Abstract
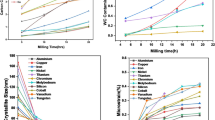
The effect of the mechanical milling of Sm2Fe17N3 nitride in a vibratory mill, in particular, the effect of the powder-to-ball mass ratio (m), milling time (tmill), milling medium, and concentration of added surfactants, has been systematically studied in order to determine optimum parameters for the high level of hysteresis properties of the magnetically anisotropic powder. It is shown that, as m increases from 15 to 50, the increase in the coercivity Hc of the powder at the beginning milling stages (tmill ≤ 4 h) is substantially accelerated; in this case, about 80% particles are less than 1 µm in size. As the milling time increases (tmill > 4 h), the coercivity continues to increase. However, the specific residual magnetization σr and maximum energy product (BH)max begin to decrease because of the developed process of particle agglomeration, which results in a deterioration of the powder allignment. The addition of a surfactant to the protective medium markedly intensifies the milling process and accelerates the kinetics of the increase of Hc at the beginning milling stages at m = 15. The best complex of magnetic hysteresis properties, σr ≥ 135 emu/g, Hc, ≥ 8 kOe, and (BH)max ≥ 18 MG Oe, is observed for powders milled in 5% solution of oleic acid in acetone, 5% solution of capronic acid in toluene, and 1% solution of methyl caproate in toluene.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. Suzuki, T. Miura, and M. Kawasaki, “Sm2Fe17Nx bonded magnets with high performance,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 29, No. 6, 2815–2817 (1993).
K. Makita and S. Hirosawa, “Coercivity of Zn evaporation-coated Sm2Fe17Nx fine powder and its bonded magnets,” J. Alloys Compd. 260, Nos. 1–2, 236–241 (1997).
W. Yamaguchi, R. Soda, and K. Takagi, “Metal-coated Sm2Fe17N3 magnet powders with an oxide-free direct metal-metal interface,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 498, 166101 (2020).
Y. Otani, A. Moukarika, H. Sun, J. M. D. Coey, E. Devlin, and I. R. Harris, “Metal bonded Sm2Fe17N3 – δ magnets,” J. Appl. Phys. 69, No. 9, 6735–6737 (1991).
W. Rodewald, B. Wall, M. Katter, M. Velicescu, and P. Schrey, “Microstructure and magnetic properties of Zn- or Sn-bonded Sm2Fe17Nx magnets,” J. Appl. Phys. 73, No. 10, 5899–5901 (1993).
M. Matsuura, T. Shiraiwa, N. Tezuka, S. Sugimoto, T. Shoji, N. Sakuma, and K. Haga, “High coercive Zn-bonded Sm–Fe–N magnets prepared using fine Zn particles with low oxygen content,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 452, 243–248 (2018).
M. Tokita, “Trends in advanced SPS spark plasma sintering systems and technology,” J. Soc. Powder Technol. Jpn. 30, No. 11, 790–804 (1993).
T. Saito, “Production of Sm–Fe–N bulk magnets by spark plasma sintering method,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 369, 184–188 (2014).
D. Zhang, M. Yue, and J. Zhang, “Structure and magnetic properties of Sm2Fel7Nx sintering magnets prepared by spark plasma sintering,” J. Rare Earths. 24, 325–328 (2006).
T. Saito, “Structures and magnetic properties of Sm–Fe–N bulk magnets produced by the spark plasma sintering method,” J. Mater. Res. 22, No. 11, 3130–3136 (2007).
K. Takagi, H. Nakayama, and K. Ozaki, “Microstructural behavior on particle surfaces and interfaces in Sm2Fe17N3 powder compacts during low-temperature sintering,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, No. 15, 2336–2341 (2012).
D. Prabhu, H. Sepehri-Amin, C. L. Mendis, T. Ohkubo, K. Hono, and S. Sugimoto, “Enhanced coercivity of spark plasma sintered Zn-bonded Sm–Fe–N magnets,” Scr. Mater. 67, No. 2, 153–156 (2012).
D. V. Dudina and A. K. Mukherjee, “Reactive spark plasma sintering: successes and challenges of nanomaterial synthesis,” J. Nanomater. 11, 625218 (2013).
T. Saito, T. Deguchi, and H. Yamamoto, “Magnetic properties of Sm–Fe–N bulk magnets produced from Cu-plated Sm–Fe–N powder,” AIP Adv. 7, 056204 (2017).
A. Kawamoto, T. Ishikawa, S. Yasuda, K. Takeya, K. Ishizaka, T. Iseki, and K. Ohmori, “Sm2Fe17N3 magnet powder made by reduction and diffusion method,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 35, 3322–3324 (1999).
J. Lee, S. Kang, P. Si, and C. Choi, “The influence of mechanical milling on the structure and magnetic properties of Sm–Fe–N powder Produced by the reduction-diffusion process,” J. Magn. 16, No. 2, 104–107 (2011).
S. Okada, K. Suzuki, E. Node, K. Takagi, K. Ozaki, and Y. Enokido, “Preparation of submicron-sized Sm2Fe17N3 fine powder with high coercivity by reduction-diffusion process,” J. Alloys Compd. 695, 1617–1623 (2017).
S. Okada, K. Suzuki, E. Node, K. Takagi, K. Ozaki, and Y. Enokido, “Improvement of magnetization of submicron-sized high coercivity Sm2Fe17N3 powder by using hydrothermally synthesized sintering-tolerant cubic hematite,” AIP Adv. 7, 056219 (2017).
P. A. P. Wendhausen, B. Gebel, D. Eckert, and K.‑H. Müller, “Effect of milling on the magnetic and microstructural properties of Sm2Fe17Nx permanent magnets,” J. Appl. Phys. 75, No. 10, 6018–6020 (1994).
K. Kobayashi, R. Skomski, and J. M. D. Coey, “Dependence of coercivity on particle size in Sm2Fe17N3 powders,” J. Alloys Compd. 222, Nos. 1–2, 1–7 (1995).
J. L. Wang, W. Z. Li, X. P. Zhong, Y. H. Gao, W. D. Qin, N. Tang, W. G. Lin, J. X. Zhang, R. W. Zhao, Q. W. Yan, and F.-m. Yang, “Study on high performance Sm2Fe17Nx magnets,” J. Alloys Compd. 222, Nos. 1–2, 23–26 (1995).
M. Xing, J. Han, F. Wan, S. Liu, C. Wang, J. Yang, and Y. Yang, “Preparation of anisotropic magnetic materials by strip casting technique,” IEEE Trans. Magn. 49, No. 7, 3248–3250 (2013).
T. Mukai and T. Fujimoto, “Kerr microscopy observation of nitrogenated Sm2Fe17 intermetallic compounds,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 103, Nos. 1–2, 165–173 (1992).
V. M. Chakka, B. Altuncevahir, Z. Q. Jin, Y. Li, and J. P. Liu, “Magnetic nanoparticles produced by surfactant-assisted ball milling,” J. Appl. Phys. 99, No. 8. 08E912 (2006).
M. Yue, Y. P. Wang, N. Poudyal, C. B. Rong, and J. P. Liu, “Preparation of Nd–Fe–B nanoparticles by surfactant-assisted ball milling technique,” J. Appl. Phys. 105, No. 7. 07A708 (2009).
N. Poudyal, C. Rong, and J. P. Liu, “Effects of particle size and composition on coercivity of Sm–Co nanoparticles prepared by surfactant-assisted ball milling,” J. Appl. Phys. 107, No. 9. 09A703 (2010).
C. A. Crouse, E. Michel, Y. Shen, S. J. Knutson, B. K. Hardenstein, J. E. Spowart, S. O. Leontsev, S. L. Semiatin, J. Horwath, Z. Turgut, and M. S. Lucas, “Effect of surfactant molecular weight on particle morphology of SmCo5 prepared by high energy ball milling,” J. Appl. Phys. 111, No. 7. 07A724 (2012).
L. Zhao, N. G. Akdogan, and G. C. Hadjipanayis, “Hard magnetic Sm2Fe17N3 flakes nitrogenized at lower temperature,” J. Alloys Compd. 554, 147–149 (2013).
M. Ullah, Md. E. Ali, and Sh. B. A. Hamid, “Surfactant-assisted ball milling: a novel route to novel materials with controlled nanostructure—A review,” Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 37, 1–14 (2014).
P. A. Rebinder and E. D. Shchukin, “Surface phenomena in solids in the processes of their deformation and destruction,” Usp. Fiz. Nauk 108, No. 1, 3–42 (1972).
X. B. Ma, L. Z. Li, S. Q. Liu, B. Y. Hu, J. Z. Han, C. S. Wang, H. L. Du, Y. C. Yang, and J. B. Yang, ”Anisotropic Sm–Fe–N particles prepared by surfactant-assisted grinding method,” J. Alloys Compd. 612, 110–113 (2014).
M. Yue, Y. Q. Li, R. M. Liu, W. Q. Liu, Z. H. Guo, and W. Li, “Abnormal size-dependent coercivity in ternary Sm–Fe–N nanoparticles,” J. Alloys Compd. 637, 297–300 (2015).
C. Lu, X. Hong, X. Bao, X. Gao, and J. Zhu, “Changing phase equilibria: A method for microstructure optimization and properties improvement in preparing anisotropic Sm2Fe17N3 powders,” J. Alloys Compd. 784, 980–989 (2019).
Y. Li, F. Wang, J. P. Liu, F. Wang, S. Wang, and J. Zhang, “Fabrication of remarkably magnetic-property-enhanced anisotropic Sm2Fe17Nx nanoflakes by surfactant assisted ball milling at low temperature,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 498, 166191 (2020).
D. A. Kolodkin, A. G. Popov, A. V. Protasov, V. S. Gaviko, D. Yu. Vasilenko, S. Kavita, D. Prabhu, and R. Gopalan, “Magnetic properties of Sm2 + αFe17Nx powders prepared from bulk and strip-cast alloys,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 518, 167416 (2021).
A. P. Menushenkov, A. G. Savchenko, V. G. Ivanov, A. A. Ivanov, I. V. Shchetinin, V. P. Menushenkov, I. A. Rudnev, A. V. Rafal’skii, D. G. Zhukov, M. Platunov, F. Vilkhel’m, and A. Rogalev, ”Effect of nitrogenation and hydrogenation on the magnetic properties and structure of the Sm2Fe17 alloy: Analysis of xmcd data,” JETP Lett. 107, No. 4, 228–232 (2018).
I. V. Shchetinin, I. G. Bordyuzhin, R. V. Sundeev, V. P. Menushenkov, A. V. Kamynin, V. N. Verbetsky, and A. G. Savchenko, “Structure and magnetic properties of Sm2Fe17Nx alloys after severe plastic deformation by high pressure torsion,” Mater. Lett. 274. 127993 (2020).
A. G. Popov, V. S. Gaviko, N. N. Shchegoleva, O. A. Golovnia, T. I. Gorbunova, and G. C. Hadjipanayis, “Effect of addition of esters of fatty acids on the microstructure and properties of sintered Nd–Fe–B magnets produced by PLP,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 386, 134–140 (2015).
V. P. Tarasov, A. S. Ignatov, and D. A. Kutepov, “Development of methods for enhancing the corrosion resistance of Sm2Fe17N3 hard magnetic materials,” Metallurg, No. 11, 74–76 (2016).
A. V. Kutepov, V. P. Tarasov, and A. S. Ignatov, “Optimization of nitriding condition of Sm2Fe17 alloys powders,” Metallurg, No. 12, 59–62 (2016).
Funding
This study was performed in terms of a state assignment of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education (theme Magnit, no. АААА-А18-118020290129-5). The X-ray diffraction studies and measurements of magnetic properties were carried out at the Center for Collective Use of the Mikheev Institute of Metal Physics, Ural Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences, Yekaterinburg, Russia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by N. Kolchugina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolodkin, D.A., Popov, A.G. & Gaviko, V.S. Enhancement of the Coercive Force of Sm2Fe17N3 Powders via Surfactant Added Mechanical Milling. Phys. Metals Metallogr. 122, 547–558 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X21060053
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0031918X21060053