Abstract
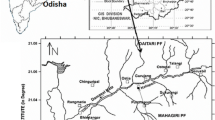
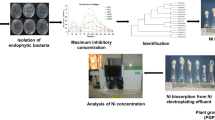
The effluent generated from fertilizer plants in Paradeep in the coast of the Bay of Bengal is the major pollutant causing health hazard in the vicinity of the area with respect to plants, animals and microbes. Samples of effluent were found to contain heavy metals (mg L−1): Cr (100), Ni (36.975), Mn (68.673), Pb (20.133), Cu (74.44), Zn (176.716), Hg (5.358) and As (24.287) as analyzed by XRF. Indigenous bacterial strains were screened for chromate and multi-metal resistance to remediate the toxic pollutants. The isolated strain G1 was identified as Serratia sp. through 16S-rDNA sequence homology. The potent strain Serratia sp. GP01 treated with 100 mg L−1 of K2Cr2O7 has shown the efficacy of reducing 69.05 mg L−1 of Cr over 48 h of incubation. Further, presence of chromate reductase gene (ChR) in Serratia sp. confirmed the enzymatic reduction of Cr(VI). SEM–EDX and SEM mapping analysis revealed substantial biosorption of Cr and other heavy metals present in effluent by Serratia sp. GP01. Antioxidant enzymes such as catalase (72.15 U mL−1), SOD (57.14 U mL−1) and peroxidase (62.49 U mL−1) were found to be higher as compared to the control condition. FTIR study also revealed the role of N–H, O–H, C = C, C–H, C–O, C–N, and C = O functional groups of the cell surface of Serratia sp. treated with K2Cr2O7 and effluent from the fertilizer industry. Isolated strain Serratia sp. could be used for the detoxification of Cr(VI) and other heavy metals in fertilizer plant effluent.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Aguilar-Barajas E, Paluscio E, Cervantes C, Rensing C (2008) Expression of chromate resistance genes from Shewanella sp. strain ANA-3 in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 285:97–100
Ashok AH, Mizuno Y, Volkow ND, Howes OD (2017) Association of stimulant use with dopaminergic alterations in users of cocaine, amphetamine, or methamphetamine: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiat 74:511–519
Avudainayagam S, Megharaj M, Owens G, Kookana RS, Chittleborough D, Naidu R (2003) Chemistry of chromium in soils with emphasis on tannery waste sites. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 178:53–91
Bagchi D, Stohs SJ, Bernard WO, Bagchi M, Preus HG (2002) Cytotoxicity and oxidative mechanism of different forms of chromium. Toxicol 180:5–22
Baruthio F (1992) Toxic effects of chromium and its compounds. Biol Trace Elem Res 32:145–153
Bharagava RN, Mishra S (2018) Hexavalent chromium reduction potential of Cellulosimicrobium sp. isolated from common effluent treatment plant of tannery industries. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:102–109
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Camargo FAO, Okeke BC, Bento FM (2003) In vitro reduction of hexavalent chromium by a cell-free extract of Bacillus sp. ES29 stimulated by Cu (II). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:569–573
Chance B, Maehly AC (1955) Assay of catalases and peroxidases. Methods Enzymol 2:773–775
Choudhary M, Jetley UK, Khan MA, Zutshi S, Fatma T (2007) Effect of heavy metal stress on proline malondialdehyde and superoxide dismutase activity in the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis-S5. Ecotox Environ Saf 66:204–209
Cosgrove DJ (1997) Relaxation in a high-stress environment: the molecular bases of extensible cell walls and cell enlargement. Plant Cell 9:1031–1041
Das S, Mishra J, Das SK, Pandey S, Rao DS, Chakraborty A, Sudarshan M, Das N, Thatoi H (2014) Investigation on mechanism of Cr (VI) reduction and removal by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, a novel chromate tolerant bacterium isolated from chromite mine soil. Chemosphere 96:112–121
Dhanwal P, Kumar A, Dudeja S, Badgujar H, Chauhan R, Kumar A, Dhull P, Chhokar V, Beniwal V (2018) Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by bacteria isolated from contaminated soil. Water Environ Res 90:424–430
Dharmendra S, Kumar MR, Chinmayee A, Ranjan SD, Ranjan PC (2020) Assessment of marine sediment contamination and detection of their potential sources at Paradip port, East Coast of India. Res J Chem Environ 24:6
Elangovan R, Abhipsa S, Rohit B, Ligy P, Chandraraj K (2006) Reduction of Cr (VI) by a Bacillus sp. Biotechnol Lett 28:247–252
Ewing JF, Janero DR (1995) Microplate superoxide dismutase assay employing a nonenzymatic superoxide generator. Anal Biochem 232:243–248
Faisal M, Hasnain S (2004) Comparative study of Cr (VI) uptake and reduction in industrial effluent by Ochrobactrum intermedium and Brevibacterium sp. Biotechnol Lett 26:1623–1628
Gadd GM (2010) Metals, minerals and microbes: geomicrobiology and bioremediation. Microbiology 156:609–643
Gimeno-Garcia E, Andreu V, Boluda R (1996) Heavy metals incidence in the application of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides to rice farming soils. Environ Pollut 92:19–25
Gutierrez AM, Cabriales JJ, Vega MM (2010) Isolation and characterization of hexavalent chromium-reducing rhizospheric bacteria from a wetland. Int J Phytoremediation 12:317–334
Ilias M, Rafiqullah IM, Debnath BC, Mannan KS, Hoq MM (2011) Isolation and characterization of chromium (VI)-reducing bacteria from tannery effluents. Indian J Microbiol 51:76–81
Jin Y, Wu S, Zeng Z, Fu Z (2017) Effects of environmental pollutants on gut microbiota. Environ Pollut 222:1–9
Joutey NT, Sayel H, Bahafid W, El Ghachtouli N (2015) Mechanisms of hexavalent chromium resistance and removal by microorganisms. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 233:45–69
Juhnke S, Peitzsch N, Hubener N, Grobe C, Nies DH (2002) New genes involved in chromate resistance in Ralstonia metallidurans strain CH34. Arch Microbiol 179:15–25
Kalsoom A, Batool R, Jamil N (2021) Highly Cr (vi)-tolerant Staphylococcus simulans assisting chromate evacuation from tannery effluent. Green Process Synth 10:295–308
Khater AE (2012) Uranium and trace elements in phosphate fertilizers–Saudi Arabia. Health Phys 102:63–70
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kowalczuk D, Pitucha M (2019) Application of FTIR method for the assessment of immobilization of active substances in the matrix of biomedical materials. Materials 12:2972
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7 molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger dataset. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Kwak YH, Lee DS, Kim HB (2003) Vibrio harveyi nitroreductase is also a chromate reductase. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4390–4395
Lenartova V, Holovska K, Javorsky P (1998) The influence of mercury on the antioxidant enzyme activity of rumen bacteria Streptococcus bovis and Selenomonas ruminantium. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 27:319–325
McLean JS, Beveridge TJ, Phipps D (2000) Isolation and characterization of a chromium-reducing bacterium from a chromated copper arsenate-contaminated site. Environ Microbiol 2:611–619
Mekki A, Sayadi S (2017) Study of heavy metal accumulation and residual toxicity in soil saturated with phosphate processing wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:215
Morais PV, Branco R, Francisco R (2011) Chromium resistance strategies and toxicity: what makes Ochrobactrum tritici 5bvl1 a strain highly resistant. Biometals 24:401–410
Morgan R (2013) Soil, heavy metals, and human health. In: Brevik EC, Burgess LC (eds) Soils and human health. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 59–82
Naik UC, Srivastava S, Thakur IS (2012) Isolation and characterization of Bacillus cereus IST105 from electroplating effluent for detoxification of hexavalent chromium. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:3005–3014
Patra RC, Malik S, Beer M, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2010) Molecular characterization of chromium (VI) reducing potential in Gram positive bacteria isolated from contaminated sites. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1857–1863
Pattanapipitpaisal P, Brown NL, Macaskie LE (2001) Short contribution: chromate reduction and 16SrRNA Identification of bacteria isolated from a Cr (VI)-contaminated Site. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:257–261
Rajkumar M, Nagendran R, Lee KJ, Lee WH (2005) Characterization of a novel Cr6+ reducing Pseudomonas sp. with plant growth-promoting potential. Curr Microbiol 50:266–271
Ramirez-Diaz MI, Diaz-Perez C, Vargas E, Riveros-Rosas H, Campos-Garcia J, Cervantes C (2008) Mechanisms of bacterial resistance to chromium compounds. Biometals 21:321–332
Sahoo H, Senapati D, Thakur IS, Naik UC (2020) Integrated bacteria-algal bioreactor for removal of toxic metals in acid mine drainage from iron ore mines. Bioresour Technol Rep 11:100422
Samuel J, Pulimi M, Paul ML, Maurya A, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2013) Batch and continuous flow studies of adsorptive removal of Cr (VI) by adapted bacterial consortia immobilized in alginate beads. Bioresour Technol 128:423–430
Schembri MA, Hjerrild L, Gjermansen M, Klemm P (2003) Differential expression of the Escherichia coli autoaggregation factor antigen 43. J Bacteriol 185:2236–2242
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 44:846–849
Sultan S, Hasnain S (2005) Chromate reduction capability of a gram positive bacterium isolated from effluent of dying industry. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:699–706
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Thacker U, Parikh R, Shouche Y, Madamwar D (2007) Reduction of chromate by cell-free extract of Brucella sp. isolated from Cr (VI) contaminated sites. Bioresour Technol 98:1541–1547
Thompson MR, Ver Berkmoes NC, Chourey K, Shah M, Thompson DK, Hettich RL (2007) Dosage-dependent proteome response of Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 to acute chromate challenge. J Proteome Res 6:1745–1757
Zahoor A, Rehman A (2009) Isolation of Cr (VI) reducing bacteria from industrial effluents and their potential use in bioremediation of chromium containing wastewater. J Environ Sci 21:814–820
Zhang L, Liu C, Li D, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Zeng X, Yang Z, Li S (2013) Antioxidant activity of an exopolysaccharide isolated from Lactobacillus plantarum C88. Int J Biol Macromol 54:270–275
Zhou S, Dong L, Deng P, Jia Y, Bai Q, Gao J, Xiao H (2017) Reducing capacity and enzyme activity of chromate reductase in a ChrT-engineered strain. Exp Ther Med 14:2361–2366
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge SERB, Govt. of India, for financial support for developing instrumentation facilities. Financial assistance to the Centre of Excellence in Environment and Public Health by Higher Education Department of Government of Odisha under OHEPEE is also gratefully acknowledged (HE-PTC-WB-02017). We are very much thankful to the technical staffs of AIRF, JNU for SEM–EDX analysis and CIF, Institute of Life Sciences at Bhubaneswar, India for sequencing of genomic DNA.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Umesh Chandra Naik designed, wrote and reviewed the manuscript. Hrudananda Sahoo and Sushama Kumari executed the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All the authors were involved in the critical review on writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahoo, H., Kumari, S. & Naik, U.C. Characterization of multi-metal-resistant Serratia sp. GP01 for treatment of effluent from fertilizer industries. Arch Microbiol 203, 5425–5435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02523-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02523-z