Abstract
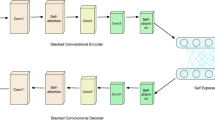
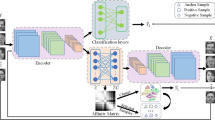
The practical visual data do not necessarily lie in linear subspaces, so deep convolutional subspace clustering network is proposed to segment the practical visual data into multiple categories accurately. The original convolutional subspace clustering network contains the stacked convolutional encoder module, the stacked convolutional decoder module and the self-expression module. We firstly alter the self-expression module, i.e., add a new k-block diagonal regularizer to the weights of the self-expression module. It means that the \(\ell _1\) or \(\ell _2\) regularizer is abandoned. The k-block diagonal regularizer is proposed to directly pursue the block diagonal matrix, so introducing this regularizer to the self-expression module will make the learned representation matrix conform with the block diagonal matrix better. Secondly, we add a new spectral clustering module to this convolutional subspace clustering network, in which the spectral clustering result is used to supervise the learning of the representation matrix. This subspace structured regularizer is introduced to the spectral clustering module, which further refines the learned representation matrix. Experimental results on three challenging datasets have demonstrated that the proposed deep learning based subspace clustering method achieves the better clustering effect over the state-of-the-arts.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2009) Sparse subspace clustering. In CVPR. pp 2790–2797
Hastie T, Simard PY (2000) Metrics and models for handwritten character recognition. Stat Sci 13(1)
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2013) Sparse subspace clustering: algorithm, theory, and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(11):2765–2781
Qian C, Brechon TP, Xu ZZ (2018) Clustering in pursuit of temporal correlation for human motion segmentation. Multimed Tools Appl 77(15):19615–19631
Basri R, Jacobs DW (2003) Lambertian reflectance and linear subspaces. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Recognit Mach Intell 25(2):218–233
Elhamifar E, Vidal R (2010) Clustering disjoint subspaces via sparse representation. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing. pp 1926–1929
You C, Robinson D, Vidal R (2016) Scalable sparse subspace clustering by orthogonal matching pursuit. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 3918–3927
Dyer EL, Studer C, Baraniuk RG (2013) Subspace clustering with dense representations. In: International conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing
Ji P, Salzmann M, Li H (2014) Efficient dense subspace clustering. In: IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision. IEEE, pp 461–468
Favar P, Vidal R, Ravichandran A (2011) A closed form solution to robust subspace estimation and clustering. In: IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 1801–1807
Vidal R, Favaro P (2014) Low rank subspace clustering (LRSC). Pattern Recognit Lett 43:47–61
Lu CY, Min H, Zhao ZQ, Zhu L, Huang DS, Yan S (2012) Robust and efficient subspace segmentation via least squares regression. European conference on computer vision. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 347–360
Cheng B, Yang J, Yan S, Huang TS (2010) Learning with \(\ell _1\)-graph for image analysis. TIP, 19(Compendex). pp 858–866
Liu G, Lin Z, Yu Y (2010) Robust subspace segmentation by low-rank representation. In: International conference on machine learning. pp 663-670
Liu G, Lin Z, Yan S, Sun J, Yu Y, Ma Y (2013) Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):171–184
Lu C, Feng J, Lin Z, Yan S (2013) Correlation adaptive subspace segmentation by trace lasso. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp 1345–1352
Xu J, Xu K, Chen K, Ruan JS (2015) Reweighted sparse subspace clustering. Comput Vis Image Underst 138:25–37
Dong W, Wu XJ, Kittler J (2019) Sparse subspace clustering via smoothed \(\ell _p\) minimization. Pattern Recognit Lett 125:206–211
Dong W, Wu XJ (2018) Robust affine subspace clustering via smoothed \(\ell _0\)-norm. Neural Process Lett 50(1):785–797
Ng AY, Jordan MI, Weiss Y (2002) On spectral clustering: analysis and an algorithm. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 14:849–856
Shi J, Malik J (2000) Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Recognit Mach Intell 22(8):888–905
Li CG, You C, Vidal R (2017) Structured sparse subspace clustering: a joint affinity learning and subspace clustering framework. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(6):2988–3001
Li CG, Vidal R (2015) Structured sparse subspace clustering: a unified optimization framework. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 277–286
Li CG, Vidal R (2016) A structured sparse plus structured low-rank framework for subspace clustering and completion. IEEE Trans Signal Process 64(24):6557–6570
Chen H, Wang W, Feng X (2018) Structured sparse subspace clustering with within-cluster grouping. Pattern Recognit 83:107–118
Chen H, Wang W, Feng X, He R (2018) Discriminative and coherent subspace clustering. Neurocomputing 284:177–186
Lu C, Feng J, Lin Z, Mei T, Yan S (2019) Subspace clustering by block diagonal representation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 41(2):487–501
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Shao L, Yang J (2018) Discriminative block-diagonal representation learning for image recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 29(7):3111–3125
Xie X, Guo X, Liu G, Wang J (2018) Implicit block diagonal low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(1):477–489
Patel VM, Vidal R (2014) Kernel sparse subspace clustering. In: IEEE international conference on image processing. pp 2849–2853
Patel VM, Nguyen HV, Vidal R (2015) Latent space sparse and low-rank subspace clustering. IEEE J Sel Topics in Signal Process 9(4):691–701
Patel VM, Nguyen HV, Vidal R (2013) Latent space sparse subspace clustering
Kang Z, Peng C, Cheng Q et al (2020) Structured graph learning for clustering and semi-supervised classification. Pattern Recognit 110:107627
Ji P, Reid I, Garg R, et al (2017) Adaptive low-rank kernel subspace clustering. arXiv:1707.04974v4
Xiao S, Tan M, Xu D et al (2016) Robust kernel low-rank representation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(11):2268–2281
Saba T, Khan MA, Rehman A et al (2019) Region extraction and classification of skin cancer: a heterogeneous framework of deep CNN features fusion and reduction. J Med Syst 43(9):1–19
Hassan MM, Alam MGR, Uddin MZ et al (2019) Human emotion recognition using deep belief network architecture. Inf Fusion 51:10–18
Peng X, Xiao S, Feng J, Yau WY, Yi Z (2016) Deep subspace clustering with sparsity prior. In: International Joint conference on artificial intelligence. pp. 1925–1931
Peng X, Feng J, Xiao S, et al (2017) Deep sparse subspace clustering. arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.08374
Ji P, Zhang T, Li H, Salzmann M (2017) Deep subspace clustering networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.02508
Kang Z, Lu X, Liang J et al (2020) Relation-guided representation learning. Neural Netw 131:93–102
Kang Z, Pan H, Hoi SC et al (2019) Robust graph learning from noisy data. IEEE Trans Cybern 50(5):1833–1843
Zhang J, Li CG, You C, et al (2019) Self-supervised convolutional subspace clustering network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 5473–5482
Huang D, Wang CD, Lai JH (2017) Locally weighted ensemble clustering. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(5):1460–1473
Huang D, Wang CD, Peng H, et al (2018) Enhanced ensemble clustering via fast propagation of cluster-wise similarities. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst
Huang D, Wang CD, Wu JS et al (2019) Ultra-scalable spectral clustering and ensemble clustering. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 32(6):1212–1226
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Project Number: 2018YFB1701903) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No: 61973138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Wang, Y. & Ji, Z. Self-Supervised Convolutional Subspace Clustering Network with the Block Diagonal Regularizer. Neural Process Lett 53, 3849–3875 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10563-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-021-10563-1