Abstract
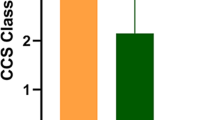
Coronary sinus Reducer (CSR) implantation is currently recommended to relieve angina in patients with refractory symptoms despite optimal medical therapy and maximally achievable revascularization. The impact of diabetes mellitus on outcome after CSR implantation is at present unknown. We aimed to explore the impact of CSR in refractory angina patients with diabetes mellitus. Data from consecutive patients undergoing CSR implantation at four different centres between 2014 and 2018 were included. Patients were divided according to the presence or absence of diabetes mellitus. Primary objective of this analysis was to evaluate the clinical response to CSR implantation defined as an improvement of ≥ 1 classes of the Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS) Classification. A total of 219 patients were included, 116 (53%) of whom had diabetes mellitus. The median age of the population was 69 years and 167 patients (76%) were male. There were no significant differences between groups of patients with and without diabetes mellitus with respect to CCS class at baseline (p value = 0.32) and at follow-up (p = 0.75). Over a median follow-up of 393 [224–1004] days, 84 (72%) of the patients with diabetes mellitus met the primary outcome, similarly to those without diabetes mellitus (p = 0.28). Fifty-three patients (24%) did not have an improvement in CCS class and no one experienced worsening of angina. CSR implantation was equally effective in improving angina symptoms among patients with refractory angina and diabetes mellitus compared to patients without diabetes mellitus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold SV, Morrow DA, Lei Y, Cohen DJ, Mahoney EM, Braunwald E, Chan PS (2009) Economic impact of angina after an acute coronary syndrome: insights from the MERLIN-TIMI 36 trial. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2(4):344–353
Verheye S, Jolicœur EM, Behan MW, Pettersson T, Sainsbury P, Hill J, Vrolix M, Agostoni P, Engstrom T, Labinaz M, de Silva R, Schwartz M, Meyten N, Uren NG, Doucet S, Tanguay JF, Lindsay S, Henry TD, White CJ, Edelman ER, Banai S (2015) Efficacy of a device to narrow the coronary sinus in refractory angina. N Engl J Med 372(6):519–527
Banai S, Ben Muvhar S, Parikh KH, Medina A, Sievert H, Seth A, Tsehori J, Paz Y, Sheinfeld A, Keren G (2007) Coronary sinus reducer stent for the treatment of chronic refractory angina pectoris: a prospective, open-label, multicenter, safety feasibility first-in-man study. J Am Coll Cardiol 49(17):1783–1789
Knuuti J, Wijns W, Saraste A, Capodanno D, Barbato E, Funck-Brentano C, Prescott E, Storey RF, Deaton C, Cuisset T, Agewall S, Dickstein K, Edvardsen T, Escaned J, Gersh BJ, Svitil P, Gilard M, Hasdai D, Hatala R, Mahfoud F, Masip J, Munaretto C, Valgimigli M, Achenbach S, Bax JJ, ESC Scientific Document Group (2019) ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J 41(3):407–477
Ielasi A, Todaro MC, Grigis G, Tespili M (2016) Coronary Sinus Reducer systemTM: a new therapeutic option in refractory angina patients unsuitable for revascularization. Int J Cardiol 209:122–130
Giannini F, Baldetti L, Ielasi A, Ruparelia N, Ponticelli F, Latib A, Mitomo S, Esposito A, Palmisano A, Chieffo A, Colombo A (2017) First experience with the coronary sinus reducer system for the management of refractory angina in patients without obstructive coronary artery disease. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 10(18):1901–1903
Picchi A, Capobianco S, Qiu T, Focardi M, Zou X, Cao JM, Zhang C (2010) Coronary microvascular dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: a review. World J Cardiol 2(11):377–390
D’Amico G, Giannini F, Massussi M, Tebaldi M, Cafaro A, Ielasi A, Sgura F, De Marco F, Stefanini GG, Ciardetti M, Versaci F, Latini RA, Saccà S, Ghiringhelli S, Picchi A, Cerrito M, Gaspardone A, Tarantini G (2021) Usefulness of coronary sinus reducer implantation for the treatment of chronic refractory angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 139:22–27
Konigstein M, Giannini F, Banai S (2018) The Reducer device in patients with angina pectoris: mechanisms, indications, and perspectives. Eur Heart J 39(11):925–933
Marchant B, Umachandran V, Stevenson R, Kopelman PG, Timmis AD (1993) Silent myocardial ischemia: role of subclinical neuropathy in patients with and without diabetes. J Am Coll Cardiol 22(5):1433–1437
Hui G, Koch B, Calara F, Wong ND (2016) Angina in coronary artery disease patients with and without diabetes: US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2001–2010. Clin Cardiol 39(1):30–36
Morrow DA, Scirica BM, Chaitman BR, McGuire DK, Murphy SA, Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E, McCabe CH, Braunwald E, MERLIN-TIMI 36 Investigators (2009) Evaluation of the glycometabolic effects of ranolazine in patients with and without diabetes mellitus in the MERLIN-TIMI 36 randomized controlled trial. Circulation 119(15):2032–2039
Arnold SV, Spertus JA, Lipska KJ, Tang F, Goyal A, McGuire DK, Cresci S, Maddox TM, Kosiborod M (2015) Association between diabetes mellitus and angina after acute myocardial infarction: analysis of the TRIUMPH prospective cohort study. Eur J Prev Cardiol 22(6):779–787
Pitkänen OP, Nuutila P, Raitakari OT, Rönnemaa T, Koskinen PJ, Lida H, Lehtimäki TJ, Laine HK, Takala T, Viikari JS, Knuuti J (1998) Coronary flow reserve is reduced in young men with IDDM. Diabetes 47(2):248–254
Lamendola P, Lanza GA, Spinelli A, Sgueglia GA, Di Monaco A, Barone L, Sestito A, Crea F (2010) Long-term prognosis of patients with cardiac syndrome X. Int J Cardiol 140(2):197–199
Baldetti L, Colombo A, Banai S, Latib A, Esposito A, Palmisano A, Giannini F (2018) Coronary sinus Reducer non-responders: insights and perspectives. EuroIntervention 13(14):1667–1669
Zivelonghi C, Vermeersch G, Verheye S, Agostoni P (2019) Incomplete coronary sinus reducer endothelialization as potential mechanism of clinical failure. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 94(1):120–122
Gallone G, Armeni P, Verheye S, Agostoni P, Timmers L, Campo G, Ielasi A, Sgura F, Tarantini G, Rosseel L, Zivelonghi C, Leenders G, Stella P, Tebaldi M, Tespili M, D’Amico G, Baldetti L, Ponticelli F, Colombo A, Giannini F (2020) Cost-effectiveness of the coronary sinus Reducer and its impact on the healthcare burden of refractory angina patients. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes 6(1):32–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GMV: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; interpretation of data; writing-original draft; final approval of the version. CZ: conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; interpretation of data; writing-original draft; final approval of the version. PA: writing—review and editing; visualization; supervision. MD: data curation; writing—review and editing; validation; MS: data curation; writing—review and editing; validation; visualization; GL: data curation; validation; writing—review and editing. JPvK: resources; data curation; supervision; LT: resources; supervision; validation; writing—review and editing; PS: writing—review and editing; visualization; SB: data curation; writing—review and editing; visualization; SV: conceptualization; writing—review and editing; visualization; project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Disclosure
S. Banai is Medical Director of Neovasc. S. Verheye and P. Agostoni are consultants for Neovasc Inc.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vescovo, G.M., Zivelonghi, C., Agostoni, P. et al. Efficacy of coronary sinus Reducer in patients with refractory angina and diabetes mellitus. Heart Vessels 37, 194–199 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01909-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-021-01909-9