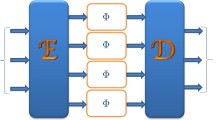
Abstract
We develop a theory of linear witnesses for detecting non-Markovianity, based on the geometric structure of the set of Choi states for all Markovian evolutions having Lindblad-type generators. We show that the set of all such Markovian Choi states form a convex and compact set under the small time interval approximation. Invoking geometric Hahn–Banach theorem, we construct linear witnesses to separate a given non-Markovian Choi state from the set of Markovian Choi states. We present examples of such witnesses for dephasing channel and Pauli channel in case of qubits. Furthermore, we have devised another method of detection NM of various qubit channels, by using projective measurements in the Bell basis. This can be done without the knowledge of what specific kind of channel we are dealing with. This gives us a huge operational advantage for NM detection. We further investigate the geometric structure of the Markovian Choi states to find that they do not form a polytope. This presents a platform to consider nonlinear improvement of non-Markovianity witnesses.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alicki, R., Lendi, K.: Quantum Dynamical Semigroups and Applications. Lecture notes in Physics. (Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg (2007)
Breuer, H. P., Petruccione, F.: The theory of open quantum systems ( Oxford University Press, address Great Clarendon Street) (2002)
Rivas, A., Huelga, S. F., Plenio, M. B.: Quantum non-Markovianity: characterization, quantification and detection, Vol. 77 ( 2014) p. 094001
Breuer, H.-P., Laine, E.-M., Piilo, J., Vacchini, B.: Colloquium, Vol. 88 ( American Physical Society, 2016) p. 021002
Wolf, M. M., Eisert, J., Cubitt, T. S., Cirac, J. I.: Assessing Non-Markovian Quantum Dynamics, Vol. 101 ( American Physical Society, 2008) p. 150402
de Vega, I., Alonso, D.: Dynamics of non-Markovian open quantum systems, Vol. 89 ( American Physical Society, 2017) p. 015001
Laine, E.-M., Piilo, J., Breuer, H.-P.: Measure for the non-Markovianity of quantum processes, Vol. 81 ( American Physical Society, 2010) p. 062115
Rivas, A., Huelga, S. F., Plenio, M. B.: Entanglement and Non-Markovianity of Quantum Evolutions, Vol. 105 ( American Physical Society, 2010) p. 050403
Bellomo, B., Lo Franco, R., Compagno, G.: Non-Markovian Effects on the Dynamics of Entanglement, Vol. 99 ( American Physical Society, 2007) p. 160502
Dijkstra, A. G., Tanimura, Y.: Non-Markovian Entanglement Dynamics in the Presence of System-Bath Coherence, Vol. 104 ( American Physical Society, 2010) p. 250401
Bhattacharya, S., Misra, A., Mukhopadhyay, C., Pati, A. K.: Exact master equation for a spin interacting with a spin bath: Non-Markovianity and negative entropy production rate, Vol. 95 ( American Physical Society, 2017) p. 012122
Mukhopadhyay, C., Bhattacharya, S., Misra, A., Pati, A. K.: Dynamics and thermodynamics of a central spin immersed in a spin bath, Vol. 96 ( American Physical Society, 2017) p. 052125
Awasthi, N., Bhattacharya, S., Sen(De), A., Sen, U.: Universal quantum uncertainty relations between nonergodicity and loss of information, Vol. 97 ( American Physical Society, 2018) p. 032103
Lu, X.-M., Wang, X., Sun, C. P.: Quantum Fisher information flow and non-Markovian processes of open systems, Vol. 82 ( American Physical Society, 2010) p. 042103
Rajagopal, A. K., Usha Devi, A. R., Rendell, R. W.: Kraus representation of quantum evolution and fidelity as manifestations of Markovian and non-Markovian forms, Vol. 82 ( American Physical Society, 2010) p. 042107
Luo, S., Fu, S., Song, H.: Quantifying non-Markovianity via correlations, Vol. 86 ( American Physical Society, 2012) p. 044101
Jiang, M., Luo, S.: Comparing quantum Markovianities: Distinguishability versus correlations, Vol. 88 ( American Physical Society, 2013) p. 034101
Lorenzo, S., Plastina, F., Paternostro, M.: Geometrical characterization of non-Markovianity, Vol. 88 ( American Physical Society, 2013) p. 020102
Dhar, H. S., Bera, M. N., Adesso, G.: Characterizing non-Markovianity via quantum interferometric power, Vol. 91 ( American Physical Society, 2015) p. 032115
Bylicka, B., Chruściński, D., Maniscalco, S.: Non-Markovianity as a Resource for Quantum Technologies (2013) arXiv:1301.2585 [quant-ph]
Horodecki, R., Horodecki, P., Horodecki, M., Horodecki, K.: Quantum entanglement, Vol. 81 ( American Physical Society, 2009) pp. 865–942
Bhattacharya, S., Bhattacharya, B., Majumdar, A. S.: Resource theory of non-Markovianity: A thermodynamic perspective (2018) arXiv:1803.06881 [quant-ph]
Horodecki, M., Horodecki, P., Horodecki, R.: Separability Mix. States: Necessar. Suffic. Cond. 223, 1–8 (1996)
Bourennane, M., Eibl, M., Kurtsiefer, C., Gaertner, S., Weinfurter, H., Gühne, O., Hyllus, P., Bruß, D., Lewenstein, M., Sanpera, A.: Experimental Detection of Multipartite Entanglement using Witness Operators, Vol. 92 (American Physical Society, 2004) p. 087902
Terhal, B.M.: Bell Inequal. Separability Criteri. 271, 319–326 (2000)
Lewenstein, M., Kraus, B., Cirac, J. I., Horodecki, P.: Optimization of entanglement witnesses, Vol. 62 (American Physical Society, 2000) p. 052310
Gühne, O., Hyllus, P., Bruß, D., Ekert, A., Lewenstein, M., Macchiavello, C., Sanpera, A.: Detection of entanglement with few local measurements, Vol. 66 (American Physical Society, 2002) p. 062305
Guhne, O., Toth, G.: Entanglement Detect. 474, 1–75 (2009)
Chruściński, D., Sarbicki, G.: Entanglement witnesses: construction, analysis and classification, Vol. 47 (2014) p. 483001
Gühne, O., Lu, C.-Y., Gao, W.-B., Pan, J.-W.: Toolbox for entanglement detection and fidelity estimation, Vol. 76 (American Physical Society, 2007) p. 030305
Zhang, C.-J., Zhang, Y.-S., Zhang, S., Guo, G.-C.: Entanglement detection beyond the computable cross-norm or realignment criterion, Vol. 77 (American Physical Society, 2008) p. 060301
Chruściński, D., Macchiavello, C., Maniscalco, S.: Detecting Non-Markovianity of Quantum Evolution via Spectra of Dynamical Maps, Vol. 118 (American Physical Society, 2017) p. 080404
Macchiavello, C., Rossi, M.: Quantum channel detection, Vol. 88 (American Physical Society, 2013) p. 042335
Orieux, A., Sansoni, L., Persechino, M., Mataloni, P., Rossi, M., Macchiavello, C.: Experimental Detection of Quantum Channels, Vol. 111 (American Physical Society, 2013) p. 220501
Kołodyński, J., Rana, S., Streltsov, A.: Entanglement negativity as a universal non-Markovianity witness, Vol. 101 (American Physical Society, 2020) p. 020303
Jamiolkowski, A.: Linear Trans. Preserve Trace Positive Semidefinit. Oper. 3, 275–278 (1972)
Choi, M.-D.: Completely Positive Linear Maps Complex Matrices 10, 285–290 (1975)
Wolf, M.M., Cirac, J.I.: Div. Quantum Channels 279, 147–168 (2008)
Berk, G. D., Garner, A. J. P., Yadin, B., Modi, K., Pollock, F. A.: Resource theories of multi-time processes: A window into quantum non-Markovianity ( 2019) p. , arXiv:1907.07003 [quant-ph]
Milz, S., Kim, M. S., Pollock, F. A., Modi, K.: Completely Positive Divisibility Does Not Mean Markovianity, Vol. 123 ( American Physical Society, 2019) p. 040401
Taranto, P., Pollock, F. A., Milz, S., Tomamichel, M., Modi, K.: Quantum Markov Order, Vol. 122 ( American Physical Society, 2019) p. 140401
Lindblad, G.: On the Generators of Quantum Dynamical Semigroups 48, 119–130 (1976)
Gorini, V., Kossakowski, A., Sudarshan, E.C.G.: Completely Positive Dynam Semigroups N-level Syst. 17, 821–825 (1976)
Hall, M. J. W., Cresser, J. D., Li, L., Andersson, E.: Canonical form of master equations and characterization of non-Markovianity, Vol. 89 ( American Physical Society, 2014) p. 042120
Cohen, J.E., Friedland, S., Kato, T., Kelly, F.P.: Eigenvalue Inequalities Products Matrix Exponentials 45, 55–95 (1982)
Rockafellar, R.: Convex Analysis (Princeton University Press, address 41 William Street, 1997)
Schlosshauer, M.: Quantum decoherence, Vol. 831 ( 2019) pp. 1–57, quantum decoherence
Pittenger, A.O., Rubin, M.H.: Convexity Separability Problem Quantum Mech. Density Matrices 346, 47–71 (2002)
Gühne, O., Lütkenhaus, N.: Nonlinear Entanglement Witnesses, Vol. 96 ( American Physical Society, 2006) p. 170502
Arrazola, J. M., Gittsovich, O., Lütkenhaus, N.: Accessible nonlinear entanglement witnesses, Vol. 85 ( American Physical Society, 2012) p. 062327
Gühne, O., Lütkenhaus, N.: Nonlinear entanglement witnesses, covariance matrices and the geometry of separable states, Vol. 67 ( 2007) p. 012004
Ioannou, L. M., Travaglione, B. C.: Quantum separability and entanglement detection via entanglement-witness search and global optimization, Vol. 73 ( American Physical Society, 2006) p. 052314
Nemhauser, G. L., Wolsey, L.: Integer and Combinatorial Optimization ( John Wiley and Sons, address Chichester, 2014)
Li, L., Hall, M. J., Wiseman, H. M.: Concepts of quantum non-Markovianity: A hierarchy, Vol. 759 ( 2018) pp. 1 – 51, concepts of quantum non-Markovianity: A hierarchy
Chruściński, D., Kossakowski, A., Rivas, A.: Measures of non-Markovianity: Divisibility versus backflow of information, Vol. 83 ( American Physical Society, 2011) p. 052128
Acknowledgements
Authors thank Manik Banik of SNBNCBS, Kolkata, for illuminating discussion. SB thanks SERB, DST, Government of India, for financial support. BB thanks DST INSPIRE programme for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharya, B., Bhattacharya, S. Convex geometry of Markovian Lindblad dynamics and witnessing non-Markovianity. Quantum Inf Process 20, 253 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03177-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03177-y