Abstract
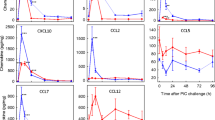
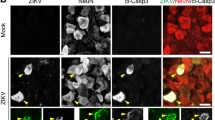
Peripheral viral infection can substantially alter brain function. We have previously shown that intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of a viral mimetic, polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (PIC), engenders hyperexcitability of cerebral neurons. Because neuronal activity is invariably associated with their expression of the Cfos gene, the present study was undertaken to determine whether PIC challenge also increases neuronal c-fos protein level. Female C57BL/6 mice were i.p. injected with PIC, and neuronal c-fos was analyzed in the motor cortex by immunohistochemistry. PIC challenge instigated a robust increase in the number of c-fos-positive neurons. This increase reached approximately tenfold over control at 24 h. Also, the c-fos staining intensity of individual neurons increased. AMG-487, a specific inhibitor of the chemokine receptor CXCR3, profoundly attenuated the accumulation of neuronal c-fos, indicating the activation of CXCL10/CXCR3 axis as the trigger of the process. Together, these results show that the accumulation of c-fos is a viable readout to assess the response of cerebral neurons to peripheral PIC challenge, and to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated for this study are available from the corresponding author.
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Adelman JS, Martin LB (2009) Vertebrate sickness behaviors: adaptive and integrated neuroendocrine immune responses. Integr Comp Biol 49:202–214
Andersen O, Lygner PE, Bergstrom T, Andersson M, Vahlne A (1993) Viral infections trigger multiple sclerosis relapses: a prospective seroepidemiological study. J Neurol 240:417–422
Baille-Le Crom V, Collombet JM, Burckhart MF, Foquin A, Pernot-Marino I, Rondouin G, Lallement G (1996) Time course and regional expression of C-FOS and HSP70 in hippocampus and piriform cortex following soman-induced seizures. J Neurosci Res 45:513–524
Barros VN, Mundim M, Galindo LT, Bittencourt S, Porcionatto M, Mello LE (2015) The pattern of c-Fos expression and its refractory period in the brain of rats and monkeys. Front Cell Neurosci 9:72
Brugger F, Erro R, Balint B, Kägi G, Barone P, Bhatia KP (2015) Why is there motor deterioration in Parkinson’s disease during systemic infections-a hypothetical view. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 1:15014
Buljevac D, Flach HZ, Hop WC, Hijdra D, Laman JD, Savelkoul HF, van Der Meche FG, van Doorn PA, Hintzen RQ (2002) Prospective study on the relationship between infections and multiple sclerosis exacerbations. Brain 125:952–960
Bullitt E (1990) Expression of c-fos-like protein as a marker for neuronal activity following noxious stimulation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 296:517–530
Chaudhuri A, Zangenehpour S, Rahbar-Dehgan F, Ye F (2000) Molecular maps of neural activity and quiescence. Acta Neurobiol Exp (wars) 60:403–410
Chung L (2015) A brief introduction to the transduction of neural activity into Fos signal. Dev Reprod 19:61–67
Dantzer R (2009) Cytokine, sickness behavior, and depression. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 29:247–264
Dudek FE (2006) Activation of Fos during spontaneous hippocampal seizures in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Curr 6:57–58
Edwards S, Zvartau M, Clarke H, Irving W, Blumhardt LD (1998) Clinical relapses and disease activity on magnetic resonance imaging associated with viral upper respiratory tract infections in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64:736–741
Fields RD, Eshete F, Stevens B, Itoh K (1997) Action potential-dependent regulation of gene expression: temporal specificity in ca2+, cAMP-responsive element binding proteins, and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. J Neurosci 17:7252–7266
Fisahn A, Heinemann SF, McBain CJ (2005) The kainate receptor subunit GluR6 mediates metabotropic regulation of the slow and medium AHP currents in mouse hippocampal neurones. J Physiol 562:199–203
George J, Bleasdale S, Singleton SJ (1997) Causes and prognosis of delirium in elderly patients admitted to a district general hospital. Age Ageing 26:423–427
Herrera DG, Robertson HA (1996) Activation of c-fos in the brain. Prog Neurobiol 50:83–107
Holmes C (2013) Review: systemic inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 39:51–68
Holmes C, El-Okl M, Williams AL, Cunningham C, Wilcockson D, Perry VH (2003) Systemic infection, interleukin 1beta, and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:788–789
Hudson AE (2018) Genetic reporters of neuronal activity: c-Fos and G-CaMP6. Methods Enzymol 603:197–220
Hunsberger HC, Konat GW, Reed MN (2017) Peripheral viral challenge elevates extracellular glutamate in the hippocampus leading to seizure hypersusceptibility. J Neurochem 141:341–346
Hunsberger HC, Wang D, Petrisko TJ, Alhowail A, Setti SE, Suppiramaniam V, Konat GW, Reed MN (2016) Peripherally restricted viral challenge elevates extracellular glutamate and enhances synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. J Neurochem 138:307–316
Joo JY, Schaukowitch K, Farbiak L, Kilaru G, Kim TK (2016) Stimulus-specific combinatorial functionality of neuronal c-fos enhancers. Nat Neurosci 19:75–83
Kawasaki M, Ponzio TA, Yue C, Fields RL, Gainer H (2009) Neurotransmitter regulation of c-fos and vasopressin gene expression in the rat supraoptic nucleus. Exp Neurol 219:212–222
Kawashima T, Okuno H, Bito H (2014) A new era for functional labeling of neurons: activity-dependent promoters have come of age. Front Neural Circuits 8:37
Kirschman LT, Borysiewicz E, Fil D, Konat GW (2011) Peripheral immune challenge with dsRNA enhances kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. Metab Brain Dis 26:91–93
Kong YF, Sha WL, Wu XB, Zhao LX, Ma LJ, Gao YJ (2021) CXCL10/CXCR3 signaling in the DRG exacerbates neuropathic pain in mice. Neurosci Bull 37:339–352
Kovács KJ (1998) c-Fos as a transcription factor: a stressful (re)view from a functional map. Neurochem Int 33:287–297
Larochelle A, Bellavance MA, Rivest S (2015) Role of adaptor protein MyD88 in TLR-mediated preconditioning and neuroprotection after acute excitotoxicity. Brain Behav Immunity 46:221–231
Li W, Jiang D, Li Q, Yao S, Sun X, Yang Y, Meng Z, Liu W (2016) Lipopolysaccharide-induced preconditioning protects against traumatic spinal cord injury by upregulating Nrf2 expression in rats. Life Sci 162:14–20
Libbey JE, Fujinami RS (2010) Potential triggers of MS. Results Probl Cell Differ 51:21–42
Luckman SM, Dyball RE, Leng G (1994) Induction of c-fos expression in hypothalamic magnocellular neurons requires synaptic activation and not simply increased spike activity. J Neurosci 14:4825–4830
Malhi SM, Jawed H, Hanif F, Ashraf N, Zubair F, Siddiqui BS, Begum S, Kabir N, Simjee SU (2014) Modulation of c-Fos and BDNF protein expression in pentylenetetrazole-kindled mice following the treatment with novel antiepileptic compound HHL-6. Biomed Res Int 2014:876712
Meng Q, Ye C, Lu Y (2020) miR-181c regulates ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced neuronal cell death by regulating c-Fos signaling. Pharmazie 75:90–93
Michalovicz LT, Konat GW (2014) Peripherally restricted acute phase response to a viral mimic alters hippocampal gene expression. Metab Brain Dis 29:75–86
Morgan JI, Cohen DR, Hempstead JL, Curran T (1987) Mapping patterns of c-fos expression in the central nervous system after seizure. Science 237:192–197
Mulle C, Sailer A, Pérez-Otaño I, Dickinson-Anson H, Castillo PE, Bureau I, Maron C, Gage FH, Mann JR, Bettler B, Heinemann SF (1998) Altered synaptic physiology and reduced susceptibility to kainate-induced seizures in GluR6-deficient mice. Nature 392:601–605
Murray AM, Levkoff SE, Wetle TT, Beckett L, Cleary PD, Schor JD, Lipsitz LA, Rowe JW, Evans DA (1993) Acute delirium and functional decline in the hospitalized elderly patient. J Gerontol 48:M181–M186
Nee LE, Lippa CF (1999) Alzheimer’s disease in 22 twin pairs–13-year follow-up: hormonal, infectious and traumatic factors. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 10:148–151
Packard AE, Hedges JC, Bahjat FR, Stevens SL, Conlin MJ, Salazar AM, Stenzel-Poore MP (2012) Poly-IC preconditioning protects against cerebral and renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:242–247
Panitch HS (1994) Influence of infection on exacerbations of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 36(Suppl):S25-28
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Petrisko T, Konat G (2017) Peripheral viral challenge triggers hippocampal production of inflammatory proteins. Metab Brain Dis 32:1249–1254
Petrisko TJ, Bloemer J, Pinky PD, Srinivas S, Heslin RT, Du Y, Setti SE, Hong H, Suppiramaniam V, Konat GW, Reed MN (2020) Neuronal CXCL10/CXCR3 axis mediates the induction of cerebral hyperexcitability by peripheral viral challenge. Front Neurosci 14:220
Poggi A, Catellani S, Fenoglio D, Borsellino G, Battistini L, Zocchi MR (2007) Adhesion molecules and kinases involved in gammadelta T cells migratory pathways: implications for viral and autoimmune diseases. Curr Med Chem 14:3166–3170
Quan N, Banks WA (2007) Brain-immune communication pathways. Brain Behav Immun 21:727–735
Rawat V, Goux W, Piechaczyk M, D’Mello SR (2016) c-Fos protects neurons through a noncanonical mechanism involving HDAC3 interaction: identification of a 21-amino acid fragment with neuroprotective activity. Mol Neurobiol 53:1165–1180
Rosenzweig HL, Lessov NS, Henshall DC, Minami M, Simon RP, Stenzel-Poore MP (2004) Endotoxin preconditioning prevents cellular inflammatory response during ischemic neuroprotection in mice. Stroke 35:2576–2581
Ruiz A (2011) Kainate receptors with a metabotropic signature enhance hippocampal excitability by regulating the slow after-hyperpolarization in CA3 pyramidal neurons. Adv Exp Med Biol 717:59–68
Scheid R, Teich N (2007) Neurologic manifestations of ulcerative colitis. Eur J Neurol 14:483–493
Shakhar K, Shakhar G (2015) Why do we feel sick when infected—can altruism play a role? PLoS Biol 13:e1002276
Sheng M, McFadden G, Greenberg ME (1990) Membrane depolarization and calcium induce c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB. Neuron 4:571–582
Shevelkin AV, Efimova OI, Nikitin VP, Anokhin KV, Sherstnev VV (2012) Specific changes in c-fos expression and colocalization with DNA in identified neuronal nuclei of edible snail following neurotransmitter application. Bull Exp Biol Med 153:734–737
Srinivasan D, Yen JH, Joseph DJ, Friedman W (2004) Cell type-specific interleukin-1beta signaling in the CNS. J Neurosci 24:6482–6488
Tellez-Zenteno JF, Matijevic S, Wiebe S (2005) Somatic comorbidity of epilepsy in the general population in Canada. Epilepsia 46:1955–1962
Thompson MA, Ginty DD, Bonni A, Greenberg ME (1995) L-type voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channel activation regulates c-fos transcription at multiple levels. J Biol Chem 270:4224–4235
Tseng CS, Chao HW, Huang HS, Huang YS (2017) Olfactory-experience- and developmental-stage-dependent control of CPEB4 Regulates c-Fos mRNA translation for granule cell survival. Cell Rep 21:2264–2276
Ulrich M, Wissenbach U, Thiel G (2020) The super-cooling compound icilin stimulates c-Fos and Egr-1 expression and activity involving TRPM8 channel activation, Ca(2+) ion influx and activation of the ternary complex factor Elk-1. Biochem Pharmacol 177:113936
Verrotti A, Tocco AM, Coppola GG, Altobelli E, Chiarelli F (2009) Afebrile benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis: a new entity? Acta Neurol Scand 120:73–79
Vezzani A, Granata T (2005) Brain inflammation in epilepsy: experimental and clinical evidence. Epilepsia 46:1724–1743
Wang PF, Fang H, Chen J, Lin S, Liu Y, Xiong XY, Wang YC, Xiong RP, Lv FL, Wang J, Yang QW (2014) Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid has therapeutic effects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through the downregulation of TLR4 signaling via TLR3. J Immunol 192:4783–4794
Zhang J, Zhang D, McQuade JS, Behbehani M, Tsien JZ, Xu M (2002) c-fos regulates neuronal excitability and survival. Nat Genet 30:416–420
Zheng KS, Dorfman BJ, Christos PJ, Khadem NR, Henchcliffe C, Piboolnurak P, Nirenberg MJ (2012) Clinical characteristics of exacerbations in Parkinson disease. Neurologist 18:120–124
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a bridge grant from WVU School of Medicine. The WVU Microscopy Imaging Facility was supported by NIH Grants P20RR016440, P30GM103488, P20GM103434, and U54GM104942.
Funding
This work was supported by a bridge grant from WVU School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GWK conceived and designed the experiments. TJP performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Both authors wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures were approved by the West Virginia University Animal Care and Use Committee and performed in accordance with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrisko, T.J., Konat, G.W. Peripheral viral challenge increases c-fos level in cerebral neurons. Metab Brain Dis 36, 1995–2002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00819-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00819-z