Abstract
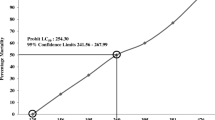
This study was conducted to determining the values of LC50, mortality rates and DNA damages (Daphnia magna) of species exposed to pozzolanic cement concentrations of 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, and 300 mg/L for 24 h. To compare the effect of increased pH value associated with the addition of cement, a NaOH group was also formed in Gammarus komareki individuals. As a result, the LC50 values in D. magna and G. komareki were calculated as 118.57 and 197.24 mg/L/24 h, respectively. It was observed that, unlike the G. komareki individuals, cement particles were accumulated on D. magna. In the comparison trial (NaOH) performed on G. komareki individuals, 60% mortality was determined. The number of deaths from cement and NaOH in the experimental groups with the same pH values were found similar. There was not statistically significant difference between control and experimental groups for DNA damage on D. magna. As a result, it has been determined that cement has a toxic effect on D. magna and G. komareki due to increasing the pH value of water.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso A, De Lange H, Peeters ETHM (2010) Contrasting sensitivities to toxicants of the freshwater amphipods Gammarus pulex and G. fossarum. Ecotoxicology 19:133–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-009-0398-y
Altinok I, Capkin E, Karahan S, Boran M (2006) Effects of water quality and fish size on toxicity of methiocarba, carbamate pesticide, to rainbow trout. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 22:20–26
Andrade VM, de Freitas TRO, Silva J (2004) Comet assay using mullet (Mugil sp.) and sea catfish (Netuma sp.) erythrocytes for the detection of genotoxic pollutants in aquatic environment. Mutation Research-Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis 560:57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2004.02.006
Barnard JL, Barnard CM (1983) Freshwater amphipoda of the world. Mt. Vernon Va Hayfield Associates, Mt. Vernon, Virginia
Boyle D, Boran H, Atfield JA, Theodore BH (2015) Use of an exposure chamber to maintain aqueous phase nanoparticle dispersions for improved toxicity testing in fish. Environ Toxicol Chem 34(3):583–588
Er A, Oztek O, Kayıs S (2019) Effects of concrete addıtıves on vıtal tıssues of raınbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykıss): a hıstologıcal examınatıon. Fresenius Environ Bulletin 28(5):3829–3833
Fikirdeşici Ş, Altindağ A, Özdemir E (2012) Investigation of acute toxicity of cadmium-arsenic mixtures to Daphnia magna with toxic unit’s approach. Turk J Zool 36(4):543–550
Gerhardt A, Kienle C, Allan IJ, Greenwood R, Guigues N, Fouillac AM, Mills GA, Gonzalez C (2007) Biomonitoring with Gammarus pulex at the Meuse (NL), Aller (GER) and Rhine (F) rivers with the online multispecies freshwater biomonitor. J Environ Monit 9:979–985
Jonczyk E, Gilron G (2005) Acute and chronic toxicity testing with Daphnia sp. In: Toxicity S-S (ed) Blaise C and Férard JF. Testing for freshwater Environments Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 337–394
Khan Q, Khan M (2008) Effect of temperature on waterflea Daphnia magna (Crustacea:Cladocera). Nature Precedings. https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2008.1909.1
Kurtoglu IZ, Kayıs S, Ak K, Gencoglu S, Duzgun A, Ulutas G, Er A (2016) Hıstopathology of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and Sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) Exposed to Sublethal Concentratıons of Cement. Fresenius Environ Bull 25(9):3523–3527
Kuriqi A, Pinheiro AN, Ward AS, Bejarano MD, Garrote L (2021) Ecological impacts of run-of-river hydropower plants—current status and future prospects on the brink of znergy transition. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 142:110833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.110833
Lee SW, Kim SM, Choi J (2009) Genotoxicity and ecotoxicity assays using the freshwater crustacean Daphnia magna and the larva of the aquatic midge Chironomus riparius to screen the ecological risks of nanoparticle exposure. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 28(2009):86–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2009.03.001
Lee JY, Hur JW (2005) Acute toxicity of cement on mortality of pond smelt (Hypomesus olidus). Korean Journal of Environmental Biology 23(1):89–92
Leight AK, Van Dolah RF (2009) Acute toxicity of the insecticides endosulfan, chlorpyrifos, and malathion to the epibenthic estuarine amphipod Gammarus palustris (Bousfield). Environ Toxicol Chem 18(5):958–964. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620180521
Loomis TA (1978) Essentials of Toxicology, 3rd edn. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 157–232
Macneil C, Dick JTA, Elwood RW (1997) The trophic ecology of freshwater Gammarus spp. (Crustacea: Amphipoda): Problems and perspectives concerning the functional feeding group concept. Biol Rev 72:349–364
Matsumoto K, Hosokawa M, Kuroda K, Endo G (2009) Toxicity of agricultural chemicals in Daphnia magna. Osaka City Med J 55(2):89–97
Mlynska A, Zielina M, Bielski A (2019) Contamination of drinking water soon after cement mortar lining renovation depending on the disinfectant doses. SN Applied Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0507-3
Naigagaa I, Kaiserb H, Mullerc WJ, Ojokd L, Mbabazie D, Magezie G, Muhumuza E (2011) Fish as bioindicators in aquatic environmental pollution assessment: a case study in Lake Victoria wetlands. Uganda, Phys Chem Earth 36:918–928
Persoone G, Janssen C R (1993) Fresh water invertebrate toxicity tests. In: Calow P (ed) Handbook of ecotoxicology, vol 1. Blackwell Science Publication, Newyork, pp 51–53
Persoone G, Baudo R, Cotman M, Blaise C, Thompson KC, Moreira-Santos M, Vollat B, Törökne A, Han T (2009) Review on the acute Daphnia magna toxicity test – Evaluation of the sensitivity and the precision of assays performed with organisms from laboratory cultures or hatched from dormant eggs. Knowl Manag Aquat Ecosyst 393:01. https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae/2009012
Peters RH, De Bernardi R (1987) Daphnia. Memorie Dell 'Istituto Italiano di Idrobiologia. p 502
Rao SVR (1986) Cadmium accumulation in fiddler crabs Uca annulipes uptake of lead chromium, cadmium and cobalt by Cladophora glomerata. Int J Environ Studies 27:219–223
Rodrigues P, Silvestre JD, Flores-Colen I, Viegas CA, Ahmed HH, de Brito KR (2020) Evaluation of the ecotoxicological potential of fly ashand recycled concrete aggregates use in concrete. Appl Sci 10(1):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010351
Sutcliffe DW, Carrick TR, Willoughby LG (2006) Effects of diet, body size, age and temperature on growth rates in the amphipod Gammarus pulex. Freshw Biol 11(2):183–214. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.1981.tb01252.x
Schmutz S, Moog O (2018) Dams: Ecological Impacts and Management. Riverine Ecosystem Management Springer International Publishing Cham, In book. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-73250-3_6
Terzi E, Verep B (2012) Effects of water hardness and temperature on the acute toxicity of mercuric chloride on rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Toxicol Ind Health 28(6):499–504. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233711416943
US Environmental Protection Agency (2002) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms, 5th edn. EPA-821-R-02-012
Villegas A, Navarro M, Rodríguez Santiago F, Ruiz Pérez R, Rodríguez Torres T, Dieck Abularach J, Reyes L (1997) Determination of LC50 from Daphnia magna in treated industrial waste waters and non-treated hospital effluents. Environ Int 23(4):535–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(97)00059-7
Wright IA, Davies PJ, Findlay SJ, Jonasson OJ (2011) A new type of water pollution: Concrete drainage infrastructure and geochemical contamination of urban waters. Mar Freshw Res 62(12):1355–1361. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF10296
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Er, A., Kayış, Ş. Acute Toxicity of Pozzolanic Cement on Two Crustacean Species, Water Flea (Daphnia magna) and Gammarus komareki. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 108, 309–314 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03345-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03345-x