Abstract
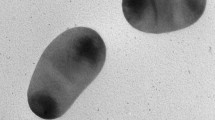
An obligate anaerobic bacterial BAD-10 T was isolated from anaerobic acetochlor-degrading sludge. The strain was Gram-stain negative, curved rod-shaped, non-motile and non-spore-forming. Growth was observed in PYT medium at pH 6.0–9.0 (optimum, pH 7.5), at 25–47 °C (37 °C) and with 0–1.0% NaCl (w/v, 0%). Strain BAD-10 T could degrade acetochlor. The major fermentation products from peptone-yeast (PY) medium were acetate and butyrate. The predominant cellular fatty acids were iso-C15:0 FAME, anteiso-C15:0 FAME and C16:0 FAME. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences revealed that the strain BAD-10 T showed closest affiliation to Proteiniclasticum ruminis D3RC-2 T, with a sequence similarity of 97.6%. Genome sequencing revealed a genome size of 2,983,986 bp, a G + C content of 51.4 mol% and protein-coding genes of 3,102. The average nucleotide identity and in silico DNA–DNA hybridization values between strain BAD-10 T and Proteiniclasticum ruminis D3RC-2 T were 71.0% and 20.4%, respectively, which were below the standard thresholds for species differentiation. On the basis of phenotypic, physiological and phylogenetic evidence, strain BAD-10 T represents a novel species in the genus Proteiniclasticum, for which the name Proteiniclasticum sediminis sp. nov. is proposed. Strain BAD-10 T (= CCTCC AB 2021091 T = KCTC 25288 T) is the type strain of the proposed novel species.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the 16S rRNA gene sequences and the whole genome of strain BAD-10 T are MW491274 and JAGSCS000000000, respectively.
References
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T et al (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75
Beveridge T, Lawrence J, Murray R (2007) Sampling and staining for light microscopy. Methods for general and molecular microbiology. American Society of Microbiology, Washington
Chen Q, Wang CH, Deng SK, Wu YD, Li Y, Yao L, Jiang JD, Yan X, He J, Li SP (2014) Novel three-component rieske non-heme iron oxygenase system catalyzing the N-dealkylation of chloroacetanilide herbicides in Sphingomonads DC-6 and DC-2. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:5078–5085
Cheng MG, Meng Q, Yang YJ, Chu CW, Chen Q, Li Y, Cheng D, Hong Q, Yan X, He J (2017) The two-component monooxygenase MeaXY initiates the downstream pathway of chloroacetanilide herbicide catabolism in Sphingomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:1–13
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, da Costa MS et al (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:461–466
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (2009) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fincker M, Spormann AM (2017) Biochemistry of catabolic reductive dehalogenation. Annu Rev Biochem 86:357–386
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Frank JA, Reich CI, Sharma S, Weisbaum JS, Olsen GJ (2008) Critical evaluation of two primers commonly used for amplification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2461–2470
Hildebrandt A, Guillamon M, Lacorte S, Tauler R, Barcelo D (2008) Impact of pesticides used in agriculture and vineyards to surface and groundwater quality (North Spain). Water Res 42:3315–3326
Hug LA, Maphosa F, Leys D et al (2013) Overview of organohalide-respiring bacteria and a proposal for a classification system for reductive dehalogenases. Philos Trans R Soc London 368:20120322
Kimura M (1980) Evolutionary rates models. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Lerro CC, Koutros S, Andreotti G, Hines CJ, Blair A, Lubin J, Ma X, Zhang Y, Beane FLE (2015) Use of acetochlor and cancer incidence in the agricultural health study (article). Int J Cancer 137:1167–1175
Liu JW, Zhang X, Xu JY, Qiu JG, Zhu JC, Cao H, He J (2020) Anaerobic biodegradation of acetochlor by acclimated sludge and its anaerobic catabolic pathway. Sci Total Environ 748:141122
Luo HF, Qi HY, Zhang HX (2004) The impact of acetochl or the bacterial diversity in soil. Acta Microbiol 44:519–522
Luo R, Liu B, Xie Y, Li Z, Huang W et al (2012) SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 1:18
Martin B, Cindy K, Jochen F, Torsten S, Gabriele D, Dobbek H (2014) Structural basis for organohalide respiration. Science 346:455–458
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Goeker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinf 14:60
Overbeek R, Olson R, Pusch GD, Olsen GJ, Davis JJ et al (2014) The SEED and the rapid annotation of microbial genomes using subsystems technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res 42:D206–D214
Richter M, Rossello-Mora R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. PNAS 106:19126–19131
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 24:189–204
Sambrook J, Fritsch E, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a Laboratory Manual, 3, 2nd edn. Cold Springs Harb Lab Press, New York
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc, Newark
Widdel F, Kohring G, Mayer F (1983) Studies on dissimilatory sulfate-reducing bacteria that decompose fatty acids-III. Characterization of the filamentous gliding Desulfonema limicola gen. nov. sp. nov., and Desulfonema magnum sp. nov. Arch Microbiol 134:286–294
Yan J, Ritalahti KM, Wagner DD, Lffler FE (2012) Unexpected specificity of interspecies cobamide transfer from Geobacter spp. to organohalide-respiring Dehalococcoides mccartyi strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:6630–6636
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286
Zhang KG, Song L, Dong XZ (2010) Proteiniclasticum ruminis gen. nov., sp. nov., a strictly anaerobic proteolytic bacterium isolated from yak rumen. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2221–2225
Zhang J, Zheng JW, Liang B, Wang CH, Cai S, Ni YY, He J, Li SP (2011) Biodegradation of chloroacetamide herbicides by Paracoccus sp. FLY-8 in vitro. J Agric Food Chem 59:4614–4621
Zhang X, Tu B, Dai LR, Lawson PA, Zheng ZZ, Liu LY, Deng Y, Zhang H, Cheng L (2018) Petroclostridium xylanilyticum gen. nov., sp nov., a xylan-degrading bacterium isolated from an oilfield, and reclassification of clostridial cluster III members into four novel genera in a new Hungateiclostridiaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:3197–3211
Funding
This work was supported by the Key research and development project of science and technology development plan of Jilin Province (20180201062NY).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, funding acquisition, and supervision: HW and JH; Laboratory work, data analysis and writing-original draft: JL; Writing-review and editing: YB, XZ, KZ and SC. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Bao, Y., Zhang, X. et al. Proteiniclasticum sediminis sp. nov., an obligate anaerobic bacterium isolated from anaerobic sludge. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 114, 1541–1549 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01620-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01620-9