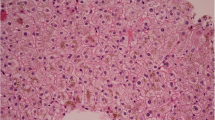
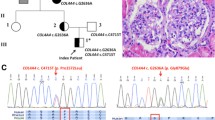
Abstract
Aceruloplasminemia (ACP) is a rare disorder of iron overload resulting from ceruloplasmin (CP) variants. Because of its rarity and heterogeneity, the diagnosis of ACP is often missed or misdiagnosed. Here, we aim to present a clinical spectrum of ACP and raise more attention to the early diagnosis. Whole exome sequencing (WES) was performed in a Chinese female patient suspected with ACP and her clinical data were collected in detail. The PubMed databases was searched for published ACP patients within the last decade, and we present a systematic review of their clinical features with data extracted from these researches. A novel pathogenic variant (c.2689delC) and a known pathogenic variant (c.606dupA) within ceruloplasmin gene were identified in our patient and confirmed the diagnosis of ACP. Then we reviewed 51 ACP patients including the case we reported here. A possible timeline of symptoms was discovered, anemia appears first (29.7 years old on average), followed by diabetes (37.3 years old) and finally neurological symptoms (50.7 years old). The delay in diagnosis was significantly shortened in patients without neurological symptoms. Biochemical triad including anemia, low to undetectable serum ceruloplasmin, low serum iron and/or hyperferritinemia, showed better sensitivity in diagnosis than clinical triad including diabetes, neurological symptoms, and retinal degeneration. Due to the variable symptom spectrum, patients with ACP often visit different departments, which can lead to misdiagnosis. Clinical attention needs to be paid to symptoms and tests that have a warning effect. Prompt diagnosis in the early stage of the disease can be beneficial.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Bethlehem C, van Harten B, Hoogendoorn M (2010) Central nervous system involvement in a rare genetic iron overload disorder. Neth J Med 68:316–318
Borges MD, Albuquerque DM, Lanaro C et al (2019) Clinical relevance of heterozygosis for aceruloplasminemia. Am J Med Genet 180:266–271. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.32723
Członkowska A, Tarnacka B, Möller JC et al (2007) Unified Wilson’s disease rating scale - a proposal for the neurological scoring of Wilson’s disease patients. Neurol Neurochir Pol 41:1–12
Dong Y, Ni W, Chen W-J et al (2016) Spectrum and classification of ATP7B variants in a large cohort of Chinese patients with Wilson’s disease guides genetic diagnosis. Theranostics 6:638–649. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.14596
Finkenstedt A, Wolf E, Höfner E et al (2010) Hepatic but not brain iron is rapidly chelated by deferasirox in aceruloplasminemia due to a novel gene mutation. J Hepatol 53:1101–1107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2010.04.039
Fujita K, Osaki Y, Harada M et al (2013) Brain and liver iron accumulation in aceruloplasminemia. Neurology 81:2145–2146. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000437304.30227.bd
Hayashida M, Hashioka S, Miki H et al (2016) Aceruloplasminemia with psychomotor excitement and neurological sign was improved by minocycline (case report). Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e3594. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000003594
Hida A, Kowa H, Iwata A et al (2010) Aceruloplasminemia in a Japanese woman with a novel mutation of CP gene: clinical presentations and analysis of genetic and molecular pathogenesis. J Neurol Sci 298:136–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2010.08.019
Jiang B, Zhou J et al (2019) Mutation screening in chinese patients with familial Alzheimer’s disease by whole-exome sequencing. Neurobiol Aging 76:215.e15–215.e21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.11.024
Kassubek R, Uttner I, Schönfeldt-Lecuona C et al (2017) Extending the aceruloplasminemia phenotype: NBIA on imaging and acanthocytosis, yet only minor neurological findings. J Neurol Sci 376:151–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2017.03.019
Kerkhof M, Honkoop P (2014) Never forget aceruloplasminemia in case of highly suggestive Wilson’s disease score. Hepatology 59:1645–1647. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26719
Kim HK, Ki CS, Kim YJ, Lee MS (2017) Radiological findings of two sisters with Aceruloplasminemia presenting with chorea. Clin Neuroradiol 27:385–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-017-0573-0
Kono S (2013) Aceruloplasminemia. Int Rev Neurobiol 110:125–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-410502-7.00007-7
Lindner U, Schuppan D, Schleithoff L et al (2015) Aceruloplasminaemia: a family with a novel mutation and long-term therapy with deferasirox. Horm Metab Res 47:303–308. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1383650
Marchi G, Busti F, Lira Zidanes A et al (2019) Aceruloplasminemia: a severe neurodegenerative disorder deserving an early diagnosis. Front Neurosci 13:325. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00325
Matsushima A, Yoshida T, Yoshida K et al (2014) Superficial siderosis associated with aceruloplasminemia. Case report J Neurol Sci 339:231–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2014.02.014
Melgari J-M, Marano M, Quattrocchi CC et al (2015) Movement disorders and brain iron overload in a new subtype of aceruloplasminemia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 21:658–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.03.014
Meral Gunes A, Sezgin Evim M, Baytan B et al (2014) Aceruloplasminemia in a Turkish adolescent with a novel mutation of ceruloplasmin gene: the first diagnosed case from Turkey. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 36:e423–e425. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPH.0000000000000053
Miyajima H, Hosoi Y (1993) Aceruloplasminemia. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA et al (eds) GeneReviews®. University of Washington, Seattle
Miyajima H, Nishimura Y, Mizoguchi K et al (1987) Familial apoceruloplasmin deficiency associated with blepharospasm and retinal degeneration. Neurology 37:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.37.5.761
Miyake Z, Nakamagoe K, Yoshida K et al (2020) Deferasirox might be effective for microcytic Anemia and neurological symptoms associated with Aceruloplasminemia: a case report and review of the literature. Intern Med 59:1755–1761. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.4178-19
Ogimoto M, Anzai K, Takenoshita H et al (2011) Criteria for early identification of aceruloplasminemia. Intern Med 50:1415–1418. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.50.5108
Ondrejkovičová M, Dražilová S, Drakulová M et al (2020) New mutation of the ceruloplasmin gene in the case of a neurologically asymptomatic patient with microcytic anaemia, obesity and supposed Wilson’s disease. BMC Gastroenterol 20:95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-020-01237-8
Pelucchi S, Pelloni I, Arosio C et al (2016) Does aceruloplasminemia modulate iron phenotype in thalassemia intermedia? Blood Cells Mol Dis 57:112–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2015.12.011
Pelucchi S, Mariani R, Ravasi G et al (2018) Phenotypic heterogeneity in seven Italian cases of aceruloplasminemia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 51:36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.02.036
Poli L, Alberici A, Buzzi P et al (2017) Is aceruloplasminemia treatable? Combining iron chelation and fresh-frozen plasma treatment. Neurol Sci 38:357–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-016-2756-x
Riboldi GM, Anstett K, Jain R et al (2018) Aceruloplasminemia and putaminal cavitation. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 51:121–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.03.003
Ronquillo CC, Sauer L, Morgan D et al (2019) Absence of macular degeneration in a patient with aceruloplasminemia. Retina (Philadelphia, Pa) 39:1824–1828. https://doi.org/10.1097/IAE.0000000000002628
Rusticeanu M, Zimmer V, Schleithoff L et al (2014) Novel ceruloplasmin mutation causing aceruloplasminemia with hepatic iron overload and diabetes without neurological symptoms. Clin Genet 85:300–301. https://doi.org/10.1111/cge.12145
Stelten BML, van Ommen W, Keizer K (2019) Neurodegeneration with brain Iron accumulation: a novel mutation in the Ceruloplasmin gene. JAMA Neurol 76:229–230. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3230
Suzuki Y, Yoshida K, Aburakawa Y et al (2013) Effectiveness of oral iron chelator treatment with deferasirox in an aceruloplasminemia patient with a novel ceruloplasmin gene mutation. Intern Med 52:1527–1530. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.52.0102
Tai M, Matsuhashi N, Ichii O et al (2014) Case of presymptomatic aceruloplasminemia treated with deferasirox. Hepatol Res 44:1253–1258. https://doi.org/10.1111/hepr.12292
Tridimas A, Gillett GT, Pollard S et al (2021) Three-year follow up of using combination therapy with fresh-frozen plasma and iron chelation in a patient with acaeruloplasminemia. JIMD Rep 57:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmd2.12176
Vila Cuenca M, Marchi G et al (2020) Genetic and clinical heterogeneity in thirteen new cases with aceruloplasminemia. atypical anemia as a clue for an early diagnosis. Int J Mol Sci 21(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21
Vroegindeweij LHP, van der Beek EH, Boon AJW et al (2015) Aceruloplasminemia presents as type 1 diabetes in non-obese adults: a detailed case series. Diabet Med 32:993–1000. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.12712
Wang B, Wang X-P (2019) Does Ceruloplasmin defend against neurodegenerative diseases? Curr Neuropharmacol 17:539–549. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X16666180508113025
Watanabe M, Asai C, Ishikawa K et al (2010) Central diabetes insipidus and hypothalamic hypothyroidism associated with aceruloplasminemia. Intern Med 49:1581–1585. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.49.3508
Watanabe M, Ohyama K, Suzuki M et al (2018) Aceruloplasminemia with abnormal compound heterozygous mutations developed neurological dysfunction during phlebotomy therapy. Intern Med 57:2713–2718. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.9855-17
Yamamura A, Kikukawa Y, Tokunaga K et al (2018) Pancytopenia and Myelodysplastic changes in Aceruloplasminemia: a case with a novel pathogenic variant in the Ceruloplasmin gene. Intern Med 57:1905–1910. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.9496-17
Zhou L, Chen Y, Li Y et al (2020) Intracranial iron distribution and quantification in aceruloplasminemia: a case study. Magn Reson Imaging 70:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2020.02.016
Funding
This work was supported by the research foundation for distinguished scholar of Zhejiang University to Zhi-Ying Wu (188020-193810101/089, Hangzhou).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Wan-Qing Xu, Wang Ni, Rou-Min Wang, Yi Dong and Zhi-Ying Wu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Wan-Qing Xu and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, WQ., Ni, W., Wang, RM. et al. A novel ceruloplasmin mutation identified in a Chinese patient and clinical spectrum of aceruloplasminemia patients. Metab Brain Dis 36, 2273–2281 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00799-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00799-0