Abstract
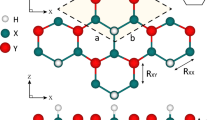
Two-dimensional thermoelectric materials have been extensively explored in recent years for their potential to recycle waste heat into clean energy. Herein, we investigate the thermoelectric properties of hexagonal- and square-shaped monolayers of ZnO for renewable energy applications. These monolayers have been originated from the 110- and 011-facets of β-BeO type structured ZnO (β-BeO-ZnO). To execute this study, the electronic structures of these monolayers have been obtained within the framework of density functional theory (DFT). The results of electronic structures have been used to obtain the thermoelectric properties against chemical potential and temperature using the semi-classical Boltzmann transport theory (BTT). The high electrical conductivities and substantial Seebeck coefficient equivalent to 1500 μV/K have been recorded for 110-monolayer and 2716.75 μV/K for 011-monolayer. As a result, large thermoelectric power factors (PF) of magnitude 7.96 × 1010 W/mK2s at 0.49 eV for 110- monolayer and 4.63 × 1010 W/mK2s at 1.83 eV recorded for 011-monolayer. The PF of these monolayers has experienced a linear increase with the rise in temperature. Moreover, the thermoelectric figure-of-merit (zT) values have been recorded as ~ 1.02 and ~ 1 for 110- and 011-monolayer. The zT of 011-monolayer has been found to decrease for an increase in temperature beyond 450 K whereas zT of 110-monolayer has been found insensitive to change in temperature. This reveals the potential of ZnO monolayers (110-monolayer in particular) for applications in high-temperature thermoelectric devices.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
This manuscript has associated data in a data repository. [Authors’ comment: The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.]
References
J.P. Heremans, M.S. Dresselhaus, L.E. Bell, D.T. Morelli, When thermoelectrics reached the nanoscale. Nat. Nanotechnol. 8, 471 (2013)
C.B. Vining, An inconvenient truth about thermoelectrics. Nat. Mater. 8, 83–85 (2009)
Y. Pei, A.D. LaLonde, H. Wang, G.J. Snyder, Low effective mass leading to high thermoelectric performance. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 7963–7969 (2012)
S. Jantrasee, P. Moontragoon, S. Pinitsoontorn, Thermoelectric properties of Al-doped ZnO: experiment and simulation. J. Semicond. 37, 092002 (2016)
M. Ohtaki, T. Tsubota, K. Eguchi, H. Arai, High-temperature thermoelectric properties of (Zn1− x Al x) O. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 1816–1818 (1996)
P. Jood, R.J. Mehta, Y. Zhang, G. Peleckis, X. Wang, R.W. Siegel, T. Borca-Tasciuc, S.X. Dou, G. Ramanath, Al-doped zinc oxide nanocomposites with enhanced thermoelectric properties. Nano Lett. 11, 4337–4342 (2011)
L. Hicks, M.S. Dresselhaus, Effect of quantum-well structures on the thermoelectric figure of merit. Phys. Rev. B 47, 12727 (1993)
M.G. Kanatzidis, Nanostructured thermoelectrics: The new paradigm? Chem. Mater. 22, 648–659 (2010)
Y. Xiao, L.-D. Zhao, Charge and phonon transport in PbTe-based thermoelectric materials. npj Quantum Mater. 3, 1–12 (2018)
C. Wang, Y. Wang, G. Zhang, C. Peng, G. Yang, Theoretical investigation of the effects of doping on the electronic structure and thermoelectric properties of ZnO nanowires. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 3771–3776 (2014)
D. Misra, A. Bhardwaj, S. Singh, Enhanced thermoelectric performance of a new half-Heusler derivative Zr 9 Ni 7 Sn 8 bulk nanocomposite: enhanced electrical conductivity and low thermal conductivity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 11913–11921 (2014)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, A. Laref, Design and characterization of novel polymorphs of single-layered tin-sulfide for direction-dependent thermoelectric applications using first-principles approaches. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 4624–4632 (2019)
B. UlHaq, S. AlFaify, A. Laref, Exploring novel flat-band polymorphs of single-layered Germanium Sulfide for high-efficiency thermoelectric applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 123, 18124–18131 (2019)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, A. Laref, R. Ahmed, M. Taib, Dimensionality reduction of germanium selenide for high-efficiency thermoelectric applications. Ceram. Int. 45, 15122–15127 (2019)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, T. Alshahrani, R. Ahmed, F.K. Butt, S.U. Rehman, Z. Tariq, Devising square-and hexagonal-shaped monolayers of ZnO for nanoscale electronic and optoelectronic applications. Sol. Energy 211, 920–927 (2020)
A.I. Boukai, Y. Bunimovich, J. Tahir-Kheli, J.-K. Yu, W.A. Goddard Iii, J.R. Heath, Silicon nanowires as efficient thermoelectric materials. Nature 451, 168–171 (2008)
Z.-Y. Hu, K.-Y. Li, Y. Lu, Y. Huang, X.-H. Shao, High thermoelectric performances of monolayer SnSe allotropes. Nanoscale 9, 16093–16100 (2017)
S. Singh, M.N. Tripathi, Enhanced optoelectronic property of ZnO under negative pressure condition: a first-principles study. Mater. Res. Express 3, 086301 (2016)
W. Sangthong, J. Limtrakul, F. Illas, S.T. Bromley, Predicting transition pressures for obtaining nanoporous semiconductor polymorphs: oxides and chalcogenides of Zn, Cd and Mg. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12, 8513–8520 (2010)
D. Zagorac, J. Schön, J. Zagorac, M. Jansen, Prediction of structure candidates for zinc oxide as a function of pressure and investigation of their electronic properties. Phys. Rev. B 89, 075201 (2014)
B.J. Morgan, First-principles study of epitaxial strain as a method of B 4→ B C T stabilization in ZnO, ZnS, and CdS,. Phys. Rev. B 82, 153408 (2010)
J. Wang, P. Xiao, M. Zhou, Z. Wang, F. Ke, Wurtzite-to-tetragonal structure phase transformation and size effect in ZnO nanorods. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 023512 (2010)
S. Shabbir, A. Shaari, B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed, M. Ahmed, Investigations of novel polymorphs of ZnO for optoelectronic applications. Optik 206, 164285 (2020)
B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed, A. Shaari, F.E.H. Hassan, M.B. Kanoun, S. Goumri-Said, Study of wurtzite and zincblende GaN/InN based solar cells alloys: first-principles investigation within the improved modified Becke-Johnson potential. Sol. Energy 107, 543–552 (2014)
B.U. Haq, A. Afaq, G. Abdellatif, R. Ahmed, S. Naseem, R. Khenata, First principles study of scandium nitride and yttrium nitride alloy system: prospective material for optoelectronics. Superlattices Microstruct. 85, 24–33 (2015)
B.U. Haq, M.B. Kanoun, R. Ahmed, M. Bououdina, S. Goumri-Said, Hybrid functional calculations of potential hydrogen storage material: complex dimagnesium iron hydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39, 9709–9717 (2014)
B. UlHaq, R. Ahmed, S. Goumri-Said, A. Shaari, A. Afaq, Electronic structure engineering of ZnO with the modified Becke-Johnson exchange versus the classical correlation potential approaches. Phase Trans. 86, 1167–1177 (2013)
B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed, S. Goumri-Said, DFT characterization of cadmium doped zinc oxide for photovoltaic and solar cell applications. Sol. Energy Mater Sol. Cells 130, 6–14 (2014)
B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed, J.Y. Rhee, A. Shaari, S. AlFaify, M. Ahmed, Composition-induced influence on the electronic band structure, optical and thermoelectric coefficients of the highly mismatched GaNSb alloy over the entire range: a DFT analysis. J Alloys Compd. 693, 1020–1027 (2017)
B.U. Haq, R. Ahmed, M. Mohamad, A. Shaari, J. Rhee, S. AlFaify, M.B. Kanoun, S. Goumri-Said, Engineering of highly mismatched alloy with semiconductor and semi-metallic substituent’s for photovoltaic applications. Curr. Appl. Phys. 17, 162–168 (2017)
D. Koller, F. Tran, P. Blaha, Merits and limits of the modified Becke-Johnson exchange potential. Phys. Rev. B 83, 195134 (2011)
D. Koller, F. Tran, P. Blaha, Improving the modified Becke-Johnson exchange potential. Phys. Rev. B 85, 155109 (2012)
F. Tran, P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, Band gap calculations with Becke-Johnson exchange potential. J. Phys. Condensed Matter 19, 196208 (2007)
P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, G.K. Madsen, D. Kvasnicka, J. Luitz, WIEN2K, An Augmented Plane Wave+ Local Orbitals Program for Calculating Crystal Properties, ed. by K. Schwarz (Vienna University of Technology, Austria, 2001)
G.K. Madsen, D.J. Singh, BoltzTraP. A code for calculating band-structure dependent quantities. Comput. Phys. Commun. 175, 67–71 (2006)
P. Sikam, C. Sararat, P. Moontragoon, T. Kaewmaraya, S. Maensiri, Enhanced thermoelectric properties of N-doped ZnO and SrTiO3: a first-principles study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 446, 47–58 (2018)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, T. Alshahrani, R. Ahmed, Q. Mahmood, D. Hoat, S. Tahir, Investigations of thermoelectric properties of ZnO monolayers from the first-principles approach. Phys. E Low-dimensional Syst. Nanostruct. 126, 114444 (2021)
B.U. Haq, First-principles calculations to investigate thermoelectric properties of new monolayers of ZnO. Optik 238, 166782 (2021)
B.U. Haq, S. AlFaify, T. Al-shahrani, S. Al-Qaisi, R. Ahmed, A. Laref, S. Tahir, First-principles investigations of ZnO monolayers derived from zinc-blende and 5–5 phases for advanced thermoelectric applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 149, 109780 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through the General Research Program under Grant No. G.R.P/67/42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ul Haq, B., AlFaify, S. & Ahmed, R. Thermoelectric properties of the hexagonal- and square-shaped monolayers of ZnO. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 136, 794 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01777-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01777-2