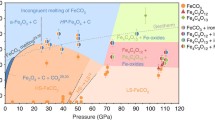
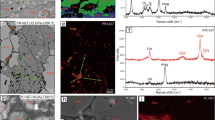
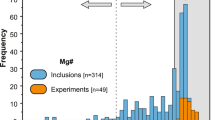
Abstract
Carbonates are considered to be important hosts of oxidized carbon during subduction processes. Here we investigate the redox interactions between dolomite and metallic iron in laser-heated diamond anvil cells up to ∼20 GPa. The identification of recovered samples via in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction and ex-situ Raman spectroscopy shows that the reaction occurs with the formation of ferropericlase, graphite and hexagonal diamond, while CaCO3 remains stable. The experimental results indicate dolomite and metallic iron phases cannot coexist and demonstrate a possible formation mechanism of ultradeep diamonds via redox reaction between dolomite and iron under the mantle transition zone conditions. The results are significant for understanding carbon transportation during subduction processes and have further implications to the processes in the more complex systems regarding to carbonate-silicate-metal phase relations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Ballhaus, C., 1995. Is the Upper Mantle Metal-Saturated? Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 132(1/2/3/4): 75–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821x(95)00047-g
Bayarjargal, L., Fruhner, C. J., Schrodt, N., et al., 2018. CaCO3 Phase Diagram Studied with Raman Spectroscopy at Pressures up to 50 GPa and High Temperatures and DFT Modeling. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 281: 31–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2018.05.002
Brenker, F. E., Vollmer, C., Vincze, L., et al., 2007. Carbonates from the Lower Part of Transition Zone or even the Lower Mantle. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 260(1/2): 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.02.038
Bureau, H., Frost, D. J., Bolfan-Casanova, N., et al., 2016. Diamond Growth in Mantle Fluids. Lithos, 265: 4–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2016.10.004
Chen, M., Shu, J. F., Xie, X. D., et al., 2018. Natural Diamond Formation by Self-Redox of Ferromagnesian Carbonate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(11): 2676–2680. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1720619115
Dasgupta, R., Hirschmann, M. M., 2006. Melting in the Earth’s Deep Upper Mantle Caused by Carbon Dioxide. Nature, 440(7084): 659–662. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04612
Dasgupta, R., Hirschmann, M. M., 2010. The Deep Carbon Cycle and Melting in Earth’s Interior. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 298(1/2): 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2010.06.039
Dorfman, S. M., Badro, J., Nabiei, F., et al., 2018. Carbonate Stability in the Reduced Lower Mantle. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 489: 84–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2018.02.035
Drewitt, J. W. E., Walter, M. J., Zhang, H. L., et al., 2019. The Fate of Carbonate in Oceanic Crust Subducted into Earth’s Lower Mantle. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 511: 213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2019.01.041
Dubrovinsky, L., Glazyrin, K., McCammon, C., et al., 2009. Portable Laser-Heating System for Diamond Anvil Cells. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 16(6): 737–741. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0909049509039065
Farsang, S., Facq, S., Redfern, S. A. T., 2018. Raman Modes of Carbonate Minerals as Pressure and Temperature Gauges up to 6 GPa and 500. American Mineralogist, 103(12): 1988–1998. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2018-6442
Fei, Y. W., Zhang, L., Corgne, A., et al., 2007. Spin Transition and Equations of State of (Mg, Fe)O Solid Solutions. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(17): L17307. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gl030712
Fiquet, G., Guyot, F., Kunz, M., et al., 2002. Structural Refinements of Magnesite at very High Pressure. American Mineralogist, 87(8/9): 1261–1265. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2002-8-927
Gao, J., Niu, J. J., Qin, S., et al., 2017. Ultradeep Diamonds Originate from Deep Subducted Sedimentary Carbonates. Science China Earth Sciences, 60(2): 207–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-016-5151-4
Hammersley, A. P., Svensson, S. O., Hanfland, M., et al., 1996. Two-Dimensional Detector Software: From Real Detector to Idealised Image or Two-Theta Scan. High Pressure Research, 14(4/5/6): 235–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/08957959608201408
Jephcoat, A. P., Finger, L. W., Cox, D. E., 1992. High Pressure, High Resolution Synchrotron X-Ray Powder Diffraction with a Position-Sensitive Detector. High Pressure Research, 8(5/6): 667–676. https://doi.org/10.1080/08957959208206318
Kaminsky, F., Matzel, J., Jacobsen, B., et al., 2016. Isotopic Fractionation of Oxygen and Carbon in Decomposed Lower-Mantle Inclusions in Diamond. Mineralogy and Petrology, 110(2/3): 379–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-015-0401-7
Kaminsky, F., Wirth, R., Matsyuk, S., et al., 2009. Nyerereite and Nahcolite Inclusions in Diamond: Evidence for Lower-Mantle Carbonatitic Magmas. Mineralogical Magazine, 73(5): 797–816. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.2009.073.5.797
Li, X. Y., Zhang, Z. G., Lin, J. F., et al., 2018. New High-Pressure Phase of CaCO3 at the Topmost Lower Mantle: Implication for the Deep-Mantle Carbon Transportation. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(3): 1355–1360. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017gl076536
Litvin, Y. A., Spivak, A. V., Dubrovinsky, L. S., 2016. Magmatic Evolution of the Material of the Earth’s Lower Mantle: Stishovite Paradox and Origin of Superdeep Diamonds (Experiments at 24–26 GPa). Geochemistry International, 54(11): 936–947. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0016702916090032
Liu, J., Dubrovinsky, L., Boffa Ballaran, T., et al., 2007. Equation of State and Thermal Expansivity of LiF and NaF. High Pressure Research, 27(4): 483–489. https://doi.org/10.1080/08957950701684690
Maeda, F., Ohtani, E., Kamada, S., et al., 2017. Diamond Formation in the Deep Lower Mantle: A High-Pressure Reaction of MgCO3 and SiO2. Scientific Reports, 7: 40602. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40602
Mao, H. K., Bassett, W. A., Takahashi, T., 1967. Effect of Pressure on Crystal Structure and Lattice Parameters of Iron up to 300 kbar. Journal of Applied Physics, 38(1): 272–276. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1708965
Mao, Z., Armentrout, M., Rainey, E., et al., 2011a. Dolomite: A New Candidate Lower Mantle Carbonate. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(22): L22303. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011gl049519
Mao, Z., Lin, J. F., Liu, J., et al., 2011b. Thermal Equation of State of Lower-Mantle Ferropericlase across the Spin Crossover. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(23): L23308. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011gl049915
Martinez, I., Zhang, J., Reeder, R. J., 1996. In situ X-Ray Diffraction of Aragonite and Dolomite at High Pressure and High Temperature: Evidence for Dolomite Breakdown to Aragonite and Magnesite. American Mineralogist, 81(5/6): 611–624. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-1996-5-608
Martirosyan, N. S., Litasov, K. D., Lobanov, S. S., et al., 2019a. The Mg-Carbonate-Fe Interaction: Implication for the Fate of Subducted Carbonates and Formation of Diamond in the Lower Mantle. Geoscience Frontiers, 10(4): 1449–1458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2018.10.003
Martirosyan, N. S., Shatskiy, A., Chanyshev, A. D., et al., 2019b. Effect of Water on the Magnesite-Iron Interaction, with Implications for the Fate of Carbonates in the Deep Mantle. Lithos, 326/327: 435–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2019.01.004
Martirosyan, N. S., Litasov, K. D., Shatskiy, A. F., et al., 2015a. Reactions of Iron with Calcium Carbonate at 6 GPa and 1 273–1 873 K: Implications for Carbonate Reduction in the Deep Mantle. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 56(9): 1322–1331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgg.2015.08.008
Martirosyan, N. S., Litasov, K. D., Shatskiy, A., et al., 2015b. The Reactions between Iron and Magnesite at 6 GPa and 1 273–1 873 K: Implication to Reduction of Subducted Carbonate in the Deep Mantle. Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 110(2): 49–59. https://doi.org/10.2465/jmps.141003a
Martirosyan, N. S., Yoshino, T., Shatskiy, A., et al., 2016. The CaCO3-Fe Interaction: Kinetic Approach for Carbonate Subduction to the Deep Earth’s Mantle. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 259: 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2016.08.008
Merlini, M., Cerantola, V., Gatta, G. D., et al., 2017. Dolomite-IV: Candidate Structure for a Carbonate in the Earth’s Lower Mantle. American Mineralogist, 102(8): 1763–1766. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2017-6161
Merlini, M., Crichton, W. A., Hanfland, M., et al., 2012. Structures of Dolomite at Ultrahigh Pressure and Their Influence on the Deep Carbon Cycle. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(34): 13509–13514. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1201336109
Németh, P., Garvie, L. A. J., Aoki, T., et al., 2014. Lonsdaleite is Faulted and Twinned Cubic Diamond and does not Exist as a Discrete Material. Nature Communications, 5: 5447. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6447
Nestola, F., Korolev, N., Kopylova, M., et al., 2018. CaSiO3 Perovskite in Diamond Indicates the Recycling of Oceanic Crust into the Lower Mantle. Nature, 555(7695): 237–241. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25972
Oganov, A. R., Hemley, R. J., Hazen, R. M., et al., 2013. Structure, Bonding, and Mineralogy of Carbon at Extreme Conditions. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 75(1): 47–77. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2013.75.3
Palyanov, Y. N., Bataleva, Y. V., Sokol, A. G., et al., 2013. Mantle-Slab Interaction and Redox Mechanism of Diamond Formation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(51): 20408–20413. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1313340110
Patterson, J. R., Kudryavtsev, A., Vohra, Y. K., 2002. X-Ray Diffraction and Nanoindentation Studies of Nanocrystalline Graphite at High Pressures. Applied Physics Letters, 81(11): 2073–2075. https://doi.org/10.1063/L1508169
Pócsik, I., Hundhausen, M., Koós, M., et al., 1998. Origin of the D Peak in the Raman Spectrum of Microcrystalline Graphite. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 227–230(2): 1083–1086. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3093(98)00349-4
Reich, S., Thomsen, C., 2004. Raman Spectroscopy of Graphite. Philosophical Transactions Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences, 362(1824): 2271–2288. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2004.1454
Rohrbach, A., Ballhaus, C., Golla-Schindler, U., et al., 2007. Metal Saturation in the Upper Mantle. Nature, 449(7161): 456–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06183
Rohrbach, A., Schmidt, M. W., 2011. Redox Freezing and Melting in the Earth’s Deep Mantle Resulting from Carbon-Iron Redox Coupling. Nature, 472(7342): 209–212. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09899
Santillán, J., Williams, Q., Knittle, E., 2003. Dolomite-: A High-Pressure Polymorph of CaMg(CO3)2. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(2): 1054. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002gl016018
Sato, K., Katsura, T., 2001. Experimental Investigation on Dolomite Dissociation into Aragonite+Magnesite up to 8.5 GPa. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 184(2): 529–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(00)00346-0
Schindler, T. L., Vohra, Y. K., 1995. A Micro-Raman Investigation of High-Pressure Quenched Graphite. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 7(47): L637–L642. https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/7/47/001
Smith, D. C., Godard, G., 2009. UV and VIS Raman Spectra of Natural Lonsdaleites: Towards a Recognised Standard. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 73(3): 428–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2008.10.025
Stagno, V., Frost, D. J., McCammon, C. A., et al., 2015. The Oxygen Fugacity at which Graphite or Diamond Forms from Carbonate-Bearing Melts in Eclogitic Rocks. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 169(2): 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-015-1111-1
Sung, J., 2000. Graphite →Diamond Transition under High Pressure: AKinetics Approach. Journal of Materials Science, 35(23): 6041–6054. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1026779802263
Thomson, A. R., Kohn, S. C., Bulanova, G. P., et al., 2014. Origin of Sub-Lithospheric Diamonds from the Juina-5 Kimberlite (Brazil): Constraints from Carbon Isotopes and Inclusion Compositions. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 168(6): 1–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-014-1081-8
Thomson, A. R., Walter, M. J., Kohn, S. C., et al., 2016. Slab Melting as a Barrier to Deep Carbon Subduction. Nature, 529(7584): 76–79. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16174
Toby, B. H., 2001. EXPGUI, a Graphical User Interface for GSAS. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 34(2): 210–213. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889801002242
van der Hilst, R. D., Widiyantoro, S., Engdahl, E. R., 1997. Evidence for Deep Mantle Circulation from Global Tomography. Nature, 386(6625): 578–584. https://doi.org/10.1038/386578a0
van Westrenen, W., Li, J., Fei, Y. W., et al., 2005. Thermoelastic Properties of (Mg0.64Fe0.36)O Ferropericlase Based on in situ X-Ray Diffraction to 26.7 GPa and 2 173 K. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 151(1/2): 163–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2005.03.001
Walter, M. J., Kohn, S. C., Araujo, D., et al., 2011. Deep Mantle Cycling of Oceanic Crust: Evidence from Diamonds and Their Mineral Inclusions. Science, 334(6052): 54–57. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1209300
Yang, J. S., Shen, T. T., Zhang, C., et al., 2019. Preface: Introduction of IGCP 649 Project—Diamonds and Recycled Mantle. Journal of Earth Science, 30(3): 429–430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-019-1229-6
Zhang, X., Yang, S. Y., Zhao, H., et al., 2019. Effect of Beam Current and Diameter on Electron Probe Microanalysis of Carbonate Minerals. Journal of Earth Science, 30(4): 834–842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0939-x
Zhu, F., Li, J., Liu, J. C., et al., 2019. Kinetic Control on the Depth Distribution of Superdeep Diamonds. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(4): 1984–1992. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018gl080740
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41772034). We thank the two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments. The final publication is available at Springer via https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1410-6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, T., Huang, S., Qin, S. et al. Redox-Induced Destabilization of Dolomite at Earth’s Mantle Transition Zone. J. Earth Sci. 32, 880–886 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1410-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1410-6