Abstract
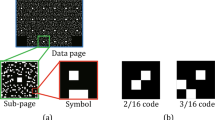
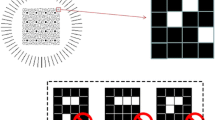
We developed a modulation code using a complex amplitude and established a method to demodulate the code based on a convolutional neural network (CNN) for holographic data storage. The developed 20:9 modulation code consists of nine symbols, each of which contains 4 bits of data representing the symbol position on which the complex amplitude is superimposed and 16 bits of data representing the actual complex amplitude value. By solving an optimization problem, the complex amplitude signal combines four amplitude values and a different phase value for each amplitude; thus, the data are robust against amplitude and phase noise, and the amplitude and phase values are distributed over a uniform distance in the constellation diagram. Modulation tables were also optimized using a genetic algorithm. Because the occurrence of bit errors due to amplitude and phase noise must be considered when reproducing data, two CNNs separately demodulate the symbol position signal and the complex amplitude signal superimposed thereon. By inputting reproduced data and label information indicating the demodulation target, we created a compact CNN. We confirmed that the CNN demodulation can accurately demodulate both signals; moreover, the total bit errors were reduced to less than half of those for the conventional hard decision demodulation method.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ushiyama, Z., Kurata, H., Tsukamoto, Y., Yoshida, S., Yamamoto, M.: Shift-peristrophic multiplexing for high density holographic data storage. Appl. Sci. (2014). https://doi.org/10.3390/app4020148
Ayres, M., Anderson, K., Askham, F., Sissom, B., Urness, A.: Multi-terabit/in2 holographic data storage demonstration, vol. 9587. SPIE Optical Engineering + Applications (2015)
Hoshizawa, T., Shimada, K., Fujita, K., Tada, Y.: Practical angular-multiplexing holographic data storage system with 2 terabyte capacity and 1 gigabit transfer rate. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. (2016). https://doi.org/10.7567/jjap.55.09sa06
Nobukawa, T., Nomura, T.: Multilevel recording of complex amplitude data pages in a holographic data storage system using digital holography. Opt. Express 24(18), 21001–21011 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.24.021001
Bunsen, M., Tateyama, S.: Detection method for the complex amplitude of a signal beam with intensity and phase modulation using the transport of intensity equation for holographic data storage. Opt. Express 27(17), 24029–24042 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.27.024029
Honma, S., Funakoshi, H.: A two-step exposure method with interleaved phase pages for recording of SQAM signal in holographic memory. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. (2019). https://doi.org/10.7567/1347-4065/ab2be1
Nakamura, Y., Hoshizawa, T.: Two high-density recording methods with run-length limited turbo code for holographic data storage system. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. (2016). https://doi.org/10.7567/jjap.55.09sa01
Hesselink, L., Orlov, S.S., Bashaw, M.C.: Holographic data storage systems. Proc. IEEE 92(8), 1231–1280 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/jproc.2004.831212
Shimobaba, T., Kuwata, N., Homma, M., Takahashi, T., Nagahama, Y., Sano, M., Hasegawa, S., Hirayama, R., Kakue, T., Shiraki, A., Takada, N., Ito, T.: Convolutional neural network-based data page classification for holographic memory. Appl. Opt. 56(26), 7327–7330 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.56.007327
Katano, Y., Muroi, T., Kinoshita, N., Ishii, N., Hayashi, N.: Data demodulation using convolutional neural networks for holographic data storage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. (2018). https://doi.org/10.7567/jjap.57.09sc01
Katano, Y., Muroi, T., Kinoshita, N., Ishii, N.: Demodulation of multi-level data using convolutional neural network in holographic data storage. In: 2018 Digital image computing: techniques and applications (DICTA), 10–13, pp. 1–5 (2018)
Awatsuji, Y., Fujii, A., Kubota, T., Matoba, O.: Parallel three-step phase-shifting digital holography. Appl. Opt. 45(13), 2995–3002 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.45.002995
He, M., Cao, L., Tan, Q., He, Q., Jin, G.: Novel phase detection method for a holographic data storage system using two interferograms. J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 11(6), 065705 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1464-4258/11/6/065705
Liu, J., Horimai, H., Lin, X., Huang, Y., Tan, X.: Phase modulated high density collinear holographic data storage system with phase-retrieval reference beam locking and orthogonal reference encoding. Opt. Express 26(4), 3828–3838 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.26.003828
Kinoshita, N., Katano, Y., Nobukawa, T., Muroi, T., Ishii, N.: Improvement of signal quality for multi-level amplitude modulation in holographic data storage. In: Shimura, T. (ed.) International symposium on imaging, sensing, and optical memory, pp. 67–68 (2019)
Fletcher, R.: Practical methods of optimization, 2nd edn. A Wiley-Interscience publication, Wiley (2000)
Goto, Y., Okamoto, A., Takabayashi, M., Ogawa, K., Tomita, A.: Experimental implementation of multiplexing/demultiplexing in digital images using virtual phase conjugation for holographic data storage. Opt. Rev. 25(5), 549–554 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-018-0446-z
Yoneda, N., Saita, Y., Komuro, K., Nobukawa, T., Nomura, T.: Transport-of-intensity holographic data storage based on a computer-generated hologram. Appl. Opt. 57(30), 8836–8840 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.008836
Ishii, N., Katano, Y., Muroi, T., Kinoshita, N.: 10:9 modulation code for multi-level recording and error correction method using spatially coupled LDPC in HDS. In: Shimura, T. (ed.) International symposium on imaging, sensing, and optical memory, pp. 149–150 (2019)
Goldberg, D.E., Lingle, R.: Alleles, loci, and the traveling salesman problem. In: Grefenstette, J.J. (ed.) Proceedings of an international conference on genetic algorithms and their applications 1985, pp. 154–159. Lawrence Erlbaum Hillsdale, NJ
Kurokawa, S., Yoshida, S.: Convolutional neural network based demodulation for constant-weight codes in holographic data storage. In: Shimura, T. (ed.) International symposium on imaging, sensing, and optical memory, pp. 67–68 (2020)
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Maas, A.L., Hannun, A.Y., Ng, A.Y.: Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In: Dasgupta, S., McAllester, D. (eds.) Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning 2013, vol. 1
Muroi, T., Katano, Y., Kinoshita, N., Ishii, N.: Spatial filter and combination of angle and peristrophic multiplexings to achieve recording density of 1 Tbit/inch2 in holographic data storage. ITE Trans. Media Technol. Appl. 9(3), 153–160 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3169/mta.9.153
Katano, Y., Nobukawa, T., Muroi, T., Kinoshita, N., Ishii, N.: Efficient decoding method for holographic data storage combining convolutional neural network and spatially coupled low-density parity-check code. ITE Trans. Media Technol. Appl. 9(3), 161–168 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3169/mta.9.161
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katano, Y., Nobukawa, T., Muroi, T. et al. CNN-based demodulation for a complex amplitude modulation code in holographic data storage. Opt Rev 28, 662–672 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-021-00687-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10043-021-00687-z