xing, X. (2020). Optimization of sowing date, irrigation and nitrogen management of summer maize by using the DSSAT-CERES-maize model in the Guanzhong Plain, China. Transactions of the ASABE, 63, 789–797.
Shokati, B., & Feizizadeh, B. (2019). Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of agro-ecological modeling for saffron plant cultivation using GIS spatial decision-making methods. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 62, 517–533.
Tan, J., Cui, Y., & Luo, Y. (2017). Assessment of uncertainty and sensitivity analyses for ORYZA model under different ranges of parameter variation. European Journal of Agronomy, 91, 54–62.
Wang, J., Li, X., Lu, L., & Fang, F. (2013). Parameter sensitivity analysis of crop growth models based on the extended Fourier Amplitude Sensitivity Test method. Environmental Modelling & Software, 48, 171–182.
Wang, Y., Liu, Y., & Ma, X. (2021). Updated kriging-assisted shape optimization of a gravity dam. Water, 13, 87.
Xi, M. L., Lu, D. A., Gui, D. W., Qi, Z. M., & Zhang, G. N. (2017). Calibration of an agricultural-hydrological model (RZWQM2) using surrogate global optimization. Journal of Hydrology, 544, 456–466.
Xiao, D., Li Liu, D., Wang, B., Feng, P., & Waters, C. (2020). Designing high-yielding maize ideotypes to adapt changing climate in the North China Plain. Agricultural Systems, 181, 102805.
Xu, X., Shen, S., Xiong, S., Ma, X., Fan, Z., & Han, H., (2021). Water stress is a key factor influencing the parameter sensitivity of the WOFOST model in different agro-meteorological conditions. International Journal of Plant Production, 1–12.
Xu, X., Sun, C., Huang, G., & Mohanty, B. P. (2016). Global sensitivity analysis and calibration of parameters for a physically-based agro-hydrological model. Environmental Modelling & Software, 83, 88–102.
Yuan, Z., Liang, P., Silva, T., Yu, K., & Mottershead, J. E. (2019). Parameter selection for model updating with global sensitivity analysis. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 115, 483–496.
Zhuo, W., Huang, J., Li, L., Zhang, X., Ma, H., Gao, X., Huang, H., Xu, B., & Xiao, X. (2019). Assimilating soil moisture retrieved from Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data into WOFOST model to improve winter wheat yield estimation. Remote Sensing, 11, 1618.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51279167) and the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2017YFC0403202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflicts of interest are reported by the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Guo, F., Shen, H. et al. Global Sensitivity Analysis and Evaluation of the DSSAT Model for Summer Maize (Zea mays L.) Under Irrigation and Fertilizer Stress. Int. J. Plant Prod. 15, 523–539 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-021-00157-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-021-00157-1