Abstract
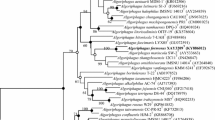
A bacterial strain, designated M625T, was isolated from the surface of a marine red alga. Phylogenetic trees were reconstructed based on the 16S rRNA gene and RpoB protein sequences, which indicated that the strain belongs to the genus Aquimarina within the family Flavobacteriaceae. Strain M625T showed high sequence similarities to A. aggregata RZW4-3-2 T (95.7%), A. seongsanensis CBA3208T (95.3%) and A. versatilis CBA3207T (95.0%). The AAI and POCP values between strain M625T and A. muelleri DSM 19832 T were 71.8% and 57.9% respectively. The dDDH and ANI values between strain M625T and A. aggregata were 19.5% and 74.6% respectively. The strain was Gram-stain negative, strictly aerobic, non-motile and long rod-shaped, and positive for hydrolysis of starch, cellulose, alginate, DNA and Tween 20. The dominant respiratory quinone was MK-6. The major fatty acids were iso-C15:0, iso-C17:0 3-OH, and iso-C15:1 G, and the polar lipids consisted of phosphatidylethanolamine, one unidentified phospholipid, two unidentified aminolipids, and seven unidentified lipids. Based on the polyphasic comparisons, strain M625T is proposed to represent a novel species within the genus Aquimarina, for which the name Aquimarina algicola sp. nov. (type strain M625T = MCCC 1H00399T = KCTC 72685 T) was proposed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auch AF, von Jan M, Klenk HP, Goker M (2010) Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand in Genomic Sci 2(1):117–134. https://doi.org/10.4056/sigs.531120
Bowman JP (2000) Description of Cellulophaga algicola sp. nov., isolated from the surfaces of Antarctic algae, and reclassification of Cytophaga uliginosa (ZoBell and Upham 1944) Reichenbach 1989 as Cellulophaga uliginosa comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1861–1868. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-50-5-1861
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR et al (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002516
Du ZJ, Wang Y, Dunlap C, Rooney AP, Chen GJ (2014) Draconibacterium orientale gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from two distinct marine environments, and proposal of Draconibacteriaceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1690–1696. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.056812-0
Fang DB, Han JR, Liu Y, Du ZJ (2017) Seonamhaeicola marinus sp. nov., isolated from marine algae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:4857–4861. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002396
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Hudson J, Kumar V, Egan S (2019) Comparative genome analysis provides novel insight into the interaction of Aquimarina sp. AD1, BL5 and AD10 with their macroalgal host. Mar Genomics 46:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2019.02.005
Jordan EM, Thompson FL, Zhang XH, Li Y, Vancanneyt M (2007) Sneathiella chinensis gen. nov., sp nov., a novel marine alphaproteobacterium isolated from coastal sediment in Qingdao. China Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64478-0
Kalitnik AA, Nedashkovskaya OI, Stenkova AM, Yermak IM, Kukhlevskiy AD (2018) Carrageenanolytic enzymes from marine bacteria associated with the red alga Tichocarpus crinitus. J Appl Phycol 30:2071–2081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1355-4
Kennedy J, Margassery LM, O’Leary ND, O’Gara F, Morrissey J, Dobson ADW (2014) Aquimarina amphilecti sp. nov., isolated from the sponge Amphilectus fucorum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:501–505. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.049650-0
Kroppenstedt RM (1982) Separation of bacterial menaquinones by HPLC using reverse phase (RP18) and a silver loaded ion exchanger as stationary phases. J Liq Chrom 5:2359–2367. https://doi.org/10.1080/01483918208067640
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Lee I, Chalita M, Ha S-M, Na S-I, Yoon S-H, Chun J (2017) ContEst16S: an algorithm that identifies contaminated prokaryotic genomes using 16S RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2053–2057. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001872
Li R, Zhu H, Ruan J, Qian W, Fang X, Shi Z, Li Y, Li S, Shan G, Kristiansen K, Li S, Yang H, Wang J, Wang J (2010) De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequencing. Genome Res 20:265–272. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.097261.109
Nedashkovskaya OI, Kim SB, Suzuki M, Shevchenko LS, Lee MS, Lee KH, Park MS, Frolova GM, Oh HW, Bae KS, Park HY, Mikhailov VV (2005) Pontibacter actiniarum gen nov., sp. Nov., a novel member of the phylum “Bacteroidetes”, and proposal of Reichenbachiella gen. nov. as a replacement for the illegitimate prokaryotic generic name Reichenbachia Nedashkovskaya et al 2003. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2583–2588. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63819-0
Park SC, Choe HN, Baik KS, Seong CN (2012) Aquimarina mytili sp. nov., isolated from the gut microflora of a mussel, Mytilus coruscus, and emended description of Aquimarina macrocephali. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1974–1979. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.032904-0
Qin QL, Xie BB, Zhang XY, Chen XL, Zhou BC, Zhou J, Oren A, Zhang YZ (2014) A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J Bacteriol 196:2210–2215. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01688-14
Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2014) Bypassing cultivation to identify bacterial species. Microbe 9:111–118. http://enve-omics.gatech.edu/sites/default/files/2014-Rodriguez_R-Konstantinidis_Microbe_Magazine.pdf
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki EP, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt KD, Borodovsky M, Ostell J (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 44:6614–6624. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar
Tindall BJ, Sikorski J, Smibert RA, Krieg NR (2007) Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics. In: Methods for General and Molecular Microbiology, 3rd Edition. Washington, DC: American Society for Microbiology; pp. 330–393. https://doi.org/10.1128/9781555817497.ch15
Wang Y, Ming H, Guo WY, Chen HL, Zhou CY (2016) Aquimarina aggregata sp nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:3406–3412. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001209
Wang NN, Zhou LY, Li YX, Du ZJ (2018b) Aquimarina sediminis sp. nov., isolated from coastal sediment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:2257–2265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1115-8
Wang NN, Sang J, Wang XQ, Li YX, Du ZJ (2018a) Primorskyibacter marinus sp nov., isolated from coastal sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68(10):3169–3174. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002959
Xu T, Yu M, Lin H, Zhang Z, Liu J, Zhang XH (2015) Genomic insight into Aquimarina longa SW024T: its ultra-oligotrophic adapting mechanisms and biogeochemical functions. BMC Genomics 16:772. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2005-3
Xu W, Chen XY, Wei XT, Lu DC, Du ZJ (2020) Polaribacter aquimarinus sp. nov., isolated from the surface of a marine red alga. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113:407–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01350-z
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Yu T, Zhang Z, Fan X, Shi X, Zhang XH (2014) Aquimarina megaterium sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:122–127. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.055517-0
Zhou YX, Wang C, Du ZJ, Chen GJ (2015) Aquimarina agarivorans sp. nov., a genome-sequenced member of the class Flavobacteriia isolated from Gelidium amansii. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:2684–2688. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.000323
Acknowledgements
This work of scanning electron microscope was supported by Physical-Chemical Materials Analytical & Testing Center of Shandong University at Weihai.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070002, 31770002) and National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (2019FY100700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XKS analyzed most of the data and wrote the manuscript. YLZ contributed to providing critical revisions to this article. XYC was responsible for collecting samples and isolating the novel microorganism. ZJD and GJC designed all the experiments and supervised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of Aquimarina algicola M625T is MN822655, and the draft genome has been deposited in GenBank under the accession number VFWZ00000000.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, XK., Zhong, YL., Chen, XY. et al. Aquimarina algicola sp. nov., isolated from the surface of a marine red alga. Arch Microbiol 203, 5397–5403 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02524-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02524-y