Abstract
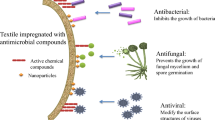
This paper describes the potential use of silver intercalated clay as an antimicrobial finishing agent for cotton textiles meant for health and hygiene applications. Montmorillonite clay (2:1) was intercalated with silver ion through ion exchange reaction. The modified clay was characterized using wide angle X-ray diffractometer (WAXD), Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and inductive coupled plasma spectroscopy (ICP). Results of WAXD revealed that the clay was partly exfoliated after ion exchange reaction. EDX and ICP analysis confirmed the presence of silver ion in modified clay. The silver intercalated clay was integrated on the cotton fabric using pad dry cure method along with low formaldehyde dimethyloldihydroxy ethylene urea (DMDHEU). The antimicrobial and mechanical properties of the finished fabric were studied. The fabric showed excellent antimicrobial activity up to 10 machine washes. The silver ion releases from the fabric and inhibited the growth of bacteria on the surface of the fabric. The release of silver ion from the finished fabric at different perspiration and saline water were analyzed. It was found that the silver ion releases faster in alkaline perspiration medium compared to acid perspiration medium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Purwar and M. Joshi, AATCC Rev., 4, 22 (2004).
M. Rai, A. Yadav, and A. Gade, Biotechnol. Adv., 27, 76 (2009).
Q. L. Feng, J. Wu, G. Q. Chen, F. Z. Cui, T. N. Kim, and J. O. Kim, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 52, 662 (2000).
D. V. Parikh, J. V. Edwards, B. D. Condon, and A. D. Parikh, AATCC Rev., 8, 38 (2008).
N. Vigneshwaran, A. A. Kathe, P. V. Varadarajan, R. P. Nachane, and R. H. Balasubramanya, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 7, 1893 (2007).
A. S. M. Raja, G. Thilagavathi, and T. Kannaian, Indian J. Fibre Text. Res., 35, 59 (2010).
A. I. Wasif and S. K. Laga, Autex Res. J., 9, 5 (2009).
S. Ghosh, S. Yadav, N. Vasanthan, and G. Sekosan, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 115, 716 (2010).
B. Tomsic, B. Simoncic, B. Orel, M. Zerjav, H. Schroers, A. Simoncic, and Z. Samardzijia, Carbohydr. Polym., 75, 618 (2009).
I. Perlshtein, G. Applerot, G. G. Perkas, S. Mikhailov, and A. Gedanken, Nanotechnology, 19, 245075 (2008).
B. Madheswaran, S. Shanmugam, and S. Tetsuo, J. Coat. Technol. Res., 14, 735 (2017).
S. Jiang, E. Newton, C.-W. M. Yuen, and C.-W. Kan, Text. Res. J., 77, 85 (2007).
E. Hontañón, J. Meyer, M. Blanes, V. Cambra, and X. Guo, Inter. J. Theor. Appl. Nanotechnol., 4, 17 (2016).
M. Alexandre and P. Dubois, Mater. Sci. Eng., 28, 1 (2000).
R. Purwar, K. Sai Goutham, and C. Mohan Srivastava, Fiber. Polym., 17, 1206 (2016).
S. M. Magaña, P. Quintana, D. H. Aguilar, J. A. Toledo, C. Ángeles-Chávez, M. A. Cortés, L. León, Y. Freile-Pelegrín, T. López, and R. M. Torres Sánchez, J. Mol. Catal. A Chem., 281, 192 (2008).
K. Malachová, P. Praus, Z. Pavlíčková, and M. Turicová, Appl. Clay Sci., 43, 364 (2009).
P. Praus, M. Turicova, and M. Valskova, J. Braz. Chem. Soc., 19, 549 (2008).
M. Joshi, R. Purwar, J. S. Udakhe, and R. Sreedevi, U. S. Patent, 9192625 (2015).
H. Nakashima, N. Miyano, and T. Takatuka, J. Health Sci., 54, 390 (2008).
A. S. Maryan, M. Montazerb, and T. Harifi, Carbohydr. Polym., 115, 568 (2015).
A. Hebeish, A. El-Shafei, and S. Sharaf, Carbohydr. Polym., 103, 442 (2014).
Y. Yan, Y. Haifeng, L. Junfang, L. Xiaojing, and W. Chao, Text. Res. J., 82, 1422 (2012).
E. E. Hossam and M. K. Zahran, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 75, 106 (2015).
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the M/S Lockheed & Martine, USA for the financial support for conducting the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Begam, R., Joshi, M. & Purwar, R. Antimicrobial Finishing of Cotton Textiles using Silver Intercalated Clay. Fibers Polym 23, 148–154 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-3178-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-021-3178-9