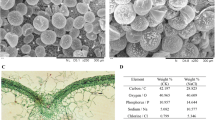
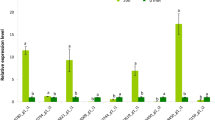
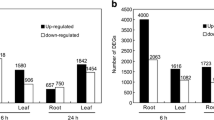
Abstract
Zygophyllum xanthoxylum, a succulent xerophyte, possesses excellent salt tolerance which is closely associated with vacuolar Na+ compartmentation via ZxNHX1. RNA interference (RNAi)-mediated ZxNHX1 silencing impaired the characteristics of Na+ accumulation and thus inhibited normal growth of Z. xanthoxylum. To explore the molecular mechanisms underlying the changed phenotype, here we compared the different expression of salt-responsive genes between ZxNHX1-RNAi line and wild type at transcriptome level. The result showed that vast genes were differently expressed in leaves or roots between ZxNHX1-RNAi line and wild type under control condition or salt treatment. Among them, 142 unigenes were differently expressed in both roots and leaves under 50 mM NaCl for 6 h and 24 h between ZxNHX1-RNAi line and WT. These differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were related to transmembrane transportation based on Gene Ontology (GO) annotations. In terms of ion transport, 49 DEGs were identified, in which some genes associated with Na+ and K+ homeostasis were down-regulated; meanwhile, silencing of ZxNHX1 triggered the differential expression of several genes involved in the transport of important nutrient elements including N, P, Ca, and Mg. Besides, silencing of ZxNHX1 affected the expression level of 18 and 26 genes related to photosynthesis and ROS scavenging, respectively. This study provided strong evidences to indicate the dominant role of ZxNHX1 in maintaining the characteristics of salt accumulation and regulating the salt tolerance of Z. xanthoxylum.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahanger MA, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L, Alamri SA, Alam P, Ashraf M, Ahmad P (2018) Potential of exogenously sourced kinetin in protecting Solanum lycopersicum from NaCl-induced oxidative stress through up-regulation of the antioxidant system, ascorbate-glutathione cycle and glyoxalase system. PLoS One. 13:e0202175. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202175
Ahanger MA, Aziz U, Alsahli AA, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2019) Influence of exogenous salicylic acid and nitric oxide on growth, photosynthesis, and ascorbate-glutathione cycle in salt stressed Vigna angularis. Biomolecules 10:42. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010042
Ahmad P, Ahanger MA, Alam P, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L, Ali S, Ashraf M (2019) Silicon (Si) supplementation alleviates NaCl toxicity in Mung Bean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] through the modifications of physio-biochemical attributes and key antioxidant enzymes. J Plant Growth Regul 38:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-018-9810-2
Alam P, Albalawi TH, Altalayan FH, Bakht MA, Ahanger MA, Raja V, Ashraf M, Ahmad P (2019) 24-Epibrassinolide (EBR) confers tolerance against NaCl stress in soybean plants by up-regulating antioxidant system, ascorbate-glutathione cycle, and glyoxalase system. Biomolecules 9:640. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom91106405
Bao AK, Wang YW, Xi JJ, Liu C, Zhang JL, Wang SM (2013) Co-expression of xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum ZxNHX and ZxVP1-1 enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Lotus corniculatus by increasing cations accumulation. Funct Plant Biol 41:203–214. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP13106
Bao AK, Du BQ, Touil L, Kang P, Wang QL, Wang SM (2016) Co-expression of tonoplast Cation/H+ antiporter and H+-pyrophosphatase from xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum improves alfalfa plant growth under salinity, drought and field conditions. Plant Biotechnol J 14:964–975. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12451
Bassil E, Zhang S, Gong H, Tajima H, Blumwald E (2019) Cation specificity of vacuolar NHX-type cation/H+ antiporters. Plant Physiol 179:616–629. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01103
Brett CL, Donowitz M, Rao R (2005) Evolutionary origins of eukaryotic sodium/proton exchangers. Am J Physiol-Cell Physiol 288:C223–C239. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00360.2004
Broadley M, Brown P, Cakmak I, Rengel Z, Zhao F (2012) Chapter 7–Function of Nutrients: Micronutrients. In: Marschner P (ed) Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 191–248
Cai J-Y, Ma Q, Zhou X-R, Wang S (2011) Physiological role of Na+ in adaptation of Zygophyllum xanthoxylum to osmotic stress. Acta Pratacul Sin 20:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0883-9
Chai WW, Wang WY, Ma Q, Yin HJ, Hepworth SR, Wang SM (2019) Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals unique genetic adaptations conferring salt tolerance in a xerohalophyte. Funct Plant Biol 46:670–683. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP18295
Chanroj S, Wang G, Venema K, Zhang MW, Delwiche CF, Sze H (2012) Conserved and diversified gene families of monovalent cation/H+ antiporters from algae to flowering plants. Front Plant Sci 3:25. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.00025
Chen X, Bao H, Guo J, Jia W, Tai F, Nie L, Jiang P, Feng J, Lv S, Li Y (2014) Na+/H+ exchanger 1 participates in tobacco disease defence against Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae by affecting vacuolar pH and priming the antioxidative system. J Exp Bot 65:6107–6122. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru351
Chen Z, Zhao PX, Miao ZQ, Qi GF, Wang Z, Yuan Y, Ahmad N, Cao MJ, Hell R, Wirtz M (2019) SULTR3s function in chloroplast sulfate uptake and affect ABA biosynthesis and the stress response. Plant Physiol 180:593–604. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.01439
Corso M, Doccula FG, de Melo JRF, Costa A, Verbruggen N (2018) Endoplasmic reticulum-localized CCX2 is required for osmotolerance by regulating ER and cytosolic Ca2+ dynamics in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:3966–3971. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1720422115
Czempinski K, Frachisse JM, Maurel C, Barbier-Brygoo H, Mueller-Roeber B (2002) Vacuolar membrane localization of the Arabidopsis ‘two-pore’ K+ channel KCO1. Plant J 29:809–820. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2002.01260.x
Dansana PK, Kothari KS, Vij S, Tyagi AK (2014) OsiSAP1 overexpression improves water-deficit stress tolerance in transgenic rice by affecting expression of endogenous stress-related genes. Plant Cell Rep 33:1425–1440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-014-1626-3
Demidchik V, Davenport RJ, Tester M (2002) Nonselective cation channels in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:67–107. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.53.091901.161540
Djanaguiraman M, Prasad PVV (2013) Effects of salinity on ion transport, water relations and oxidative damage. In: Ahmad P, Azooz MM, Prasad MNV (eds) Ecophysiology and Responses of Plants under Salt Stress. Springer, New York, pp 89–114
Elsawy HI, Mekawy AMM, Elhity MA, Abdel-dayem SM, Abdelaziz MN, Assaha DV, Ueda A, Saneoka H (2018) Differential responses of two Egyptian barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars to salt stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 127:425–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.04.012
Elumalai RP, Nagpal P, Reed JW (2002) A mutation in the Arabidopsis KT2/KUP2 potassium transporter gene affects shoot cell expansion. Plant Cell 14:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.010322
Fahmideh L, Fooladvand Z (2018) Isolation and semi quantitative PCR of Na+/H+ Antiporter (SOS1 and NHX) genes under salinity stress in Kochia scoparia. Biol Proced Online 20:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12575-018-0076-7
Fan SC, Lin CS, Hsu PK, Lin SH, Tsay YF (2009) The Arabidopsis nitrate transporter NRT1.7, expressed in phloem, is responsible for source-to-sink remobilization of nitrate. Plant Cell 21:2750–2761. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.067603
Fan W, Deng G, Wang H, Zhang H, Zhang P (2014) Elevated compartmentalization of Na+ into vacuoles improves salt and cold stress tolerance in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas). Physiol Plant 154:560–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12301
Flowers TJ, Colmer TD (2015) Plant salt tolerance: adaptations in halophytes. Ann Bot 115:327–331. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu267
Gao TG, Ma CM, Yuan HJ, Liu HS, Ma Q, Flowers TJ, Wang SM (2021) ZxNHX1 indirectly participates in controlling K+ homeostasis in the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Funct Plant Biol 48:402–410. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP20185
García-Cerdán JG, Kovács L, Tóth T, Kereïche S, Aseeva E, Boekema EJ, Mamedov F, Funk C, Schröder WP (2011) The PsbW protein stabilizes the supramolecular organization of photosystem II in higher plants. Plant J 65:368–381. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04429.x
Gaxiola RA, Palmgren MG, Schumacher K (2007) Plant proton pumps. FEBS Lett 581:2204–2214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.050
Gebert M, Meschenmoser K, Svidová S, Weghuber J, Schweyen R, Eifler K, Lenz H, Weyand K, Knoop V (2009) A root-expressed magnesium transporter of the MRS2/MGT gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana allows for growth in low-Mg2+ environments. Plant Cell 21:4018–4030. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.070557
Gobert A, Park G, Amtmann A, Sanders D, Maathuis FJM (2006) Arabidopsis thaliana cyclic nucleotide gated channel 3 forms a non-selective ion transporter involved in germination and cation transport. J Exp Bot 57:791–800. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj064
Gong Z, Xiong L, Shi H, Yang S, Herrera-Estrella LR, Xu G, Chao DY, Li J, Wang PY, Qin F, Li J, Ding Y, Shi Y, Wang Y, Yang Y, Guo Y, Zhu JK (2020) Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci China Life Sci 63:635–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-020-1683-x
Hirsch RE, Lewis BD, Spalding EP, Sussman MR (1998) A role for the AKT1 potassium channel in plant nutrition. Science 280:918–921. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.280.5365.918
Hsu PK, Tsay YF (2013) Two phloem nitrate transporters, NRT1.11 and NRT1.12, are important for redistributing xylem-borne nitrate to enhance plant growth. Plant Physiol 163:844–856. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.226563
Huang G, Shan C (2018) Lanthanum improves the antioxidant capacity in chloroplast of tomato seedlings through ascorbate-glutathione cycle under salt stress. Sci Hortic 232:264–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.01.025
Huang X, Hu P, Zhang J (2020) Genomic analysis of the prognostic value of colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) and colony-stimulating factor receptors (CSFRs) across 24 solid cancer types. Ann Transl Med. 16:994. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-5363
Jin Y, Jing W, Zhang Q, Zhang W (2015) Cyclic nucleotide gated channel 10 negatively regulates salt tolerance by mediating Na+ transport in Arabidopsis. J Plant Res 128:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-014-0679-2
Kaur H, Sirhindi G, Bhardwaj R, Alyemeni MN, Siddique KHM, Ahmad P (2018) 28-homobrassinolide regulates antioxidant enzyme activities and gene expression in response to salt- and temperature-induced oxidative stress in Brassica juncea. Sci Rep 8:8735. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27032-w
Kaya C, Higgs D, Ashraf M, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2020) Integrative roles of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in melatonin-induced tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants to iron deficiency and salt stress alone or in combination. Physiol Plant 168:256–277. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12976
Kudo M, Kidokoro S, Yoshida T, Mizoi J, Todaka D, Fernie AR, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2017) Double overexpression of DREB and PIF transcription factors improves drought stress tolerance and cell elongation in transgenic plants. Plant Biotechnol J 15:458–471. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12644
Li Z, Wang X, Chen J, Gao J, Zhou X, Kuai B (2016) CCX1, a putative cation/Ca2+ exchanger, participates in regulation of reactive oxygen species homeostasis and leaf senescence. Plant Cell Physiol 57:2611–2619. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcw175
Lilley RM, Holborow K, Walker D (1974) Magnesium activation of photosynthetic CO2-fixation in a reconstituted chloroplast system. New Phytol 73:657–662. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.1974.tb01292.x
Loqué D, Yuan L, Kojima S, Gojon A, Wirth J, Gazzarrini S, Ishiyama K, Takahashi H, Von Wirén N (2006) Additive contribution of AMT1;1 and AMT1;3 to high-affinity ammonium uptake across the plasma membrane of nitrogen-deficient Arabidopsis roots. Plant J 48:522–534. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02887.x
Lu M, Zhang Y, Tang S, Pan J, Yu Y, Han J, Li Y, Du X, Nan Z, Sun Q (2016) AtCNGC2 is involved in jasmonic acid-induced calcium mobilization. J Exp Bot 67:809–819. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv500
Ma Q, Yue LJ, Zhang JL, Wu GQ, Bao AK, Wang SM (2012) Sodium chloride improves photosynthesis and water status in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Tree Physiol 32:4–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpr098
Ma Q, Bao AK, Chai WW, Wang WY, Zhang JL, Li YX, Wang SM (2016) Transcriptomic analysis of the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum in response to salt treatment and osmotic stress. Plant Soil 402:343–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-016-2809-1
Ma Q, Hu J, Zhou XR, Yuan HJ, Kumar T, Luan S, Wang SM (2017) ZxAKT1 is essential for K+ uptake and K+/Na+ homeostasis in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Plant J 90:48–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13465
Mabbitt PD, Wilbanks SM, Eaton-Rye JJ (2014) Structure and function of the hydrophilic Photosystem II assembly proteins: Psb27, Psb28 and Ycf48. Plant Physiol Biochem 81:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.02.013
Maguire ME, Cowan JA (2002) Magnesium chemistry and biochemistry. Biometals 15:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016058229972
Manohar M, Shigaki T, Hirschi K (2011) Plant cation/H+ exchangers (CAXs): biological functions and genetic manipulations. Plant Biol 13:561–569. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2011.00466.x
Manuel NC, Reyes R, Alain C, Rivero RM, Vicente M, Isabelle G, Francisco R (2016) Uneven HAK/KUP/KT protein diversity among angiosperms: species distribution and perspectives. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00127
Mori IC, Nobukiyo Y, Nakahara Y, Shibasaka M, Furuichi T, Katsuhara M (2018) A cyclic nucleotide-gated channel, HvCNGC2-3, is activated by the co-presence of Na+ and K+ and permeable to Na+ and K+ non-selectively. Plants 7:61. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants7030061
Mullan DJ, Colmer TD, Francki MG (2007) Arabidopsis–rice–wheat gene orthologues for Na+ transport and transcript analysis in wheat–L. elongatum aneuploids under salt stress. Mol Genets Genomics 277:199–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-006-0184-y
Nieves-Cordones M, Martínez V, Benito B, Rubio F (2016) Comparison between Arabidopsis and Rice for Main Pathways of K+ and Na+ Uptake by Roots. Front Plant Sci 7:992. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00992
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 49:249–279. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.249
Pardo JM, Cubero B, Leidi EO, Quintero FJ (2006) Alkali cation exchangers: roles in cellular homeostasis and stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 57:1181–1199. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erj114
Qi J, Song CP, Wang B, Zhou J, Kangasjärvi J, Zhu JK, Gong Z (2018) Reactive oxygen species signaling and stomatal movement in plant responses to drought stress and pathogen attack. J Integr Plant Biol 60:805–826. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12654
Reguera M, Bassil E, Blumwald E (2014) Intracellular NHX-type cation/H+ antiporters in plants. Mol Plant 7:261–263. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/sst091
Rodríguez-Rosales MP, Gálvez FJ, Huertas R, Aranda MN, Baghour M, Cagnac O, Venema K (2009) Plant NHX cation/proton antiporters. Plant Signal Behav 4:265–276. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.4.4.7919
Rosas-Santiago P, Lagunas-Gómez D, Barkla BJ, Vera-Estrella R, Lalonde S, Jones A, Frommer WB, Zimmermannova O, Sychrová H, Pantoja O (2015) Identification of rice cornichon as a possible cargo receptor for the Golgi-localized sodium transporter OsHKT1;3. J Exp Bot 66:2733–2748. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv069
Shabala S (2013) Learning from halophytes: physiological basis and strategies to improve abiotic stress tolerance in crops. Ann Bot 112:1209–1221. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mct205
Shalata A, Mittova V, Volokita M, Guy M, Tal M (2001) Response of the cultivated tomato and its wild salt-tolerant relative Lycopersicon pennellii to salt-dependent oxidative stress: the root antioxidative system. Physiol Plant 112:487–494. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2001.1120405.x
Sonoda Y, Ikeda A, Saiki S, Nv W, Yamaya T, Yamaguchi J (2003) Distinct expression and function of three ammonium transporter genes (OsAMT1;1–1;3) in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 44:726–734. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcg083
Sunarpi HT, Motoda J, Kubo M, Yang H, Yoda K, Horie R, Chan WY, Leung HY, Hattori K, Konomi M, Osumi M, Yamagami M, Schroeder JI, Uozumi N (2005) Enhanced salt tolerance mediated by AtHKT1 transporter-induced Na+ unloading from xylem vessels to xylem parenchyma cells. Plant J 44:928–938. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02595.x
Terry KL (1982) Nitrate uptake and assimilation in Thalassiosira weissflogii and Phaeodactylum tricornutum: interactions with photosynthesis and with the uptake of other ions. Mar Biol 69:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00396956
Toranj S, Aliabad KK, Abbaspour H, Saeedpour A (2020) Effect of salt stress on the genes expression of the vacuolar H+ -pyrophosphatase and Na+/H+ antiporter in Rubia tinctorum. Mol Biol Rep 47:235–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-019-05124-8
Wang SM, Wan CG, Wang YR, Chen H, Zhou ZY, Fu H, Sosebee RE (2004) The characteristics of Na+, K+ and free proline distribution in several drought-resistant plants of the Alxa Desert, China. J Arid Environ 56:525–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-1963(03)00063-6
Wang YF, Munemasa S, Nishimura N, Ren HM, Robert N, Han M, Puzõrjova I, Kollist H, Lee S, Mori I (2013) Identification of cyclic GMP-activated nonselective Ca2+-permeable cation channels and associated CNGC5 and CNGC6 genes in Arabidopsis guard cells. Plant Physiol 163:578–590. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.225045
Wang Y, Kang Y, Ma C, Miao R, Wu C, Long Y, Ge T, Wu Z, Hou X, Zhang J (2017) CNGC2 is a Ca2+ influx channel that prevents accumulation of apoplastic Ca2+ in the leaf. Plant Physiol 173:1342–1354. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01222
Wang WY, Chai WW, Zhao CY, Rowland O, Wang BS, Song X, Liu YQ, Ma Q, Wang SM (2019) Under drought conditions NaCl improves the nutritional status of the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum but not of the glycophyte Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 182:597–606. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201970050
Wei T, Deng K, Wang H, Zhang L, Wang C, Song W, Zhang Y, Chen C (2018) Comparative transcriptome analyses reveal potential mechanisms of enhanced drought tolerance in transgenic Salvia miltiorrhiza plants expressing AtDREB1A from Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci 19:827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030827
Wu GQ, Xi JJ, Wang Q, Bao AK, Ma Q, Zhang JL, Wang SM (2011) The ZxNHX gene encoding tonoplast Na+/H+ antiporter from the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum plays important roles in response to salt and drought. J Plant Physiol 168:758–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2010.10.015
Yin HJ, Li MZ, Li DD, Khan S-A, Hepworth SR, Wang SM (2019) Transcriptome analysis reveals regulatory framework for salt and osmotic tolerance in a succulent xerophyte. BMC Plant Biol 19:88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1686-1
Yuan L, Loqué D, Kojima S, Rauch S, Ishiyama K, Inoue E, Takahashi H, von Wirén N (2007) The organization of high-affinity ammonium uptake in Arabidopsis roots depends on the spatial arrangement and biochemical properties of AMT1-type transporters. Plant Cell 19:2636–2652. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.052134
Yuan HJ, Ma Q, Wu GQ, Wang P, Hu J, Wang SM (2015) ZxNHX controls Na+ and K+ homeostasis at the whole-plant level in Zygophyllum xanthoxylum through feedback regulation of the expression of genes involved in their transport. Ann Bot 115:495–507. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu177
Yue LJ, Li SX, Ma Q, Zhou XR, Wu GQ, Bao AK, Zhang JL, Wang SM (2012) NaCl stimulates growth and alleviates water stress in the xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. J Arid Environ 87:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2012.06.002
Zelm E, Zhang Y, Testerink C (2020) Salt tolerance mechanisms of plants. Ann Rev Plant Biol 71:403–433. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-100005
Zhao C, Zhang H, Song C, Zhu JK, Shabala S (2020) Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. The Innovation 1:100017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2020.100017
Zhou J, Zhou HJ, Chen P, Zhang LL, Zhu JT, Li PF, Yang J, Ke YZ, Zhou YH, Li JN, Du H (2020) Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of the KT/HAK/KUP family in Brassica napus and its potential roles in the response to K+ deficiency. Int J Mol Sci 24:9487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21249487
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31730093 and 31971405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.-M.W. and Q.M. contributed to the study conception and design. C.-M.M. and X.-N.G. performed the material preparation. H.-S.L. and W.-W.Ch performed data collection and analysis. H.-S.L. completed the first draft of the manuscript. W.-W.Ch., R.-X.Zh., P.-Q.L., Q.M., and S.-M.W. revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Saddam Hussain.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HS., Guo, XN., Chai, WW. et al. RNAi-Based Transcriptome Suggests Candidate Genes Regulated by ZxNHX1 to Affect The Salt Tolerance of Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. J Plant Growth Regul 41, 2476–2490 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10460-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10460-w