Abstract
Heart failure (HF) is a rising epidemic and public health burden in modern society. It is of great need to find new biomarkers to ensure a timely diagnosis and to improve treatment and prognosis of the disease. The mouse model of HF was established by thoracic aortic constriction. Color Doppler ultrasound was performed to detect left ventricular end-diastolic diameter. Hematoxylin and eosin staining was conducted to observe the pathological changes of mouse myocardium. The RT-qPCR analysis was performed to detect miR-590-5p and RTN4 expression levels. Western blot was conducted to detect protein levels of the indicated genes. We found that the expression of miR-590-5p was downregulated in cardiac tissues of HF mice. Injection of AAV-miR-590-5p attenuated myocardium hypertrophy and myocyte apoptosis. Additionally, miR-590-5p overexpression promoted viability, inhibited apoptosis, and decreased ANF, BNP and beta-MHC protein levels in H9c2 cell. Mechanistically, miR-590-5p binds to RTN4 3′‐untranslated region, as predicted by starBase online database and evidenced by luciferase reporter assay. Furthermore, miR-590-5p negatively regulates RTN4 mRNA expression and suppresses its translation. The final rescue experiments revealed that miR-590-5p modulated cardiomyocyte phenotypes by binding to RTN4. In conclusion, miR-590-5p modulates myocardium hypertrophy and myocyte apoptosis in HF by downregulating RTN4.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo L et al (2004) A new role for Nogo as a regulator of vascular remodeling. Nat Med 10:382–388. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1020
Bullard TA, Protack TL, Aguilar F, Bagwe S, Massey HT, Blaxall BC (2008) Identification of Nogo as a novel indicator of heart failure. Physiol Genomics 32:182–189. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00200.2007
Care A et al (2007) MicroRNA-133 controls cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Med 13:613–618. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1582
Chaudhry MA (2019) Heart failure. Curr Hypertens Rev 15:7. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340211501190129144451
Chouvarine P, Geldner J, Giagnorio R, Legchenko E, Bertram H, Hansmann G (2020) Trans-right-ventricle and transpulmonary microRNA gradients in human pulmonary arterial. Hypertens Pediatr Critic Care Med 21:340–349. https://doi.org/10.1097/pcc.0000000000002207
da Costa Martins PA et al (2008) Conditional dicer gene deletion in the postnatal myocardium provokes spontaneous cardiac remodeling. Circulation 118:1567–1576. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.108.769984
Di Sano F, Bernardoni P, Piacentini M (2012) The reticulons: guardians of the structure and function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Exp Cell Res 318:1201–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.03.002
Domarkiene I et al (2013) RTN4 and FBXL17 genes are associated with coronary heart disease in genome-wide association analysis of lithuanian families. Balkan J Med Genetics 16:17–22. https://doi.org/10.2478/bjmg-2013-0026
Eulalio A, Mano M, Dal Ferro M, Zentilin L, Sinagra G, Zacchigna S, Giacca M (2012) Functional screening identifies miRNAs inducing cardiac regeneration. Nature 492:376–381. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11739
Gao B, Xu Y, Leng J, Wang K, Xia B, Huang J (2015) Clinical implications of increased Nogo-B levels in patients with acute coronary syndromes and stable angina pectoris. Int Heart J 56:341–344. https://doi.org/10.1536/ihj.14-397
Germano JF, Sawaged S, Saadaeijahromi H, Andres AM, Feuer R, Gottlieb RA, Sin J (2019) Coxsackievirus B infection induces the extracellular release of miR-590–5p, a proviral microRNA. Virology 529:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2019.01.025
Henderson KK, Danzi S, Paul JT, Leya G, Klein I, Samarel AM (2009) Physiological replacement of T3 improves left ventricular function in an animal model of myocardial infarction-induced congestive heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 2:243–252. https://doi.org/10.1161/circheartfailure.108.810747
Hernandez AF, Felker GM (2011) Advanced heart failure. Progress Cardiovasc Dis 54:77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2011.07.001
Kuang E, Wan Q, Li X, Xu H, Zou T, Qi Y (2006) ER stress triggers apoptosis induced by Nogo-B/ASY overexpression. Exp Cell Res 312:1983–1988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.02.024
Lakhani HV et al (2018) Developing a panel of biomarkers and miRNA in patients with myocardial infarction for early intervention strategies of heart failure in West Virginian population. PLoS ONE 13:e0205329. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0205329
Li Z et al (2017) miR-199a impairs autophagy and induces cardiac hypertrophy through mTOR activation. Cell Death Differen 24:1205–1213. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2015.95
Lin X et al (2016) Common miR-590 variant rs6971711 present only in African Americans reduces miR-590 biogenesis. PLoS ONE 11:e0156065. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0156065
Oertle T, Klinger M, Stuermer CA, Schwab ME (2003) A reticular rhapsody: phylogenic evolution and nomenclature of the RTN/Nogo gene family. FASEB J 17:1238–1247. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.02-1166hyp
Oka T, Akazawa H, Naito AT, Komuro I (2014) Angiogenesis and cardiac hypertrophy: maintenance of cardiac function and causative roles in heart failure. Circ Res 114:565–571. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.114.300507
Pathak GP et al (2018) RTN4 knockdown dysregulates the AKT pathway, destabilizes the cytoskeleton, and enhances paclitaxel-induced cytotoxicity in cancers. Mol Therapy 26:2019–2033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.05.026
Sasagawa S et al (2016) Downregulation of GSTK1 is a common mechanism underlying hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Frontiers Pharmacol 7:162. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00162
Sergeeva IA, Hooijkaas IB, Van Der Made I, Jong WM, Creemers EE, Christoffels VM (2014) A transgenic mouse model for the simultaneous monitoring of ANF and BNP gene activity during heart development and disease. Cardiovasc Res 101:78–86. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvt228
Tambe Y, Isono T, Haraguchi S, Yoshioka-Yamashita A, Yutsudo M, Inoue H (2004) A novel apoptotic pathway induced by the drs tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene 23:2977–2987. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207419
Tham YK, Bernardo BC, Ooi JY, Weeks KL, McMullen JR (2015) Pathophysiology of cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure: signaling pathways and novel therapeutic targets. Arch Toxicol 89:1401–1438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1477-x
The L (2018) Heart failure: the need for improved treatment and care. Lancet (lond, Engl) 392:451. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31737-9
Ucar A et al (2012) The miRNA-212/132 family regulates both cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyocyte autophagy. Nat Commun 3:1078. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2090
Vegter EL, van der Meer P, de Windt LJ, Pinto YM, Voors AA (2016) MicroRNAs in heart failure: from biomarker to target for therapy. Eur J Heart Fail 18:457–468. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejhf.495
Wang L, Qin D, Shi H, Zhang Y, Li H, Han Q (2019) MiR-195–5p promotes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by targeting MFN2 and FBXW7. BioMed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1580982
Wehbe N, Nasser SA, Pintus G, Badran A, Eid AH, Baydoun E (2019) MicroRNAs in cardiac hypertrophy. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194714
Xu L, Wang H, Jiang F, Sun H, Zhang D (2020a) LncRNA AK045171 protects the heart from cardiac hypertrophy by regulating the SP1/MG53 signalling pathway. Aging 12:3126–3139
Xu L, Wang H, Jiang F, Sun H, Zhang D (2020b) Correction for: LncRNA AK045171 protects the heart from cardiac hypertrophy by regulating the SP1/MG53 signalling pathway. Aging. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102975
Yang YS, Strittmatter SM (2007) The reticulons: a family of proteins with diverse functions. Genome Biol 8:234. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2007-8-12-234
Zhang Y, Carreras D, de Bold AJ (2003) Discoordinate re-expression of cardiac fetal genes in N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) hypertension. Cardiovasc Res 57:158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0008-6363(02)00654-5
Zhao Y et al (2007) Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1–2. Cell 129:303–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.03.030
Zheng D et al (2019) Long noncoding RNA Crnde attenuates cardiac fibrosis via Smad3-Crnde negative feedback in diabetic cardiomyopathy. FEBS J 286:1645–1655. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14780
Zhu B et al (2017) Knockout of the Nogo-B gene attenuates tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular. Carcinoma Neoplasia (new York, NY) 19:583–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.02.007
Zyrianova IM, Koval’chuk SN (2018) Bovine leukemia virus pre-miRNA genes’ polymorphism. RNA Biol 15:1440–1447. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2018.1555406
Zytnicki M, Gaspin C (2020) mmannot: How to improve small-RNA annotation? PLoS ONE 15:e0231738. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231738
Zywicki M, Bakowska-Zywicka K, Polacek N (2012) Revealing stable processing products from ribosome-associated small RNAs by deep-sequencing data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 40:4013–4024. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10735_2021_10009_MOESM1_ESM.tif
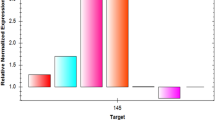
Supplementary file1 Expression of miR-590-5p and RTN4 in adrenal, brain, fat, kidney, andsmall intestine tissues. A. Based on “HPA RNA-seq normal tissues” project (RNA-seq was performedof tissue samples from 95 human individuals representing 27 different tissues to determine tissuespecificityof all protein-coding genes), expression of RTN4 in 27 different tissues was identified (datawas obtained from NCBI). B-C. Expression of RTN4 and miR-590-5p in adrenal, brain, fat, kidney, andsmall intestine tissues isolated from sham mice and HF mice (TIF 596 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, P., Zhang, L., Cheng, T. et al. MiR-590-5p inhibits pathological hypertrophy mediated heart failure by targeting RTN4. J Mol Histol 52, 955–964 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10009-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10009-x