Abstract
Background
Circular RNA (circRNA) has been demonstrated to play key roles in regulating glioma progression. Understanding the regulatory mechanism of circRNA in glioma is vital to reveal the pathogenesis of glioma and develop novel therapeutic strategies. Therefore, our study focuses on the role and underlying mechanism of Circ_CLIP2 in glioma.
Methods
The expression of Circ_CLIP2, miR-195-5p and HMGB3 in glioma cells and tissues were analyzed using qRT-PCR. Cell proliferation was determined with colony formation and MTT assays. Cell cycle and apoptosis were examined by flow cytometry. Western blot was conducted for analyzing HMGB3, PCNA, Bax, Bcl-2, cleaved-caspase 3, Wnt-1 and β-catenin. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was measured to investigate the interaction among Circ_CLIP2, miR-195-5p and HMGB3.
Results
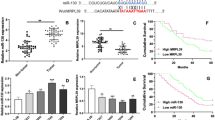
The expression of Circ_CLIP2 and HMGB3 were increased while miR-195-5p was down-regulated in glioma cells and patients. Silencing of Circ_CLIP2 inhibited cell proliferation, enhanced cell apoptosis and inhibited the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Circ_CLIP2 suppressed miR-195-5p expression by directly sponging miR-195-5p. MiR-195-5p inhibited HMGB3 expression via directly targeting HMGB3. Knockdown of miR-195-5p facilitated cell proliferation, inhibited cell apoptosis and activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which were reversed by silencing of HMGB3.
Conclusion
Knockdown of Circ_CLIP2 suppresses glioma progression by targeting miR-195-5p/HMGB3 thus inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling. This study may provide potential therapeutic targets against glioma.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Reni M, Mazza E, Zanon S, Gatta G, Vecht CJ (2017) Central nervous system gliomas. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 113:213–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.03.021
Ostrom QT, Bauchet L, Davis FG, Deltour I, Fisher JL, Langer CE, Pekmezci M, Schwartzbaum JA, Turner MC, Walsh KM, Wrensch MR, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2014) The epidemiology of glioma in adults: a “state of the science” review. Neuro Oncol 16:896–913. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou087
Chen R, Smith-Cohn M, Cohen AL, Colman H (2017) Glioma Subclassifications and their clinical significance. Neurotherapeutics 14:284–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-017-0519-x
Chowdhary MM, Ene CI, Silbergeld DL (2015) Treatment of gliomas: how did we get here? Surg Neurol Int 6:S85-88. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.151348
Li F, Liu Z, Sun H, Li C, Wang W, Ye L, Yan C, Tian J, Wang H (2020) PCC0208017, a novel small-molecule inhibitor of MARK3/MARK4, suppresses glioma progression in vitro and in vivo. Acta pharmaceutica Sinica B 10:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2019.09.004
He ZQ, Duan H, Ke C, Zhang XH, Guo CC, Al-Nahari F, Zhang J, Chen ZH, Chen YS, Liu ZG, Wang J, Chen ZP, Jiang XB, Mou YG (2017) Evaluation of cumulative prognostic score based on pretreatment plasma fibrinogen and serum albumin levels in patients with newly diagnosed high-grade gliomas. Oncotarget 8:49605–49614. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17849
Steinbach JP, Weller M (2004) Apoptosis in gliomas: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J Neurooncol 70:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-2753-4
Sun J, Li B, Shu C, Ma Q, Wang J (2020) Functions and clinical significance of circular RNAs in glioma. Mol Cancer 19:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1121-0
Rynkeviciene R, Simiene J, Strainiene E, Stankevicius V, Usinskiene J, Miseikyte Kaubriene E, Meskinyte I, Cicenas J, Suziedelis K (2018) Non-Coding RNAs in Glioma. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11010017
Mizoguchi M, Guan Y, Yoshimoto K, Hata N, Amano T, Nakamizo A, Sasaki T (2012) MicroRNAs in human malignant gliomas. J Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/732874
Zhang X, Yang H, Zhao L, Li G, Duan Y (2019) Circular RNA PRKCI promotes glioma cell progression by inhibiting microRNA-545. Cell Death Dis 10:616. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1863-z
Song X, Zhang N, Han P, Moon BS, Lai RK, Wang K, Lu W (2016) Circular RNA profile in gliomas revealed by identification tool UROBORUS. Nucleic Acids Res 44:e87. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw075
Wang X, Li XD, Fu Z, Zhou Y, Huang X, Jiang X (2020) Long noncoding RNA LINC00473/miR1955p promotes glioma progression via YAP1TEAD1Hippo signaling. Int J Oncol 56:508–521. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2019.4946
Jia Y, Tian Y, An S, Yang D (2020) Effects of microRNA-195 on the prognosis of glioma patients and the proliferation and apoptosis of human glioma cells. Pathology Oncology Research: POR 26:753–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00622-3
Wang Y, Mo Y, Gong Z, Yang X, Yang M, Zhang S, Xiong F, Xiang B, Zhou M, Liao Q, Zhang W, Li X, Li X, Li Y, Li G, Zeng Z, Xiong W (2017) Circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol Cancer 16:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0598-7
Nemeth MJ, Curtis DJ, Kirby MR, Garrett-Beal LJ, Seidel NE, Cline AP, Bodine DM (2003) Hmgb3: an HMG-box family member expressed in primitive hematopoietic cells that inhibits myeloid and B-cell differentiation. Blood 102:1298–1306. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-11-3541
Liu J, Wang L, Li X (2018) HMGB3 promotes the proliferation and metastasis of glioblastoma and is negatively regulated by miR-200b-3p and miR-200c-3p. Cell Biochem Funct 36:357–365. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3355
Li Y, Ma Y, Zhang T, Feng C, Liu Y (2020) High-mobility group box 3 (HMGB3) silencing inhibits non-small cell lung cancer development through regulating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Biol Chem. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2020-0144
Mu F, Huang J, Xing T, Jing Y, Cui T, Guo Y, Yan X, Li H, Wang N (2019) The Wnt/beta-catenin/LEF1 pathway promotes cell proliferation at least in part through direct upregulation of miR-17-92 cluster. Front Genet 10:525. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00525
Clevers H (2006) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127:469–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.10.018
Panda AC (2018) Circular RNAs Act as miRNA sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:67–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_6
Chen TY, Liu Y, Chen L, Luo J, Zhang C, Shen XF (2020) Identification of the potential biomarkers in patients with glioma: a weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Carcinogenesis 41:743–750. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgz194
Liu J, Zhao K, Huang N, Zhang N (2019) Circular RNAs and human glioma. Cancer Biol Med 16:11–23. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2018.0425
Wang R, Zhang S, Chen X, Li N, Li J, Jia R, Pan Y, Liang H (2018) CircNT5E Acts as a sponge of miR-422a to promote glioblastoma tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 78:4812–4825. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0532
Li M, Li J, Liu L, Li W, Yang Y, Yuan J (2013) MicroRNA in human glioma cancers (Basel) 5:1306–1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers5041306
Wang BC, Ma J (2015) Role of NicroRNAs in malignant glioma. Chin Med J (Engl) 128:1238–1244. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.156141
Chen J, Chen T, Zhu Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Li X, Xie X, Wang J, Huang M, Sun X, Ke Y (2019) circPTN sponges miR-145-5p/miR-330-5p to promote proliferation and stemness in glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:398. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1376-8
Yilaz Susluer S, Biray Avci C, Dodurga Y, Ozlem Dogan Sigva Z, Oktar N, Gunduz C (2015) Downregulation of miR-195 via cyclosporin A in human glioblastoma cells. J BUON 20:1337–1340
Hui W, Yuntao L, Lun L, WenSheng L, ChaoFeng L, HaiYong H, Yueyang B (2013) MicroRNA-195 inhibits the proliferation of human glioma cells by directly targeting cyclin D1 and cyclin E1. PloS ONE 8:e54932. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0054932
Kulcheski FR, Christoff AP, Margis R (2016) Circular RNAs are miRNA sponges and can be used as a new class of biomarker. J Biotechnol 238:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.09.011
Song N, Wang B, Feng G, Duan L, Yuan S, Jia W, Liu Y (2019) Knockdown of high mobility group box 3 impairs cell viability and colony formation but increases apoptosis in A549 human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Lett 17:2937–2945. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.9927
Gu J, Xu T, Huang QH, Zhang CM, Chen HY (2019) HMGB3 silence inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth by interacting with hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Cancer Manag Res 11:5075–5089. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S204357
Kang R, Chen R, Zhang Q, Hou W, Wu S, Cao L, Huang J, Yu Y, Fan XG, Yan Z, Sun X, Wang H, Wang Q, Tsung A, Billiar TR, Zeh HJ 3rd, Lotze MT, Tang D (2014) HMGB1 in health and disease. Mol Aspects Med 40:1–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2014.05.001
Wang P, Zhang L, Yin S, Xu Y, Tai S, Zhang LI, Liang C (2021) hsa_circ_0062019 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of prostate cancer cells via the miR-195-5p/HMGA2 axis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 53:815–822. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmab058
Pang B, Fan H, Zhang IY, Liu B, Feng B, Meng L, Zhang R, Sadeghi S, Guo H, Pang Q (2012) HMGA1 expression in human gliomas and its correlation with tumor proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis. J Neurooncol 106:543–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0710-6
Zeng Y, Que T, Lin J, Zhan Z, Xu A, Wu Z, Xie C, Luo J, Ding S, Long H, Zhang X, Song Y (2021) Oncogenic ZEB2/miR-637/HMGA1 signaling axis targeting vimentin promotes the malignant phenotype of glioma. Mol Ther Nucl acids 23:769–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.12.029
Wang J, Xu X, Mo S, Tian Y, Wu J, Zhang J, Zhao J (2016) Involvement of microRNA-1297, a new regulator of HMGA1, in the regulation of glioma cell growth in vivo and in vitro. Am J Transl Res 8:2149–2158
Puca F, Tosti N, Federico A, Kuzay Y, Pepe A, Morlando S, Savarese T, D’Alessio F, Colamaio M, Sarnataro D, Ziberi S, De Martino M, Fusco A, Battista S (2019) HMGA1 negatively regulates NUMB expression at transcriptional and post transcriptional level in glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Cycle 18:1446–1457. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1618541
Bilir B, Kucuk O, Moreno CS (2013) Wnt signaling blockage inhibits cell proliferation and migration, and induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Transl Med 11:280. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-11-280
Lu C, Jia S, Zhao S, Shao X (2019) MiR-342 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Biomark 25:115–126. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-192399
Garg M, Maurya N (2019) WNT/beta-catenin signaling in urothelial carcinoma of bladder. World J Nephrol 8:83–94. https://doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v8.i5.83
Funding
This work was supported by Jiangxi provincial department of education natural science foundation youth project (Grant No. GJJ180153), Science and technology plan of Jiangxi provincial health commission (Grant No. 20201063) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81760445).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BX: conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, validation, visualization, investigation, methodology; SL: methodology; MW: software; XS: data curation; WT: visualization; MY: conceptualization, writing- original draft preparation, supervision, writing—reviewing and editing; XZ: conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation, supervision, writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Our study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University.
Informed consent
Written informed consent were provided by all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, B., Lv, Sg., Wu, Mj. et al. Circ_CLIP2 promotes glioma progression through targeting the miR-195-5p/HMGB3 axis. J Neurooncol 154, 131–144 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03814-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-021-03814-7