Abstract
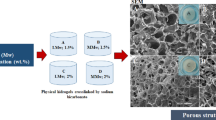
Chitosan and carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogels were prepared by crosslinking the biobased polymers with hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI). The hydrogels were obtained in a simple one-pot route, using water as solvent, at room temperature and without the use of other additives. The obtained materials were characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Thermogravimetric analysis (TG/DTG), X-ray diffraction (XRD), elemental analysis (CHN) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) techniques. The water absorption capacity and absorption kinetics were also studied at different pH values. The comparison between the hydrogels obtained from the different biopolymers showed remarkable differences including water absorption capacity (swelling ratio) which is up to ~ 15 for the chitosan-based hydrogel and reached ~ 64 for the carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogel. In addition, the morphologies obtained for each sample were also considerably different. The chitosan-based hydrogels did not present pores before the swelling process, and after that, only the presence of a heterogeneous pores structure was observed. On the other hand, for the CMC-based hydrogels a homogeneous porous structure was noticed before and after the swelling process, and a significant increase in pore size was observed after water absorption. Since the two kinds of hydrogels obtained here were prepared through an easy and efficient route, using water as solvent and present potential biodegradability, simultaneously with a good swelling capacity, particularly for the CMC-based hydrogels, the obtained materials can find application in different areas such as agricultural or biomedical.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed EM (2015) Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J Adv Res 6:105–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2013.07.006
Koetting MC, Peters JT, Steichen SD, Peppas NA (2015) Stimulus-responsive hydrogels: Theory, modern advances, and applications. Mater Sci Eng R Reports 93:1–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2015.04.001
Wang N, Yu KK, Shan YM et al (2020) HClO/ClO-Indicative Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels as Intelligent Bioactive Materials for Wound Healing. ACS Appl Bio Mater 3:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.9b00806
Saeedi Garakani S, Davachi SM, Bagher Z et al (2020) Fabrication of chitosan/polyvinylpyrrolidone hydrogel scaffolds containing PLGA microparticles loaded with dexamethasone for biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol 164:356–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.138
Peppas NA, Khademhosseini A (2016) Make better, safer biomaterials. Nature 540:335–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/540335a
Guilherme MR, Aouada FA, Fajardo AR et al (2015) Superabsorbent hydrogels based on polysaccharides for application in agriculture as soil conditioner and nutrient carrier: A review. Eur Polym J 72:365–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2015.04.017
Li S, Chen G (2020) Agricultural waste-derived superabsorbent hydrogels: Preparation, performance, and socioeconomic impacts. J Clean Prod 251:119669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119669
Guilherme MR, Reis AV, Takahashi SH et al (2005) Synthesis of a novel superabsorbent hydrogel by copolymerization of acrylamide and cashew gum modified with glycidyl methacrylate. Carbohydr Polym 61:464–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.06.017
Senna AM, Botaro VR (2017) Biodegradable hydrogel derived from cellulose acetate and EDTA as a reduction substrate of leaching NPK compound fertilizer and water retention in soil. J Control Release 260:194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.06.009
Ohm Y, Pan C, Ford MJ et al (2021) An electrically conductive silver-polacrylamide-alginate hydrogel composite for soft electronics. Nat Electron 4:185–192. https://doi.org/10.1184/R1/14039801
Zhou W, Li Q, Ma R et al (2021) Modified Alginate-Based Hydrogel as a Carrier of the CB2 Agonist JWH133 for Bone Engineering. ACS Omega 6:6861–6870. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c06057
MaDRG C, Postma A, Frith JE, Meagher L (2021) Printability and bio-functionality of shear thinning methacrylated xanthan - gelatin composite bioink. Biofabrication. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/abec2d
Zhao X, Lang Q, Yildirimer L et al (2016) Photocrosslinkable Gelatin Hydrogel for Epidermal Tissue Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater 5:108–118. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201500005
Ravishankar K, Dhamodharan R (2020) Advances in chitosan-based hydrogels: Evolution from covalently crosslinked systems to ionotropically crosslinked superabsorbents. React Funct Polym 149:104517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104517
Irene DR-R (2020) Evaluation of Collagen-Polyurethane-Chitosan Hydrogels for Lead Ions Removal from Water. Mediterr J Basic Appl Sci 04:93–104. https://doi.org/10.46382/mjbas.2020.4209
Wei Q, Bai J, Wang H et al (2021) Photo-induced programmable degradation of carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym 256:117609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117609
Zamani A, Henriksson D, Taherzadeh MJ (2010) A new foaming technique for production of superabsorbents from carboxymethyl chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 80:1091–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.01.029
Zargar V, Asghari M, Dashti A (2015) A Review on Chitin and Chitosan Polymers: Structure, Chemistry, Solubility, Derivatives, and Applications. ChemBioEng Rev 2:204–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/cben.201400025
Divya K, Jisha MS (2018) Chitosan nanoparticles preparation and applications. Environ Chem Lett 16:101–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0670-y
Mourya VK, Inamdar NN, Tiwari A (2010) Carboxymethyl chitosan and its applications. Adv Mater Lett 1:11–33. https://doi.org/10.5185/amlett.2010.3108
Shariatinia Z (2018) Carboxymethyl chitosan: Properties and biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol 120:1406–1419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.131
Chen XG, Park HJ (2003) Chemical characteristics of O-carboxymethyl chitosans related to the preparation conditions. Carbohydr Polym 53:355–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(03)00051-1
Farag RK, Mohamed RR (2013) Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan nanogels for swelling studies and antimicrobial activity. Molecules 18:190–203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18010190
Lin-Gibson S, Walls HJ, Kennedy SB, Welsh ER (2003) Reaction kinetics and gel properties of blocked diisocyinate crosslinked chitosan hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym 54:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(03)00159-0
Welsh ER, Price RR (2003) Chitosan cross-linking with a water-soluble, blocked diisocyanate. 2. Solvates and hydrogels Biomacromolecules 4:1357–1361. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm034111c
Chen Y, Tan H, min, (2006) Crosslinked carboxymethylchitosan-g-poly(acrylic acid) copolymer as a novel superabsorbent polymer. Carbohydr Res 341:887–896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2006.01.027
Pavia DL, Lampman GM, Kriz GS (2001) Introduction to spectroscopy, 3rd edn. Thomson Learning, USA
Spinks GM, Lee CK, Wallace GG et al (2006) Swelling behavior of chitosan hydrogels in ionic liquid-water binary systems. Langmuir 22:9375–9379. https://doi.org/10.1021/la061586r
Tronci G, Neffe AT, Pierce BF, Lendlein A (2010) An entropy-elastic gelatin-based hydrogel system. J Mater Chem 20:8875–8884. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0jm00883d
Qu J, Liang Y, Shi M et al (2019) Biocompatible conductive hydrogels based on dextran and aniline trimer as electro-responsive drug delivery system for localized drug release. Int J Biol Macromol 140:255–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.120
Baumann H, Faust V (2001) Concepts for improved regioselective placement of O-sulfo, N-sulfo, N-acetyl, and N-carboxymethyl groups in chitosan derivatives. Carbohydr Res 331:43–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6215(01)00009-X
Pavianatto A, Fiamingo A, de Bukzem AL et al (2017) Chemically Modified Chitosan Derivatives. In: Dotto GL, Campana-Filho SP, de Pinto LAA (eds) Frontiers in Biomaterials. Chitosan Based Materials and its Applications, vol 3 online. Bentham ebooks, Sharjah, UAE, pp 107–132
Siahaan P, Mentari NC, Wiedyanto UO et al (2017) The optimum conditions of carboxymethyl chitosan synthesis on drug delivery application and its release of kinetics study. Indones J Chem 17:291–300. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.24252
Deepuppha N, Kadnaim A, Rutnakornpituk B, Rutnakornpituk M (2020) Poly(ester urethane)-crosslinked carboxymethylchitosan as a highly water swollen hydrogel. J Met Mater Miner 30:48–56. https://doi.org/10.14456/jmmm.2020.6
Jankaew R, Rodkate N, Lamlertthon S et al (2015) “Smart” carboxymethylchitosan hydrogels crosslinked with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and poly(acrylic acid) for controlled drug release. Polym Test 42:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2014.12.010
Kadnaim A, Janvikul W, Wichai U, Rutnakornpituk M (2008) Synthesis and properties of carboxymethylchitosan hydrogels modified with poly(ester-urethane). Carbohydr Polym 74:257–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.02.007
Flory PJ (1953) Principles of polymer chemistry, 1st ed. Ithaca, New York, USA
Mei J, Mo S, Zhang H et al (2020) Removal of Sr(II) from water with highly-elastic carboxymethyl chitosan gel. Int J Biol Macromol 163:1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.038
Chen L, Tian Z, Du Y (2004) Synthesis and pH sensitivity of carboxymethyl chitosan-based polyampholyte hydrogels for protein carrier matrices. Biomaterials 25:3725–3732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.09.100
Yu R, Cornette de Saint-Cyr L, Soussan L et al (2021) Anti-bacterial dynamic hydrogels prepared from O-carboxymethyl chitosan by dual imine bond crosslinking for biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol 167:1146–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.068
Luo Y, Teng Z, Wang X, Wang Q (2013) Development of carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel beads in alcohol-aqueous binary solvent for nutrient delivery applications. Food Hydrocoll 31:332–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.11.011
Wahid F, Yin JJ, Xue DD et al (2016) Synthesis and characterization of antibacterial carboxymethyl Chitosan/ZnO nanocomposite hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol 88:273–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.03.044
Zhao L, Mitomo H, Nagasawa N et al (2003) Radiation synthesis and characteristic of the hydrogels based on carboxymethylated chitin derivatives. Carbohydr Polym 51:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(02)00210-2
Janvikul W, Thavornyutikarn B (2003) New Route to the Preparation of Carboxymethylchitosan Hydrogels. J Appl Polym Sci 90:4016–4020. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.13129
Rodríguez-Rodríguez R, Espinosa-Andrews H, Velasquillo-Martínez C, García-Carvajal ZY (2020) Composite hydrogels based on gelatin, chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol to biomedical applications: a review. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 69:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2019.1581780
dos Santos TC, Hernández R, Rescignano N et al (2018) Nanocomposite chitosan hydrogels based on PLGA nanoparticles as potential biomedical materials. Eur Polym J 99:456–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2017.12.039
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank CNPq (EDT Universal Nº 28/2018) and Fapemig (EDT Universal N° 1/2017, EDT PPM XI N°2/2017) and INCT-MIDAS for financial support. Centro de Microscopia-UFMG is also gratefully acknowledged for providing the images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ladeira, N.M.B., Donnici, C.L., de Mesquita, J.P. et al. Preparation and characterization of hydrogels obtained from chitosan and carboxymethyl chitosan. J Polym Res 28, 335 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02682-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02682-z