Abstract
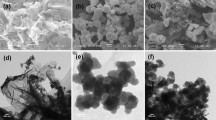
An electrochemical sensor constructed by intercalated composites was developed for determination of heavy metal ions. The intercalated composites were composed of hydrosulphonyl functional covalent organic frameworks (COF-SH) and graphene (G). The presence of numerous adsorption sites, such as 18 sulfur atoms and 30 nitrogen atoms per big circle of COFs on COF-SH, was beneficial for the accumulation of heavy metals, while the graphene enhanced the electrical conductivity. The obtained sensor under the optimal conditions successfully detected the presence of heavy metal ions in coastal water samples at concentrations ranging from 1 to 1000 μg L−1. The detection limits of Cd (II), Pb (II), Cu (II), and Hg (II) were 0.3, 0.2, 0.2, and 1.1 μg L−1, respectively. Furthermore, the sensor still exhibited good stability after multiple uses less than 5%. When it is used in the analysis of actual samples, the recovery of standard addition is higher than 95%. In sum, the combination of hydrosulphonyl functional COFs with graphene looks very promising for the assembly of sensors with high sensitivity toward the determination of heavy metal ions for coastal environmental monitoring.
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Awual R, Hasan M, Islam A, Rahman MM, Asiri AM, Khaleque A, Sheikh C (2019) Offering an innovative composited material for effective lead (II) monitoring and removal from polluted water. J Clean Prod 231:214–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.125
Gaulier C, Zhou C, Guo W, Bratkic A, Superville P, Billon G, Baeyens W, Gao Y (2019) Trace metal speciation in North Sea coastal waters. Sci Total Environ 692:701–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.314
Sun Z, Liu Y, Srinivasakannan C (2020) One-pot fabrication of rod-like magnesium silicate and its adsorption for Cd2+. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104380
Horak F, Nagl A, Föttinger K, Limbeck A (2020) Application of micro-dried droplets for quantitative analysis of particulate inorganic samples with LA-ICP-MS demonstrated on surface-modified nanoparticle TiO2 catalyst materials. Microchim Acta 187:641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04609-9
Huang Y, Zhang S, Chen Y, Wang L, Long Z, Hughes SS, Ni S, Cheng X, Wang J, Li T, Wang R, Liu C (2020) Tracing Pb and possible correlated Cd contamination in soils by using lead isotopic compositions. J Hazard Mater 385:121528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121528
Pan DW, Wang Y, Chen Z, Lou T, Qin W (2009) Nanomaterial/ionophore-based electrode for anodic stripping voltammetric determination of lead: an electrochemical sensing platform toward heavy metals. Anal Chem 81:5088–5094. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac900417e
Schroeder V, Savagatrup S, He M, Lin S, Swager TM (2019) Carbon nanotube chemical sensors. Chem Rev 119:599–663. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00340
Tesarova E, Baldrianova L, Hocevar SB, Svancara I, Vytras K, Ogorevc B (2009) Anodic stripping voltammetric measurement of trace heavy metals at antimony film carbon paste electrode. Electrochim Acta 54:1506–1510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2008.09.030
Nehru R, Hsu YF, Wang SF, Dong CD, Govindasamy M, Habila MA, AlMasoud N (2021) Graphene oxide@Ce-doped TiO2 nanoparticles as electrocatalyst materials for voltammetric detection of hazardous methyl parathion. Microchim Acta 188:216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04847-5
Jiao Z, Zhang P, Chen H, Li C, Chen L, Fan H (2019) Differentiation of heavy metal ions by fluorescent quantum dot sensor array in complicated samples. Sensors Actuators B Chem 295:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.05.059
Canossa S, Wuttke S (2020) Functionalization chemistry of porous materials. Adv Funct Mater 30:2003875. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202003875
Li G, Ye J, Fang QR, Liu F (2019) Amide-based covalent organic frameworks materials for efficient and recyclable removal of heavy metal lead (II). Chem Eng J 370:822–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.260
Shi R, Liu L, Lu Y, Wang C, Li Y, Li L, Yan Z, Chen J (2020) Nitrogen-rich covalent organic frameworks with multiple carbonyls for high-performance sodium batteries. Nat Commun 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13739-5
Calik M, Auras F, Salonen LM, Bader K, Grill I, Handloser M, Medina DD, Dogru M, Löbermann F, Trauner D, Hartschuh A, Bein T (2014) Extraction of photogenerated electrons and holes from a covalent organic framework integrated heterojunction. J Am Chem Soc 136:17802–17807. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja509551m
Han X, Xia Q, Huang J, Liu Y, Tan C, Cui Y (2017) Chiral covalent organic frameworks with high chemical stability for heterogeneous asymmetric catalysis. J Am Chem Soc 139:8693–8697. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b04008
Li Y, Chen M, Han Y, Feng Y, Zhang Z, Zhang B (2020) Fabrication of a new corrole-based covalent organic framework as a highly efficient and selective chemosensor for heavy metal ions. Chem Mater 32:2532–2540. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b05234
Shinde DB, Cao L, Wonanke ADD, Li X, Kumar S, Liu X, Hedhili MN, Emwas AH, Addicoat M, Huang KW, Lai Z (2020) Pore engineering of ultrathin covalent organic framework membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration and molecular sieving. Chem Sci 11:5434–5440. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0sc01679a
Segura JL, Royuela S, Ramos MM (2019) Post-synthetic modification of covalent organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 48:3903–3945. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CS00978C
Shang W, Sheng Z, Shen Y, Ai B, Zheng L (2016) Study on oil absorbency of succinic anhydride modified banana cellulose in ionic liquid. Carbohydr Polym 141:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.01.009
Kim T, Lee TK, Kim BS, Park SC, Lee S, Im SS, Bisquert J, Kang YS (2017) Triumphing over charge transfer limitations of PEDOT nanofiber reduction catalyst by 1,2-ethanedithiol doping for quantum dot solar cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:1877–1884. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12536
Ma X, Wu Z, Zhou M, Ding J (2013) Electrochemical scission of C – S bond in ethanethiol on a modified b -PbO2 anode in aqueous solution. Sep Purif Technol 109:72–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.02.030
Heidari M, Ghanemi K, Nikpour Y (2020) Applying Al2O3@Ag@trithiocyanuric acid as an efficient metal ion scavenger for the selective extraction of iron (III) and lead (II) from environmental waters. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 203:110995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110995
Osaka N, Ishitsuka M, Hiaki T (2009) Infrared reflection absorption spectroscopic study of adsorption structure of self-assembled monolayer film of trithiocyanuric acid on evaporated silver film. J Mol Struct 921:144–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.12.051
Deng Y, Zhang Z, Du PY, Ning XM, Wang Y, Zhang DX, Liu J, Zhang ST, Lu XQ (2020) Bridging ultrasmall Au clusters into the pores of a covalent organic framework for enhanced photostability and photocatalytic performance. Angew Chem Int Ed 59:6082–6089
Wang LY, Yang YX, Liang HH, Wu N, Peng X, Wang L, Song YH (2021) A novel N, S-rich COF and its derived hollow N, S-doped carbon@Pd nanorods for electrochemical detection of Hg2+ and paracetamol. J Hazard Mater 409:124528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124528
Wang N, Zhao W, Shen ZY, Sun SJ, Dai HX, Ma HY, Lin M (2020) Sensitive and selective detection of Pb (II) and Cu (II) using a metal-organic framework/polypyrrole nanocomposite functionalized electrode. Sensor Actuat B-chem 304:127286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127286
Han J, Yu J, Guo Y, Wang L, Song Y (2020) COFBTLP-1/three-dimensional macroporous carbon electrode for simultaneous electrochemical detection of Cd2+, Pb2+, Cu2+ and Hg2+. Sensors Actuators B Chem 321:128498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128498
Zhang T, Gao CW, Huang W, Chen YL, Wang Y, Wang JM (2018) Covalent organic framework as a novel electrochemical platform for highly sensitive and stable detection of lead. Talanta 188:578–583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.06.032
Funding
This work was supported by the Basic Research Fund for Central Universities (531118010314), the Environmental Protection Science and Technology Project of Hunan Province (20190011), the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFD0901103), the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB42000000), and the Key R & D Program of Hunan Province (2019SK2281).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Fei Pan and Chunyi Tong are the first author.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1064 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, ., Tong, ., Wang, Z. et al. Nanocomposite based on graphene and intercalated covalent organic frameworks with hydrosulphonyl groups for electrochemical determination of heavy metal ions. Microchim Acta 188, 295 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04956-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04956-1