Abstract
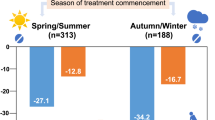
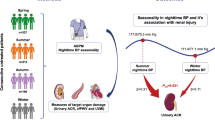
The risk factors for intradialytic systolic blood pressure decline remain poorly understood. We aimed to identify clinical and laboratory predictors of the intradialytic systolic blood pressure decline, considering its seasonal variation. In a retrospective cohort of 47,219 hemodialysis sessions of 307 patients undergoing hemodialysis over one year in three dialysis clinics, the seasonal variation and the predictors of intradialytic systolic blood pressure decline (predialysis systolic blood pressure––nadir intradialytic systolic blood pressure) were assessed using cosinor analysis and linear mixed models adjusted for baseline or monthly hemodialysis-related variables, respectively. The intradialytic systolic blood pressure decline was greatest and least in the winter and summer, respectively, showing a clear seasonal pattern. In both models adjusted for baseline and monthly hemodialysis-related parameters, calcium channel blocker use was associated with a smaller decline (−4.58 [95% confidence interval (CI), −5.84 to −3.33], P < 0.001; −3.66 [95% CI, −5.69 to −1.64], P < 0.001) and α blocker use, with a greater decline (3.25 [95% CI, 1.53–4.97], P < 0.001; 3.57 [95% CI, 1.08–6.06], P = 0.005). Baseline and monthly serum phosphorus levels were positively correlated with the decline (1.55 [95% CI, 0.30–2.80], P = 0.02; 0.59 [95% CI, 0.16–1.00], P = 0.007), and baseline and monthly normalized protein catabolic rates were inversely correlated (respectively, −22.41 [95% CI, −33.53 to −11.28], P < 0.001; 9.65 [95% CI, 4.60–14.70], P < 0.001). In conclusion, calcium channel blocker use, α blocker avoidance, and serum phosphorus-lowering therapy may attenuate the intradialytic systolic blood pressure decline and should be investigated in prospective trials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nitta K, Masakane I, Hanafusa N, Hoshino J, Taniguchi M, Jyoki N, et al. Annual dialysis data report, JSDT renal data registry. J Jpn Soc Dial Ther. 2020;53:579–632. 2019 (Japanese).
Kikuchi K, Hamano T, Wada A, Nakai S, Masakane I. Predilution online hemodiafiltration is associated with improved survival compared with hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2019;95:929–38.
Kanbay M, Ertuglu LA, Afsar B, Ozdogan E, Siriopol D, Covic A, et al. An update review of intradialytic hypotension: concept, risk factors, clinical implications and management. Clin Kidney J. 2020;13:981–93.
Yu J, Liu Z, Shen B, Teng J, Zou J, Ding X. Intradialytic hypotension as an independent risk factor for long-term mortality in maintaining hemodialysis patients: a 5-year follow-up cohort study. Blood Purif. 2018;45:320–6.
Okoye OC, Slater HE, Rajora N. Prevalence and risk factors of intra-dialytic hypotension: a 5 year retrospective report from a single Nigerian Centre. Pan Afr Med J. 2017;28:62.
Cho A, Lee YK, Oh J, Yoon JW, Shin DH, Jeon HJ, et al. The relationship between intradialytic hypotension and vascular calcification in hemodialysis patients. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0185846.
Mc Causland FR, Brunelli SM, Waikar SS. Dialysis dose and intradialytic hypotension: results from the HEMO study. Am J Nephrol. 2013;38:388–96.
Mc Causland FR, Waikar SS. Association of predialysis calculated plasma osmolarity with intradialytic blood pressure decline. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015;66:499–506.
Correa S, Pena-Esparragoza JK, Scovner KM, Mc Causland FR. Predictors of intradialytic symptoms: an analysis of data from the hemodialysis study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;76:331–9.
Kanno Y. Blood pressure management in patients receiving renal replacement therapy. Hypertens Res. 2021;44:7–12.
Mineshima M, Takahashi S, Tomo T, Kawanishi H, Kawaguchi H, Minakuchi J, et al. A clinical significance of intermittent infusion hemodiafiltration using backfiltration of ultrapure dialysis fluid compared to hemodialysis: a multicenter randomized controlled crossover trial. Blood Purif. 2019;48:368–81.
Argilés A, Mourad G, Mion C. Seasonal changes in blood pressure in patients with end-stage renal disease treated with hemodialysis. N. Engl J Med. 1998;339:1364–70.
Cheung AK, Yan G, Greene T, Daugirdas JT, Dwyer JT, Levin NW, et al. Seasonal variations in clinical and laboratory variables among chronic hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2345–52.
Tozawa M, Iseki K, Iseki C, Morita O, Yoshi S, Fukiyama K. Seasonal blood pressure and body weight variation in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Am J Nephrol. 1999;19:660–7.
Spósito M, Nieto FJ, Ventura JE. Seasonal variations of blood pressure and overhydration in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35:812–8.
Usvyat LA, Carter M, Thijssen S, Kooman JP, van der Sande FM, Zabetakis P, et al. Seasonal variations in mortality, clinical, and laboratory parameters in hemodialysis patients: a 5-year cohort study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;7:108–15.
Flythe JE, Xue H, Lynch KE, Curhan GC, Brunelli SM. Association of mortality risk with various definitions of intradialytic hypotension. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26:724–34.
Moen AN, Boomer GS. A tandem cosine algorithm for modeling rhythmic change. Ecol Model. 2000;134:275–82.
Shahar DR, Froom P, Harari G, Yerushalmi N, Lubin F, Kristal-Boneh E. Changes in dietary intake account for seasonal changes in cardiovascular disease risk factors. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1999;53:395–400.
Sega R, Cesana G, Bombelli M, Grassi G, Stella ML, Zanchetti A, et al. Seasonal variations in home and ambulatory blood pressure in the PAMELA population. Pressione Arteriose Monitorate E Loro Associazioni. J Hypertens. 1998;16:1585–92.
Tsuruya K, Kanda E, Nomura T, Iseki K, Hirakata H. Postdialysis blood pressure is a better predictor of mortality than predialysis blood pressure in Japanese hemodialysis patients: the Japan Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Hypertens Res. 2020;43:791–7.
Argilés A, Lorho R, Servel MF, Chong G, Kerr PG, Mourad G. Seasonal modifications in blood pressure are mainly related to interdialytic body weight gain in dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004;65:1795–801.
Yanai M, Satomura A, Uehara Y, Murakawa M, Takeuchi M, Kumasaka K. Circannual rhythm of laboratory test parameters among chronic haemodialysis patients. Blood Purif. 2008;26:196–203.
Uchiyama K, Wakino S, Irie J, Miyamoto J, Matsui A, Tajima T, et al. Contribution of uremic dysbiosis to insulin resistance and sarcopenia. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2020;35:1501–17.
Sherman RA, Casale P, Cody R, Horton MW. Effect of predialysis verapamil on intradialytic blood pressure in chronic hemodialysis patients. ASAIO Trans. 1990;36:67–69.
Tepel M, Hopfenmueller W, Scholze A, Maier A, Zidek W. Effect of amlodipine on cardiovascular events in hypertensive haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2008;23:3605–12.
Krapf R, Hulter HN. Arterial hypertension induced by erythropoietin and erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESA). Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4:470–80.
Goodman WG, London G, Amann K, Block GA, Giachelli C, Hruska KA, et al. Vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43:572–9.
Jono S, McKee MD, Murry CE, Shioi A, Nishizawa Y, Mori K, et al. Phosphate regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. Circ Res. 2000;87:E10–E17.
Ducy P, Zhang R, Geoffroy V, Ridall AL, Karsenty G. Osf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell. 1997;89:747–54.
Reiss AB, Miyawaki N, Moon J, Kasselman LJ, Voloshyna I, D’Avino R Jr, et al. CKD, arterial calcification, atherosclerosis and bone health: Inter-relationships and controversies. Atherosclerosis. 2018;278:49–59.
Bordicchia M, Liu D, Amri EZ, Ailhaud G, Dessì-Fulgheri P, Zhang C, et al. Cardiac natriuretic peptides act via p38 MAPK to induce the brown fat thermogenic program in mouse and human adipocytes. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:1022–36.
Van Buren PN, Inrig JK. Mechanisms and treatment of intradialytic hypertension. Blood Purif. 2016;41:188–93.
Assimon MM, Wang L, Flythe JE. Intradialytic hypertension frequency and short-term clinical outcomes among individuals receiving maintenance hemodialysis. Am J Hypertens. 2018;31:329–39.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all participants in this research project. The authors acknowledge Dr. Shigeaki Ohtsuki for technical and statistical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchiyama, K., Shibagaki, K., Yanai, A. et al. Seasonal variation and predictors of intradialytic blood pressure decline: a retrospective cohort study. Hypertens Res 44, 1417–1427 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00714-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00714-1