Abstract—
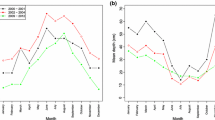
The long-term dynamics (over more than 70 years) of pike infection by cestodes Triaenophorus crassus and T. nodulosus in the Rybinsk Reservoir (the Volga River) has been studied in a comparative aspect. Cestode T. crassus is an invasive species that has entered the reservoir together with vendace Coregonus albula (the second intermediate host) from Lake Beloe; T. nodulosus is a native species that develops with the involvement of perch as a second intermediate host. Climate warming in the Rybinsk Reservoir manifests itself in a consistently growing average water temperature. This has led to a gradual decrease in the rate of pike infection by cestode T. crassus as a result of disturbances in the set of complex ecological relationships between the parasite and its hosts: a decrease in the abundance of large pike, fluctuations in the reservoir water level, and mass death of vendace in years with abnormally hot summers and the alternation of strong and weak year-classes in this short-cycle species (age 1+ to 3+). The long-term dynamics of pike infection by T. nodulosus is characterized by its consistently high rates and slight fluctuations. The abundance of perch population in the Rybinsk Reservoir remains high, and its age composition is stable, which contributes to a high rate of infection of both perch and pike by T. nodulosus. Cestode T. crassus occurs only in large pike (30 cm long or more); the rate of infection increases with age; T. nodulosus parasitizes mainly young pike (starting from young of the year), with the infection rate decreasing in large pike.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Walther, G.-R., Post, E., Convey, P., et al., Ecological responses to recent climate change, Nature, 2002, vol. 416, pp. 389–395.
Root, T.L., Price, J.T., Hall, K.R., et al., Fingerprints of global warming on animals and plants, Nature, 2003, vol. 421, pp. 57–60.
Yunchis, O.N., Possible changes in fish parasite fauna under global warming, in Problemy ikhtiopatologii v nachale XXI veka: Sb. nauchn. trudov GosNIORKh (Problems of Ichthyopathology in the Early 21st Century: GosNIORKh Collected Works), St. Petersburg, 2009, no. 338, pp. 240–246.
Hellmann, J.J., Byers, J.E., Bierwagen, B.G., and Dukes, J.S., Five potential consequences of climate change for invasive species, Conserv. Biol., 2008, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 534–543. .https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2008.00951.x
Marcogliese, D.J., The impact of climate change on the parasites and infectious diseases of aquatic animals, Rev. Sci. Tech. OIE, 2008, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 467–484.
Litvinov, A.S., Zakonnova, A.V., and Poddubnyi, S.A., Climate and hydrological regime, in Struktura i funktsionirovanie ekosistemy Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha v nachale XXI veka (The Structure and Functioning of the Rybinsk Reservoir Ecosystem in the Early 21st Century), Lazarev, V.I., Ed., Moscow: Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2018, pp. 32–50.
Litvinov, A.S. and Zakonnova, A.V., Ecological conditions in the Rybinsk Reservoir under climate warming, Geogr. Vestnik, 2014, no. 2 (29), pp. 41–45.
Litvinov, A.S. and Roshchupko, V.F., Long-term changes in components of the hydrometeorological regime of Rybinsk Reservoir, Meteorol. Gidrol., 2010, no. 7, pp. 65–75.
Lazareva, V.I., Zooplankton, in Struktura i funktsionirovanie ekosistemy Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha v nachale XXI veka (The Structure and Functioning of the Rybinsk Reservoir Ecosystem in the Early 21st Century), Lazarev, V.I., Ed., Moscow: Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2018, pp. 317–324.
Shcherbina G.Kh., Perova S.N., and Pryanichnikova E.G. Invasive benthic species, in Struktura i funktsionirovanie ekosistemy Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha v nachale XXI veka (The Structure and Functioning of the Rybinsk Reservoir Ecosystem in the Early 21st Century), Lazarev, V.I., Ed., Moscow: Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2018, pp. 324–329.
Borovikova, E.A., Gerasimov, Yu.V., and Karabanov, D.P., Fishes, in Struktura i funktsionirovanie ekosistemy Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha v nachale XXI veka (The Structure and Functioning of the Rybinsk Reservoir Ecosystem in the Early 21st Century), Lazarev, V.I., Ed., Moscow: Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Ross. Akad. Nauk, 2018, pp. 329–339.
Kuperman B. I. Lentochnye chervi roda Triaenophorus – parazity ryb (Tapeworms of the Genus Triaenophorus: Parasites of Fishes), Leningrad: Nauka, 1973.
Petrushevskii, G.K., On fish disease in Lake Beloye, Izv. VNIORKh, 1957, vol. 42, pp. 278–282.
Grevtseva, M.A., A systematic review of helminthes parasitizing fishes in the Vyatka River basin, Tr. Kirov. S-kh. Inst., Perm, 1976, vol. 12, pp. 64–71.
Kostarev, G.F., Fish parasite fauna in the Chusovaya River, Uch. Zap. Perm. Gs. Univ., 1969, vol. 179, pp. 230–238.
Stolyarov, V.P., Dynamics of the parasite fauna of commercial fish species in the Rybinsk Reservoir, Tr. Leningr. O-va Estestvoisp., 1954, vol. 72, no. 4, pp. 160–187.
Stolyarov, V.P., Parasitic diseases of fishes in the Upper Volga stretch across Yaroslavl and Kalinin oblasts, Zap. Leningr. S.-kh. Inst., 1955, no. 9, pp. 180–201.
Ermolin, V.P., Composition of the ichthyofauna of the Saratov Reservoir, J. Ichthyol., 2010, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 211–215.https://doi.org/10.1134/S0032945210020098
Solomatova, V.P., Triaenophorosis in salmonid fishes cultivated by industrial methods, in VII Vses. soveshch. po parazitam i boleznyam ryb (Abstr. VII All-Union Conf. on Fish Parasites and Diseases), Leningrad: Nauka, 1979, pp. 103–104.
Voronin, V.N., Chernysheva, N.B., and Strel’bitskaya, I.N., Characteristics of a trout triaenophorosis focus and measures of disease control under conditions of cage fish farming, in Problemy parazitologii i boleznei ryb v sovremennykh industrial’nykh rybovodnykh khozyaistvakh (Problems of Fish Parasitology and Diseases in Modern Industrial Fish Farms), Sb. Nauchn. Tr. GosNIORKh, St. Petersburg, vol. 311, pp. 9–22.
Bogdanova E.A. and Nikol’skaya N.P., Fish parasitology in the Volga River prior to damming, in Parazitofauna ryb basseina r. Volgi i voprosy zagryazneniya Permskogo vodokhranilishcha (Fish Parasitology in the Volga Basin and Problems of Pollution of the Perm Reservoir Pollution), Izv. GosNIIORKh, 1965, vol. 60, pp. 5–110.
Izyumova, N.A., On the dynamics of fish parasite fauna in the Rybinsk Reservoir, Tr. Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1959, no. 2 (5), pp. 174–190.
Izyumova, N.A., Seasonal dynamics of parasite fauna in fishes of the Rybinsk Reservoir (pike, blue bream, silver bream), Tr. Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1960, no. 3 (6), pp. 284–299.
Gerasimov, Yu.V., Ivanova, M.N., and Svirskaya, A.N., The pike, in Ryby Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha: populyatsionnaya dinamika i ekologiya (Fishes of the Rybinsk Reservoir: Population Dynamics and Ecology), Yaroslavl: Filigran’, 2015, pp. 184–198.
Gerasimov, Yu.V., Borovikova, E.A., and Stolbunov, I.A., The vendace, in Ryby Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha: populyatsionnaya dinamika i ekologiya (Fishes of the Rybinsk Reservoir: Population Dynamics and Ecology), Yaroslavl: Filigran’, 2015, pp. 157–169.
Kuperman, B.I., Ecological analysis of cestodes parasitizing fishes in water bodies of the Volga–Baltic system, Tr. Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1979, no. 38 (41), pp. 133–159.
Ieshko, E.P., Anikieva, L.V., Lebedeva, D.I., and Il’mast N.V., Specific features of population biology of Triaenophorus cestodes in natural and technogenically transformed water bodies, Parazitologiya, 2012, vol. 46, no. 6, pp. 434–443.
Evlanov, I.A., Distribution and regulation mechanisms of Triaenophorus nodulosus plerocercoids (Cestoda, Triaenophoridae), Parazitologiya, 1987, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 654–658.
Gerasimov, Y.V., Ivanova, M.N., and Svirskaya, A.N., Spatial distribution and population structure of the pike Esox lucius L. in the Rybinsk Reservoir during the climate warming period, J. Ichthyol., 2018, vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 38–51.
Gerasimov, Yu.V., Ivanova, M.N., Stolbunov, I.A., and Pavlov, D.D., The perch, in Ryby Rybinskogo vodokhranilishcha: populyatsionnaya dinamika i ekologiya (Fishes of the Rybinsk Reservoir: Population Dynamics and Ecology), Yaroslavl: Filigran’, 2015, pp. 331–348.
Shakirova, F.M. and Severov, Y.A., Species composition of ichthyofauna of the Kuibyshev Reservoir, J. Ichthyol., 2014, vol. 54, no. 8, pp. 513–525.
Funding
This study was performed under the state assignment from the RF Ministry of Science and Higher Education (no. AAAA-A18-118012690100-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed
Additional information
Translated by D. Zabolotny
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhokhov, A.E., Pugacheva, M.N. Long-term Dynamics of Pike Infection by Parasites Triaenophorus crassus and T. nodulosus (Plathelminthes, Cestoda) in the Rybinsk Reservoir: Effect of Hydraulic Construction and Climate Warming. Russ J Ecol 52, 307–315 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1067413621030115
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1067413621030115