Abstract
This paper reports the hydrochemistry and activity concentration of the natural radionuclides 238U, 234U, and 210Po for three compartments of the hydrological/hydrogeological system in Araxá city, Minas Gerais State, Brazil: 1) mineral waters from the prominent springs Dona Beja (DBS) and Andrade Júnior (AJS), occurring at Barreiro area; 2) surface waters from Barreiro area and vicinity; and 3) rainwater. According to the Rule for Mineral Waters in Brazil (Register 7841) for temperature, the DBS water is cold (< 25 °C), while AJS is hypothermal (25–33 °C). The TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) concentration of DBS is low (70 mg/L), but high in AJS (2898 mg/L). The hydrogeochemical facies corresponded to sodium–(bi)carbonate for AJS and sodium/potassium–bicarbonate for DBS. The hydrochemical differences of DBS and AJS waters reflect the distinct characteristics of their respective aquifer systems. The DBS classification for TDS is the same of the Barreiro basin surface waters (mean TDS = 102 mg/L). Such value is somewhat higher than that of the rainwater and surface waters used for human consumption at Araxá city (TDS < 50 mg/L). The dataset reported in this paper indicated that fluoride and barium exceeded the WHO limits proposed in 2011 for drinking water. Among the natural radionuclides analyzed here that offer potential hazards for the human health is 210Po, whose WHO’s limiting value of 100 mBq/L in drinking water was exceeded in rainwater, thus, restricting the use of this resource as a possible supply of drinking water for the local community.


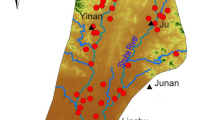
adapted from FUNTEC (1984). In the bottom are more details of Barreiro area







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The author declares that all available data are reported in this paper.
References
Alvarez, J. A., Rezende, K. M. P. C., Marocho, S. M. S., Alves, F. B. T., Celiberti, P., & Ciamponi, A. L. (2009). Dental fluorosis: exposure, prevention and management. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Dentistry, 1(1), e14-18.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2004). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Balkema.
Baran, A., & Tarnawski, M. (2015). Assessment of heavy metals mobility and toxicity in contaminated sediments by sequential extrac-tion and a battery of bioassays. Ecotoxicology, 24(6), 1279–1293.
Baskaran, M. (2012). Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. Springer.
Beato, D. A. C., Viana, H. S., & Davis, E. G. (2000). Evaluation and hydrogeological diagnosis of mineral waters aquifers from Barreiro, Araxá, MG, Brazil. In ABAS (Brazilian Association of Groundwater) (Ed.), Proc. I Joint World Congress on Groundwater (pp 1–20). Fortaleza: ABAS.
Bhardwaj, V., & Singh, D. S. (2011). Surface and groundwater quality characterization of Deoria district, Ganga plain, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 63, 383–395.
Birke, M., Rauch, U., & Lorenz, H. (2009). Uranium in stream and mineral water of the Federal Republic of Germany. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 31(6), 693–706.
Birke, M., Rauch, U., Lorenz, H., & Kringel, R. (2010). Distribution of uranium in German bottled and tap water. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 107, 272–282.
Bonotto, D. M. (2006). Hydro(radio)chemical relationships in the giant Guarani aquifer, Brazil. Journal of Hydrology, 323, 353–386.
Bonotto, D. M. (2010). The Poços de Caldas Hot Spot: A Big Blast for Nuclear Energy in Brazil. Nova Science.
Bonotto, D. M., Caprioglio, L., Bueno, T. O., & Lazarindo, J. R. (2009). Dissolved 210Po and 210Pb in Guarani aquifer groundwater, Brazil. Radiation Measurements, 44, 311–324.
Bonotto, D. M., & Silveira, E. G. (2003). Preference ratios for mercury and other chemical elements in the Madeira river, Brazil. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 15, 911–923.
Bonotto, D. M., & Thomazini, F. O. (2019). Comparative study of mineral and surface waters of Araxá spa, Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78, 542.
Braga, J. R. K., & Born, H. (1988). Geological and mineralogical characteristics of the apatite mineralization at Araxá. In SBG (Brazilian Society of Geology) (Ed.), Proc. XXXV Brazilian Congress of Geology (pp 219–226). Belém: SBG.
Castro, L. O., & Souza, J. M. (1970). Study of uranium and rare earths associated to niobium from Araxá – MG. Belo Horizonte: IPR (Institute for Researches in Radioactivity).
Chubaka, C. E., Ross, K. E., & Edwards, J. W. (2017). Rainwater for drinking water: a study of household attitudes. WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment, 216, 299–311.
CPRM (Brazilian Geological Survey) (2012). The Brazilian industry of mineral waters. http://www.cprm.gov.br/. Accessed 20 February 2018.
Cresswell, R. G., & Bonotto, D. M. (2008). Some possible evolutionary scenarios suggested by 36Cl measurements in Guarani aquifer groundwaters. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 66, 1160–1174.
Custodio, E. G., & LLamas, M. R. (1976). Underground hydrology. Omega.
DFPM (Division for Supporting the Mineral Production). (1966). The mining code, the mineral waters code and how applying research in a mineral deposit. DFPM.
DiBello, P. M., Manganaro, J. L., & Aguinaldo, E. R. (1991). Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology: Barium compounds. John Wiley and Sons.
DNPM (National Department of Mineral Production) (1987). Major mineral deposits of Brazil. Brasília: DNPM.
Dreesen, D. R., Williams, J. M., Marple, M. L., Gladney, E. S., & Perrin, D. R. (1982). Mobility and bioavailability of uranium mill tailings contaminants. Environmental Science Technology, 16, 702–709.
Edmunds, W. M., & Smedley, P. L., et al. (2013). Fluoride in natural waters. In O. Selinus, B. Alloway, J. A. Centeno, R. B. Finkelman, R. Fuge, & U. Lindh (Eds.), Essentials of Medical Geology (pp. 311–336). Springer.
Fernandes, F. R. C., Enriquez, M. A., & Alamino, R. C. J. (2011). Mineral resources & territorial sustainability. CETEM/MCTI.
Fordyce, F. M., Vrana, K., Zhovinsky, E., Povoroznuk, V., Toth, G., Hope, B. C., et al. (2007). A health risk assessment for fluoride in Central Europe. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 29, 83–102.
Fritz, P., & Fontes, J. C. (1980). Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. Elsevier.
FUNTEC (Minas Gerais Technological Center Foundation) (1984). Ecological conflict diagnosis report including recommended works and measures for mitigation of the ecological impact due to mining. Technical Report. Araxá: ECOS–Geology Consulting and Services Ltd.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science, 170, 1088–1090.
Gibson, S. A., Thompson, R. N., Leonardos, O. K., Dickin, A. P., & Mitchell, J. G. (1995). The late cretaceous impact of the Trindade mantle plume - evidence from large-volume, mafic, potassic magmatism in SE Brazil. Journal of Petrology, 36, 189–229.
Gomes, C. B., & Comin-Chiaramonti, P. (2005). Some notes on the Alto Paranaíba Igneous Province. In P. Comin-Chiaramonti, & C. B. Gomes (Eds.), Mesozoic to Cenozoic Alkaline Magmatism in the Brazilian Platform (pp 317–340). São Paulo: EDUSP.
Hach (1992). Water Analysis Handbook. Loveland: Hach Co.
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters. U.S.G.S. Water-Supply Paper, 2254.
Waterloo Hydrogeologic (2003). AquaChem User´s Manual: Water Quality Data Analysis, Plotting & Modeling. Waterloo: Waterloo Hydrogeologic.
Issa Filho, A., Lima, P. R. A. S., & Souza, O. M. (1984). Geological aspects of Barreiro carbonatite complex, Araxá, MG, Brasil. In C. S. Rodrigues, & P. R. A. S. Lima (Eds.), Carbonatite complexes in Brazil: Geology (pp 20–44). São Paulo: CBMM.
Ivanovich, M., & Harmon, R. S. (1992). Uranium Series Disequilibrium: Applications to Environmental Problems. Clarendon Press.
Jacks, G. (1973). Chemistry of groundwater in a district in Southern India. Journal of Hydrology, 18, 185–200.
Khayan, K., Husodo, A. H., Astuti, I., Sudarmadji, S., & Djohan, T. S. (2019). Rainwater as a source of drinking water: health impacts and rainwater treatment. Journal of Environmental Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1760950
Kumar, M., Kumari, K., Singh, U. K., & Ramanathan, A. (2009). Hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Muktsar, Punjab: conventional graphical and multivariate statistical approach. Environmental Geology, 57, 873–884.
Kumar, P. J. S. (2014). Evolution of groundwater chemistry in and around Vaniyambadi industrial area: differentiating the natural and anthropogenic sources of contamination. Chemie Der Erde, 74, 641–651.
Lemos Jr, M. A. (2012). Studies for evaluating the capacity of the niobium wastes reservoir. M.Sc. Dissertation. Ouro Preto: School of Mines, Federal University of Ouro Preto.
Lokhande, P. B., & Mujawar, H. A. (2016). Graphic interpretation and assessment of water quality in the Savitri River basin. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 7(3), 1113–1123.
Lyerly, P. J., & Longenecker, D. E. (1957). Salinity control in irrigation and agriculture. Texas Agricultural Extension Service Bulletins, 876, 1–20.
Magalhães, M. C. (1945). The spa of Araxá. Buenos Aires: Medical Association of Argentina.
Manassaram, D. M., Backer, L. C., & Moll, D. M. (2006). A review of nitrates in drinking water: maternal exposure and adverse reproductive and developmental outcomes. Environmental Health Perspective, 114, 320–327.
Marandi, A., & Shand, P. (2018). Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs diagram. Applied Geochemistry, 97, 209–212.
Mirabbasi, R., Mazloumzadeh, S. M., & Rahnama, M. B. (2008). Evaluation of irrigation water quality using Fuzzy Logic. Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2, 340–352.
Mourão, B. M. (1992). Hydrological medicine – modern therapy of mineral waters and healing spas. Poços de Caldas: Municipal Secretary of Education.
Okiongbo, K. S., & Akpofure, E. (2014). Identification of hydrogeochemical processes in groundwater using major ion chemistry: a case study of Yenagoa and environs, southern Nigeria. Global Journal of Geological Sciences, 12, 39–52.
Osmond, J. K., & Cowart, J. B. (1976). The theory and uses of natural uranium isotopic variations in hydrology. Atomic Energy Review, 14, 621–679.
Pinto, C. L. L., Dutra, J. I. G., Salum, M. J. G., Ganine, J. F., & Oliveira, M. S. (2011). Study case: Major center producing phosphate and niobium in the country. In F. R. C. Fernandes, M. A. Enriquez, & R. C. J. Alamino (Eds.), Mineral resources & territorial sustainability (pp. 283–305). CETEM/MCTI.
Piper, A. M. A. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Transactions of the American Geophysical Union, 25, 914–928.
Rajesh, R., Brindha, K., Murugan, R., & Elango, L. (2012). Influence of hydrogeochemical processes on temporal changes in groundwater quality in a part of Nalgonda district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 65, 1203–1213.
Reddy, D. V., Nagabhushanam, P., Sukhija, B. S., Reddy, A. G. S., & Smedley, P. (2010). Fluoride dynamics in the granitic aquifer of the Wailapally watershed, Nalgonda District, India. Chemical Geology, 269, 278–289.
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (1998). Chemical elements in the environment: Factsheets for the geochemist and environmental scientist. Springer-Verlag.
Rice, E. W., Baird, R. B., Eaton, A. D., & Clesceri, L. S. (2012). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation.
Ritter, S. M. (2012). Geothermometry on natural spring waters from Poços de Caldas, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Monograph (pp 1–56). Heidelberg: University of Heidelberg.
Santos, M. S., Carneiro, L. G., Medeiros, G., Sampaio, C., Martorell, A. B.T., Gouvea, S., et al. (2011). PIXE analyses applied to characterize water samples. In ABEN (Brazilian Association of Nuclear Energy) (Ed.), Proc. International Nuclear Atlantic Conference – INAC (pp 1–6). Belo Horizonte: ABEN.
Schoeller, H. (1962). Groundwaters. Masson & Cie.
SEBRAE (Service for Supporting the Small Businesses in São Paulo State) (2012). Mineral waters business. http://www.sebrae-sc.com.br/ideais/default.asp?vcdtexto= 31586&%5E%5E. Accessed 20 February 2018.
Serra, S. H. (2009). Mineral waters from Brazil. Campinas: Millenium Editora.
Smedley, P. L., Nicolli, H. B., Macdonald, D. M. J., Barros, A. J., & Tullio, J. O. (2002). Hydrogeochemistry of arsenic and other inorganic constituents in groundwaters from La Pampa, Argentina. Applied Geochemistry, 17, 259–284.
Stallard, R. F., & Edmond, J. M. (1983). Geochemistry of the Amazon: 2. The influence of geology and weathering environment on the dissolved load. Journal of Geophysical Research, 88, 9671–9688.
Traversa, G., Gomes, C. B., Brotzu, P., Buraglini, N., Morbidelli, L., Principato, M. S., et al. (2001). Petrography and mineral chemistry of carbonatites and mica-rich rocks from the Araxá complex (Alto Paranaíba Province, Brazil). Anais Da Academia Brasileira De Ciências, 73, 71–98.
USGS (U. S. Geological Survey) (2018). Mineral Resources On-Line Spatial Data: Araxá. https://mrdata.usgs.gov/mrds/show-mrds.php?dep_id=10068132. Accessed 29 January 2018.
USSL (U.S. Salinity Laboratory Staff) 1954. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Handbook No. 60, U. S. Department of Agriculture.
van de Wiel, H. J. (2003). Determination of elements by ICP-AES and ICP-MS. Bilthoven, The Netherlands: National Institute of Public Health and the Environment (RIVM).
van der Aa, M. (2003). Classification of mineral water types and comparison with drinking water standards. Environmental Geology, 44, 554–563.
van Wirdum, G. (1991). Vegetation and hydrology of floating rich-fens. PhD Thesis. Amsterdam: University of Amsterdam.
Viana, H. S., Davis, E. G., Beato, D. A. C., & Cabral, J. A. L. (1999). Araxá Project: geoenvironmental study of mineral springs. Belo Horizonte: CPRM (Brazilian Geological Survey).
Wanda, E., Monjerezi, M., Mwatseteza, J. F., & Kazembe, L. N. (2011). Hydrogeochemical appraisal of groundwater quality from weathered basement aquifers in Northern Malawi. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/b/c, 36, 1197–1207.
Wasserstein, R. L., & Lazar, N. A. (2016). The ASA’s statement on p-values: context, process, and purpose. The American Statistician, 70(2), 129–133.
WHO (World Health Organization). (2011). Guidelines for drinking water quality. WHO Press.
Wilcox, L. V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation waters. USDA Circular No. 969, U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Young, H. D. (1962). Statistical treatment of experimental data. McGraw Hill.
Acknowledgements
Three anonymous reviewers are greatly thanked for helpful comments that improved the readability of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Brazilian agencies CNPq-Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (Grants 400700/2016–6 and 301992/2016–9) and FAPESP- Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (Grants 2014/50945–4 and 2018/25332–0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This is an observational study that did not involve human participants or biological materials, thus, not requiring ethical approval of the Research Ethics Committee of the authors' institution.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonotto, D.M. Hydrochemical and radiometric evaluation of fresh and thermal waters from Araxá city (Minas Gerais, Brazil). Environ Geochem Health 44, 2163–2186 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01058-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01058-y