Abstract
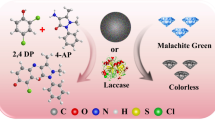
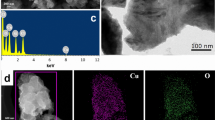
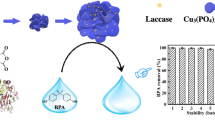
Seeking simple, green, and inexpensive preparation methods and materials of enzyme mimics has always been highly desirable. In this paper, a nanocomposite with laccase activity was successfully fabricated by using a simple self-association method with copper and tannic acid. Characterizations through SEM, XRD, FTIR, and XPS showed that the Cu-TA hybrid composites had good spherical in shape with a diameter of about 20 nm and three different valence Cu ions (Cu2+, Cu+, and Cu0). The catalytic activity was displayed against typical oxidation substrate of laccases, 2,4-DP. Compared to natural laccases, Cu-TA composites were able to better tolerate changes of pH, temperature, ionic strength, and storage conditions. The Cu-TA composites could remove malachite green (MG) from aqueous solutions effectively. The removal efficiency of MG was optimized using a series of batch tests with single-factor experiment design. Under the optimum conditions, the removal efficiency of MG still retained about 90% after 3 times cycles. Therefore, the Cu-TA composites, as a laccases-like nanozyme, have excellent developing potential in wastewater treatment due to the low-cost of TA and simplicity of preparation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chaurasia PK, Bharati SL, Sarma C (2016) Laccases in pharmaceutical chemistry: a comprehensive appraisal. Mini-Rev Org Chem 13:430–451
Kudanga T, Nemadziva B, Le Roes-Hill M (2017) Laccase catalysis for the synthesis of bioactive compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:13–33
Mohit E, Tabarzad M, Faramarzi MA (2020) Biomedical and pharmaceutical-related applications of laccases. Curr Protein Pept Sci 21:78–98
Sun T, Fu M, Xing J, Ge Z (2020) Magnetic nanoparticles encapsulated laccase nanoflowers: evaluation of enzymatic activity and reusability for degradation of malachite green. Water Sci Technol 81:29–39
Timur S, Pazarlioglu N, Pilloton R, Telefoncu A (2004) Thick film sensors based on laccases from different sources immobilized in polyaniline matrix. Sensors Actuators B Chem 97:132–136
Martinez AT, Ruiz-Duenas FJ, Camarero S, Serrano A, Linde D, Lund H, Vind J, Tovborg M, Herold-Majumdar OM, Hofrichter M, Liers C, Ullrich R, Scheibner K, Sannia G, Piscitelli A, Pezzella C, Sener ME, Kilic S, van Berkel WJH, Guallar V, Lucas MF, Zuhse R, Ludwig R, Hollmann F, Fernandez-Fueyo E, Record E, Faulds CB, Tortajada M, Winckelmann I, Rasmussen J-A, Gelo-Pujic M, Gutierre A, del Rio JC, Rencoret J, Alcalde M (2017) Oxidoreductases on their way to industrial biotransformations. Biotechnol Adv 35:815–831
Yang J, Li W, Ng TB, Deng X, Lin J, Ye X (2017) Laccases: production, expression regulation, and applications in pharmaceutical biodegradation. Front Microbiol 8
Liang H, Lin F, Zhang Z, Liu B, Jiang S, Yuan Q, Liu J (2017) Multicopper laccase mimicking nanozymes with nucleotides as ligands. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:1352–1360
Zhang S, Lin F, Yuan Q, Liu J, Li Y, Liang H (2020) Robust magnetic laccase-mimicking nanozyme for oxidizing o-phenylenediamine and removing phenolic pollutants. J Environ Sci 88:103–111
Wang J, Huang R, Qi W, Su R, Binks BP, He Z (2019) Construction of a bioinspired laccase-mimicking nanozyme for the degradation and detection of phenolic pollutants. Appl Catal B Environ 254:452–462
Ren X, Liu J, Ren J, Tang F, Meng X (2015) One-pot synthesis of active copper-containing carbon dots with laccase-like activities. Nanoscale 7:19641–19646
Bulgariu L, Belen Escudero L, Bello OS, Iqbal M, Nisar J, Adegoke KA, Alakhras F, Kornaros M, Anastopoulos I (2019) The utilization of leaf-based adsorbents for dyes removal: A review. J Mol Liq 276:728–747
Mall ID, Srivastava VC, Agarwal NK, Mishra IM (2005) Adsorptive removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution by bagasse fly ash and activated carbon-kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 264:17–28
Shang N, Ding M, Dai M, Si H, Li S, Zhao G (2019) Biodegradation of malachite green by an endophytic bacterium Klebsiella aerogenes S27 involving a novel oxidoreductase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:2141–2153
Thung W-E, Ong S-A, Ho L-N, Wong Y-S, Ridwan F, Lehl HK, Oon Y-L, Oon Y-S (2018) Biodegradation of Acid Orange 7 in a combined anaerobic-aerobic up-flow membrane-less microbial fuel cell: mechanism of biodegradation and electron transfer. Chem Eng J 336:397–405
Siroosi M, Amoozegar MA, Khajeh K, Dabirmanesh B (2018) Decolorization of dyes by a novel sodium azide-resistant spore laccase from a halotolerant bacterium, Bacillus safensis sp strain S31. Water Sci Technol 77:2867–2875
Zhang X, Wang M, Lin L, Xiao G, Tang Z, Zhu X (2018) Synthesis of novel laccase-biotitania biocatalysts for malachite green decolorization. J Biosci Bioeng 126:69–77
Li C, Lou Y, Wan Y, Wang W, Yao J, Zhang B (2013) Laccase immobilized onto poly(GMA-MAA) microspheres for p-benzenediol removal from wastewater. Water Sci Technol 67:2287–2293
Khan NS, Ahmad A, Hadi SM (2000) Anti-oxidant, pro-oxidant properties of tannic acid and its binding to DNA. Chem Biol Interact 125:177–189
Shin M, Kim K, Shim W, Yang JW, Lee H (2016) Tannic Acid as a Degradable Mucoadhesive Compound. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2:687–696
Guo J, Ping Y, Ejima H, Alt K, Meissner M, Richardson JJ, Yan Y, Peter K, von Elverfeldt D, Hagemeyer CE, Caruso F (2014) Engineering multifunctional capsules through the assembly of metal-phenolic networks. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 53:5546–5551
Sileika TS, Barrett DG, Zhang R, Lau KHA, Messersmith PB (2013) Colorless multifunctional coatings inspired by polyphenols found in tea, chocolate, and wine. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 52:10766–10770
Cakar S, Ozacar M (2019) The pH dependent tannic acid and Fe-tannic acid complex dye for dye sensitized solar cell applications. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology a-Chemistry 371:282–291
Rahim MA, Ejima H, Cho KL, Kempe K, Muellner M, Best JP, Caruso F (2014) Coordination-driven multistep assembly of metal-polyphenol films and capsules. Chem Mater 26:1645–1653
Tinoco R, Pickard MA, Vazquez-Duhalt R (2001) Kinetic differences of purified laccases from six Pleurotus ostreatus strains. Lett Appl Microbiol 32:331–335
Li H, Hou J, Duan L, Ji C, Zhang Y, Chen V (2017) Graphene oxide-enzyme hybrid nanoflowers for efficient water soluble dye removal. J Hazard Mater 338:93–101
Nam S, Easson MW, Condon BD, Hillyer MB, Sun L, Xia Z, Nagarajan R (2019) A reinforced thermal barrier coat of a Na-tannic acid complex from the view of thermal kinetics. RSC Adv 9:10914–10926
Nguyen LN, Hai FI, Price WE, Leusch FDL, Roddick F, McAdam EJ, Magram SF, Nghiem LD (2014) Continuous biotransformation of bisphenol A and diclofenac by laccase in an enzymatic membrane reactor. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 95:25–32
Canas AI, Camarero S (2010) Laccases and their natural mediators: Biotechnological tools for sustainable eco-friendly processes. Biotechnol Adv 28:694–705
Li YM, Miao X, Wei ZG, Cui J, Li SY, Han RM, Zhang Y, Wei W (2016) Iron-Tannic acid nanocomplexes: facile synthesis and application for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 11:1045–1061
Ghigo G, Berto S, Minella M, Vione D, Alladio E, Nurchi VM, Lachowicz J, Daniele PG (2018) New insights into the protogenic and spectroscopic properties of commercial tannic acid: the role of gallic acid impurities. New J Chem 42:7703–7712
Chen J, Leng J, Yang X, Liao L, Liu L, Xiao A (2017) Enhanced performance of magnetic graphene oxide-immobilized laccase and its application for the decolorization of dyes. Molecules 22
Wu J, Deng X, Tian B, Wang L, Xie B (2008) Interactions between oat beta-glucan and calcofluor characterized by spectroscopic method. J Agric Food Chem 56:1131–1137
Shan Z, Lu M, Wang L, MacDonald B, MacInnis J, Mkandawire M, Zhang X, Oakes KD (2016) Chloride accelerated Fenton chemistry for the ultrasensitive and selective colorimetric detection of copper. Chem Commun 52:2087–2090
Wang L, Miao Y, Lu M, Shan Z, Lu S, Hou J, Yang Q, Liang X, Zhou T, Curry D, Oakes K, Zhang X (2017) Chloride-accelerated Cu-Fenton chemistry for biofilm removal. Chem Commun 53:5862–5865
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Disclaimer
The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Z., Wu, B., Sun, T. et al. Laccase-like nanozymes fabricated by copper and tannic acid for removing malachite green from aqueous solution. Colloid Polym Sci 299, 1533–1542 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04867-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-021-04867-w