Abstract
Introduction
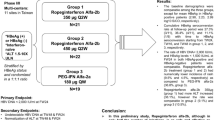
Ropeginterferon alfa-2b is a novel mono-pegylated human recombinant interferon (IFN) with the addition of N-terminal proline covalently attached by a 40-kDa polyethylene (peg) moiety. The present study aimed to evaluate the pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics (PD) profiles and safety of the product in healthy Chinese.
Methods
Forty subjects were enrolled and treated with a single subcutaneous injection of either 180 mcg peg-IFN alfa-2a or 90, 180, and 270 mcg ropeginterferon alfa-2b.
Results
The mean Tmax of ropeginterferon alfa-2b was 92–141 h and the elimination half-life was 78–129 h. Dose-related, non-proportional increase in ropeginterferon alfa-2b exposure was observed, which was higher than for peg-IFN alfa-2a. The PD parameters were similar between each dose level of ropeginterferon alfa-2b. The mean Tmax of β2-microglobulin ranged from 118 to 132 h after a single dose of ropeginterferon alfa-2b. The average Emax was 3 mcg/ml in all dose levels and the mean AUEC0–t ranged from 1608 to 1775 h/mcg/ml. The TEAEs were comparable among each treatment group and no death nor drug-related SAE was reported.
Conclusion
Ropeginterferon alfa-2b is safe and well tolerated after a single subcutaneous injection up to 270 mcg in healthy Chinese.
Clinical Trial Registration
www.chinadrugtrials.org.cn, CTR20190451.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isaacs A, Lindenman NJ. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B 1957;147:258–67.
Asmuth DM, Nguyen HH, Melcher GP, Cohen SH, Pollard RB. Treatments for hepatitis B. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:1353–62.
Fiorani C, Tonelli S, Casolari B, Sacchi S. The role of interferon-alpha in the treatment of myeloproliferative disorders. Curr Pharm Des. 1999;5:987–1013.
Lengfelder E, Berger U, Hehlmann R. Interferon alpha in the treatment of polycythemia vera. Ann Hematol. 2000;79:103–9.
Davis GL, Wong JB, McHutchison JG, Manns MP, Harvey J, Albrecht J. Early virologic response to treatment with peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003;38:645–52.
Sherman M, Yoshida EM, Deschenes M, Krajden M, Bain VG, Peltekian K, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients who failed previous interferon therapy. Gut. 2006;55:1631–8.
Dorr RT. Interferon-alpha in malignant and viral diseases. A review. Drugs. 1993;45:177–211.
Reddy KR, Wright TL, Pockros PJ, Shiffman M, Everson G, Reindollar R, et al. Efficacy and safety of pegylated (40-kd) interferon alpha-2a compared with interferon alpha-2a in noncirrhotic patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2001;33:433–8.
Lindsay KL, Trepo C, Heintges T, Shiffman ML, Gordon SC, Hoefs JC, et al. A randomized, double-blind trial comparing pegylated interferon alfa-2b to interferon alfa-2b as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2001;34:395–403.
Hsu S-J, Yu M-L, Su C-W, Peng C-Y, Chien R-N, Lin H-H, et al. Ropeginterferon Alfa-2b administered every two weeks for patients with genotype 2 chronic hepatitis C. J Formos Med Assoc. 2021;120:956–64.
Cecil BD. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis. Lancet. 2002;359:263–4.
Fried MW. Side effects of therapy of hepatitis C and their management. Hepatology. 2002;36:S237–44.
Bagheri H, Fouladi A, Barange K, Lapeyre-Mestre M, Payen J-L, Montastruc JL, et al. Follow-up of adverse drug reactions from peginterferon alfa-2b-ribavirin therapy. Pharmacotherapy. 2004;24:1546–53.
Verhoef JJF, Carpenter JF, Anchordoquy TJ, Schellekens H. Potential induction of anti-PEG antibodies and complement activation toward PEGylated therapeutics. Drug Discov Today. 2014;19:1945–52.
Huang Y-W, Hsu C-W, Lu S-N, Yu M-L, Su C-W, Su W-W, et al. Ropeginterferon alfa-2b every 2 weeks as a novel pegylated interferon for patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol Int. 2020;14:997–1008.
Miyachi N, Zagrijtschuk O, Kang L, Yonezu K, Qin A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ropeginterferon alfa-2b in healthy Japanese and caucasian subjects after single subcutaneous administration. Clin Drug Investig. 2021;41:391–404.
García-García I, Hernández-González I, Díaz-Machado A, González-Delgado CA, Pérez-Rodríguez S, García-Vega Y, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic characterization of a novel formulation containing co-formulated interferons alpha-2b and gamma in healthy male volunteers. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016;17:58.
Scagnolari C, Bellomi F, Trombetti S, Casato M, Carlesimo M, Bagnato F, et al. Expression of biomarkers of interferon type I in patients suffering from chronic diseases. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;147:270–6.
Sumpio BE, Ernstoff MS, Kirkwood JM. Urinary excretion of interferon, albumin, and beta 2-microglobulin during interferon treatment. Cancer Res. 1984;44:3599–603.
Wagner SM, Melchardt T, Greil R. Ropeginterferon alfa-2b for the treatment of patients with polycythemia vera. Drugs Today. 2020;56:195–202.
Zhu M, Wang M-X, Li Z-R, Wang W, Su X, Jiao Z. Population pharmacokinetics of ropeginterferon alfa-2b: a comparison between healthy Caucasian and Chinese subjects. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:673492.
Gisslinger H, Klade C, Georgiev P, Krochmalczyk D, Gercheva-Kyuchukova L, Egyed M, et al. Ropeginterferon alfa-2b versus standard therapy for polycythaemia vera (PROUD-PV and CONTINUATION-PV): a randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial and its extension study. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7:e196-208.
Remes K, Tienhaara A, Pelliniemi TT. Effects of alpha-interferon on serum beta-2-microglobulin. Leuk Lymphoma. 1996;21:233–8.
Matsuda F, Torii Y, Enomoto H, Kuga C, Aizawa N, Iwata Y, et al. Anti-interferon-α neutralizing antibody is associated with nonresponse to pegylated interferon-α plus ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat. 2012;19:694–703.
Acknowledgements
Funding
This study and the journal’s Rapid Service Fee was funded by PharmaEssentia Corp. The interpretation and conclusions in this study are based on the authors’ view.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Author Contributions
CLT proposed the concept for study and contributed to the design of the study. YWH acted as the medical monitor. YWH, CWT, WW, and JGZ participated in the design of the study, preparation of the protocol, CRF, review of data/analyses, internal and external presentation, as well as preparation of the CSR. YWH and CYT were major contributors in writing the manuscript. BS and MXW were investigators to conduct study and contributed to acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data. YWH, CYT, and AQ contributed to the interpretation of the results and reviewing the manuscript.
List of Investigators
Bo-Song and Mei-xia Wang were investigators in Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China.
Disclosures
Chan-Yen Tsai, Chung-Wei Tsai, Albert Qin, and Chingleou Teng work for PharmaEssentia Corporation headquarter in Taipei, Taiwan. William Wang and Jingjing Zhang work for PharmaEssentia Biotech Ltd, Beijing, China. Yi-Wen Huang was the Senior Director of Medical Research and Head of Pharmacovigilance at PharmaEssentia Corporation headquarter in Taipei, Taiwan from July 02, 2018 to May 31, 2021. Yi-Wen Huang moved to Taipei Medical University Hospital. Bo-Song and Mei-xia Wang have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
The study was conducted in accordance with the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki and its amendments, US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidance, and principles of Good Clinical Practice (GCP) from the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines. The protocol and informed consent form were reviewed and approved by IRB of Beijing Youan Hospital, Capital Medical University (Protocol Number: A17-101) prior to the screening or enrollment of the study participant. The purpose of the study was explained to the subjects before they provided their written informed consent. Subjects were provided with copies of their signed informed consent forms. At the study center, the clinical staff was available to subjects before they entered the study and throughout their participation in the study to answer questions about the study. Subjects were informed about any new development of the product during the study that might have influenced their continued participation in the study.
Data Availability
The data that support the finding of this study are available on request to PharmaEssentia Corp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, YW., Tsai, CY., Tsai, CW. et al. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Novel Long-Acting Ropeginterferon Alfa-2b in Healthy Chinese Subjects. Adv Ther 38, 4756–4770 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-021-01863-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-021-01863-y