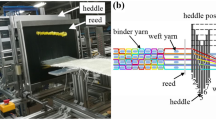
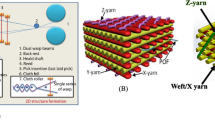
Abstract
In this paper, the effects of the stacking sequence of layup processing and creating space between layers of hybrid composites on the impact behavior were studied. The hybrid woven composites were manufactured using three different woven layers of kevlar, carbon, and glass fibers. Results show that the impact resistance of hybrid composites was better when the kevlar layer was located on the impact surface than when glass or carbon layers were placed on the impact surface. The absorbed energy of the impactor by the 3K-3G-3C sample was about 57 % higher than 3C-3G-3K and samples. Also, the absorbed energy by the 2K-2C-2K-2C sample was 67 % higher than the 4C-4K samples. The impact resistance of the hybrid woven layer composite decreases with creating space between layers. The absorbed energy by the spaced plate sample was less about 52 % than that non-spaced plate sample. Mathematical equations were generated to plot a simple geometry of woven fabric. A homogenization method was applied to finite element analyses using the unit-cell of the generated geometrical model for each composite sample. The presented methods of finite element simulations had an acceptable accuracy in predicting the high-velocity impact behavior of composites samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Silva, C. Cismaşiu, and C. Chiorean, Int. J. Impact Eng., 31, 289 (2005).
N. Naik, P. Shrirao, and B. Reddy, Int. J. Impact Eng., 32, 1521 (2006).
S. Chocron, A. J. Carpenter, N. L. Scott, R. P. Bigger, and K. Warren, Int. J. Impact Eng., 131, 39 (2019).
J. López-Puente and S. Li, Int. J. Impact Eng., 48, 54 (2012).
S. Ahmed, X. Zheng, D. Zhang, and L. Yan, Appl. Compos. Mater., 27, 285 (2020).
M. K. Dewangan and S. Panigrahi, Fiber. Polym., 21, 2389 (2020).
M. K. Dewangan and S. Panigrahi, J. Ind. Text., 1528083720970168 (2020).
L. Alonso, C. Navarro, and S. K. García-Castillo, Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct., 26, 1001 (2019).
A. S. Yaghoubi and B. Liaw, J. Compos. Mater., 48, 2011 (2014).
C. Kaboglu, I. Mohagheghian, J. Zhou, Z. Guan, W. Cantwell, S. John, B. R. Blackman, A. J. Kinloch, and J. P. Dear, J. Mater. Sci., 53, 4209 (2018).
M. Bulut, A. Erkliğ, and E. Yeter, J. Compos. Mater., 50, 1875 (2016).
J. H. Song, Fiber. Polym., 17, 600 (2016).
N. Pagano and R. B. Pipes, J. Compos. Mater., 5, 50 (1971).
A. Muc, Mech. Compos. Mater., 52, 211 (2016).
Y. Zhou, X. Gong, S. Zhang, and A. Xu, Fiber. Polym., 16, 2663 (2015).
S. Amico, C. Angrizani, and M. Drummond, J. Reinf. Plas. Compos., 29, 179 (2010).
D. F. Adams, J. Mater. Sci., 10, 1591 (1975).
M. Tehrani-Dehkordi, H. Nosraty, and M.-H. Rajabzadeh, Fiber. Polym., 16, 918 (2015).
A. Karimzadeh, M. Yahya, M. Abdullah, and K. Wong, Fiber. Polym., 21, 1583 (2020).
R. Park and J. Jang, Polym. Compos., 21, 231 (2000).
A. Riccio, G. Mozzillo, and F. Scaramuzzino, Appl. Compos. Mater., 20, 249 (2013).
S. K. García-Castillo, B. L. Buitrago, and E. Barbero, Polym. Compos., 32, 290 (2011).
M. Özen, Mech. Compos. Mater., 52, 759 (2017).
K.-Y. Kim and L. Ye, J. Mater. Sci., 47, 7280 (2012).
M. H. Pol and G. Liaghat, Polym. Compos., 37, 1173 (2016).
J. Hearle and O. Bose, J. Text. Inst. Trans., 57, T294 (1966).
J. W. Hearle, P. Grosberg, and S. Backer, “Structural Mechanics of Fibres, Yarns and Fabrics”, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1969.
Y. Chen, S. Hou, K. Fu, X. Han, and L. Ye, Compos. Struct., 168, 322 (2017).
Y. Chen, X. Han, S. Hou, K. Fu, and L. Ye, “21th International Conference on Composite Materials”, Xi’an, China, 2017.
Y. Wang and D. Zhao, Composites, 26, 115 (1995).
M. Aktaş and R. Karakuzu, Polym. Compos., 30, 1437 (2009).
M. K. Dubey and P. B. Prajwal, Int. J. Mech. Eng., 41, 2051 (2013).
M. Herráez, A. Fernández, C. Lopes, and C. González, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 374, 20150274 (2016).
H. Ullah, A. R. Harland, and V. V. Silberschmidt, Comput. Mater. Sci., 64, 130 (2012).
V. Phadnis, K. Pandya, N. Naik, A. Roy, and V. Silberschmidt, J. Phys. Conf. Ser., 451, 012019 (2013).
R. S. Sikarwar, N. S. Rajput, R. Velmurugan, and S. Naik, Mater. Today: Proc., 4, 2599 (2017).
D. S. Rao, P. R. Reddy, and S. Venkatesh, Procedia Eng., 173, 1678 (2017).
S. Singh and I. Partridge, Compos. Sci. Technol., 55, 319 (1995).
J. C. Smith, F. L. McCrackin, and H. F. Schiefer, Text. Res. J., 28, 288 (1958).
D. Roylance, A. Wilde, and G. Tocci, Text. Res. J., 43, 34 (1973).
J. Cole, C. Dougherty, and J. Huth, “Constant Strain Waves in Strings”, Rand Corp Santa Monica CA, 1953.
J. C. Smith, J. M. Blandford, and H. F. Schiefer, Text. Res. J., 30, 752 (1960).
D. Zhu, B. Mobasher, J. Erni, S. Bansal, and S. Rajan, Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf., 43, 2021 (2012).
Y. Zhou, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, and S. Jeelani, Mater. Lett., 64, 246 (2010).
J. D. Seidt, T. A. Matrka, A. Gilat, and G. B. McDonald, “Dynamic Behavior of Materials”, Vol. 1, p.187, Springer, 2011.
A. D. Bunsell, J. Mater. Sci., 10, 1300 (1975).
M. G. Babu, R. Velmurugan, and N. Gupta, Latin Am. J. Solids Struct., 3, 21 (2006).
Acknowledgment
The authors fully funded this project. No funding has been received from other sources to carry out this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delavari, K., Safavi, A. The Effect of Stacking Sequence on High-velocity Impact Resistance of Hybrid Woven Reinforced Composites: Experimental Study and Numerical Simulation. Fibers Polym 23, 184–195 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-0257-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-0257-x