Abstract
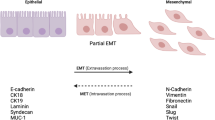
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) plays an important role in function and development of the mammary gland. However, high levels of IGF-1 has been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer development. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process where epithelial cells lose their epithelial characteristics and acquire a mesenchymal phenotype, which is considered one of the most important mechanisms in cancer initiation and promotion of metastasis. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are released into the extracellular space by different cell types, which mediate intercellular communication and play an important role in different physiological and pathological processes, such as cancer. In this study, we demonstrate that EVs from MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells stimulated with IGF-1 (IGF-1 EVs) decrease the levels of E-cadherin, increase the expression of vimentin and N-cadherin and stimulate the secretion of metalloproteinase-9 in mammary non-tumorigenic epithelial cells MCF10A. IGF-1 EVs also induce the expression of Snail1, Twist1 and Sip1, which are transcription factors involved in EMT. Moreover, IGF-1 EVs induce activation of ERK1/2, Akt1 and Akt2, migration and invasion. In summary, we demonstrate, for the first time, that IGF-1 EVs induce an EMT process in mammary non-tumorigenic epithelial cells MCF10A.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anisimov VN, Bartke A (2013) The key role of growth hormone-insulin-IGF-1 signaling in aging and cancer. Crit Rev Oncol/hematol 87:201–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.01.005
Baranwal S, Alahari SK (2009) Molecular mechanisms controlling E-cadherin expression in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384:6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.04.051
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Cano A et al (2000) The transcription factor snail controls epithelial–mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol 2:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/35000025
Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C (2014) Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 30:255–289. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326
Chen L et al (2018) HCC-derived exosomes elicit HCC progression and recurrence by epithelial–mesenchymal transition through MAPK/ERK signalling pathway. Cell Death Dis 9:513. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0534-9
Christopoulos PF, Msaouel P, Koutsilieris M (2015) The role of the insulin-like growth factor-1 system in breast cancer. Mol Cancer 14:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0291-7
Das K et al (2019) Triple-negative breast cancer-derived microvesicles transfer microRNA221 to the recipient cells and thereby promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem 294:13681–13696. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.008619
Dillon RL, Marcotte R, Hennessy BT, Woodgett JR, Mills GB, Muller WJ (2009) Akt1 and akt2 play distinct roles in the initiation and metastatic phases of mammary tumor progression. Cancer Res 69:5057–5064. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4287
Duffy MJ, McGowan PM, Crown J (2012) Targeted therapy for triple-negative breast cancer: where are we? Int J Cancer 131:2471–2477. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.27632
Espinosa-Neira R, Mejia-Rangel J, Cortes-Reynosa P, Salazar EP (2011) Linoleic acid induces an EMT-like process in mammary epithelial cells MCF10A. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 43:1782–1791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2011.08.017
Farabaugh SM, Boone DN, Lee AV (2015) Role of IGF1R in breast cancer subtypes stemness, and lineage differentiation. Front Endocrinol 6:59. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2015.00059
Firth SM, Baxter RC (2002) Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev 23:824–854. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2001-0033
Galindo-Hernandez O et al (2015) Extracellular vesicles from women with breast cancer promote an epithelial–mesenchymal transition-like process in mammary epithelial cells MCF10A. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med 36:9649–9659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3711-9
Galindo-Hernandez O, Serna-Marquez N, Castillo-Sanchez R, Salazar EP (2014) Extracellular vesicles from MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells stimulated with linoleic acid promote an EMT-like process in MCF10A cells. Prostaglandins, Leukot, Essential Fatty Acids 91:299–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2014.09.002
Gallagher EJ, LeRoith D (2010) The proliferating role of insulin and insulin-like growth factors in cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:610–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2010.06.007
Garcia-Hernandez A, Leal-Orta E, Ramirez-Ricardo J, Cortes-Reynosa P, Thompson-Bonilla R, Salazar EP (2020) Linoleic acid induces secretion of extracellular vesicles from MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells that mediate cellular processes involved with angiogenesis in HUVECs. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Med 153:106519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2020.106519
Gavert N, Ben-Ze’ev A (2008) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition and the invasive potential of tumors. Trends Mol Med 14:199–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2008.03.004
Godone RLN, Leitao GM, Araujo NB, Castelletti CHM, Lima-Filho JL, Martins DBG (2018) Clinical and molecular aspects of breast cancer: targets and therapies. Biomed Pharmacother = Biomed Pharmacother 106:14–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.066
Greening DW, Gopal SK, Mathias RA, Liu L, Sheng J, Zhu HJ, Simpson RJ (2015) Emerging roles of exosomes during epithelial–mesenchymal transition and cancer progression. Semin Cell Dev Biol 40:60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.02.008
Gross JM, Yee D (2003) The type-1 insulin-like growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase and breast cancer: biology and therapeutic relevance. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1023720928680
Gumbiner BM (2005) Regulation of cadherin-mediated adhesion in morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:622–634. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1699
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y, Hu LL (2020) ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med 19:1997–2007. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2020.8454
Hinz N, Jucker M (2019) Distinct functions of AKT isoforms in breast cancer: a comprehensive review. Cell Commun Signal: CCS 17:154. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-019-0450-3
Hulit J et al (2007) N-cadherin signaling potentiates mammary tumor metastasis via enhanced extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Can Res 67:3106–3116. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3401
Hwa V, Oh Y, Rosenfeld RG (1999) The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily. Endocr Rev 20:761–787. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv.20.6.0382
Irie HY et al (2005) Distinct roles of Akt1 and Akt2 in regulating cell migration and epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol 171:1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200505087
Jones RA, Campbell CI, Gunther EJ, Chodosh LA, Petrik JJ, Khokha R, Moorehead RA (2007) Transgenic overexpression of IGF-IR disrupts mammary ductal morphogenesis and induces tumor formation. Oncogene 26:1636–1644. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209955
Jurj A, Zanoaga O, Braicu C, Lazar V, Tomuleasa C, Irimie A, Berindan-Neagoe I (2020) A comprehensive picture of extracellular vesicles and their contents. Mol Transf Cancer Cells Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020298
Kalra H, Drummen GP, Mathivanan S (2016) Focus on extracellular vesicles: introducing the next small big thing. Int J Mol Sci 17:170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17020170
Kanada M, Bachmann MH, Contag CH (2016) Signaling by extracellular vesicles advances cancer hallmarks. Trends Cancer 2:84–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2015.12.005
Ke Z et al (2006) MMP-2 mediates ethanol-induced invasion of mammary epithelial cells over-expressing ErbB2. Int J Cancer 119:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21769
Leal-Orta E, Ramirez-Ricardo J, Cortes-Reynosa P, Galindo-Hernandez O, Salazar EP (2019) Role of PI3K/Akt on migration and invasion of MCF10A cells treated with extracellular vesicles from MDA-MB-231 cells stimulated with linoleic acid. J Cell Commun Signal 13:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-018-0490-2
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW (2006) The epithelial–mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol 172:973–981. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200601018
Li H, Batth IS, Qu X, Xu L, Song N, Wang R, Liu Y (2017) IGF-IR signaling in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and targeting IGF-IR therapy: overview and new insights. Mol Cancer 16:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-016-0576-5
Li W et al (2018) Akt1 inhibition promotes breast cancer metastasis through EGFR-mediated beta-catenin nuclear accumulation. Cell Commun Signal: CCS 16:82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-018-0295-1
Lu W, Kang Y (2019) Epithelial–mesenchymal plasticity in cancer progression and metastasis. Dev Cell 49:361–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.04.010
Min C, Eddy SF, Sherr DH, Sonenshein GE (2008) NF-kappaB and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of cancer. J Cell Biochem 104:733–744. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21695
Motallebnezhad M, Aghebati-Maleki L, Jadidi-Niaragh F, Nickho H, Samadi-Kafil H, Shamsasenjan K, Yousefi M (2016) The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) in breast cancer: biology and treatment strategies. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med 37:11711–11721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5176-x
Papa V et al (1993) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptors are overexpressed and predict a low risk in human breast cancer. Can Res 53:3736–3740
Park MJ et al (2000) Protein kinase C activation by phorbol ester increases in vitro invasion through regulation of matrix metalloproteinases/tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases system in D54 human glioblastoma cells. Neurosci Letters 290:201–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(00)01358-6
Peinado H, Portillo F, Cano A (2004) Transcriptional regulation of cadherins during development and carcinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol 48:365–375. https://doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.041794hp
Ramirez-Ricardo J et al (2020) Circulating extracellular vesicles from patients with breast cancer enhance migration and invasion via a Srcdependent pathway in MDAMB231 breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 22:1932–1948. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11259
Raposo G, Stoorvogel W (2013) Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol 200:373–383. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201211138
Redzic JS et al (2013) Extracellular vesicles secreted from cancer cell lines stimulate secretion of MMP-9, IL-6, TGF-beta1 and EMMPRIN. PLoS ONE 8:e71225. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071225
Saitoh M (2018) Involvement of partial EMT in cancer progression. J Biochem 164:257–264. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvy047
Seccareccia E, Brodt P (2012) The role of the insulin-like growth factor-i receptor in malignancy: an update. Growth Horm IGF Res: off J Growth Horm Res Soc Int IGF Res Soc 22:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ghir.2012.09.003
Thiery JP (2003) Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:740–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2003.10.006
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA (2009) Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139:871–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.007
Turturici G, Tinnirello R, Sconzo G, Geraci F (2014) Extracellular membrane vesicles as a mechanism of cell-to-cell communication: advantages and disadvantages. AmJ Physiol Cell Physiol 306:C621-633. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00228.2013
Vader P, Breakefield XO, Wood MJ (2014) Extracellular vesicles: emerging targets for cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med 20:385–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2014.03.002
Vagia E, Mahalingam D, Cristofanilli M (2020) The landscape of targeted therapies in TNBC. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12040916
Wang Y, Cao S, Chen Y (2015) Molecular treatment of different breast cancers. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 15:701–720. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520615666150129211901
Wei F et al (2020) Plasma endothelial cells-derived extracellular vesicles promote wound healing in diabetes through YAP and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Aging 12:12002–12018. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103366
Yakar S, Leroith D, Brodt P (2005) The role of the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor axis in tumor growth and progression: lessons from animal models. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:407–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2005.01.010
Yilmaz M, Christofori G (2009) EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:15–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9169-0
Zhou X et al (2019) Mesenchymal stem cellderived extracellular vesicles promote the in vitro proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through the activation of the ERK pathway. Int J Oncol 54:1843–1852. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2019.4747
Zielinska HA, Bahl A, Holly JM, Perks CM (2015) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer: a role for insulin-like growth factor I and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3? Breast Cancer 7:9–19. https://doi.org/10.2147/BCTT.S43932
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Nora Ruiz and Maria de Lourdes-Rojas (LaNSE, Cinvestav-IPN) for their technical assistance in TEM.
Funding
This research was funded by CONACYT (255429) and CONACYT-FOSISS (Salud 2015-1-261637), Mexico. Grants from CONACYT supported E L-O, J R-R and AG-H.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12079_2021_638_MOESM2_ESM.tif
IGF-1 Induces migration in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Migration assays were performed with MDA-MB-231 cells unstimuated (Basal) and stimulated with 1, 5, 10, 20 and 50 nM IGF-1 for 48. One control of migration was included (FBS). Graph represents the mean ± SD and indicate the fold of migration above basal value. *P˂0.05, ***P˂0.001. (TIF 1845 KB)
12079_2021_638_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Schematic diagram showing the general experimental procedure of stimulation of MDA-MB-231 cells with 10 nM IGF-1 for 12, 24, 36 and 48 h and the isolation of EV fractions, as well as the treatment of MCF10A or MDA-MB-231 cells with the EVs isolated. (TIF 1389 KB)
12079_2021_638_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Ctrl EVs do not regulate the expression of E- and N-cadherin. MCF10A cells were treated for various periods of time with Ctrl EVs and lysed. a and b Cell lysates were analyzed by WB with anti-E-cadherin Ab, anti-N-cadherin Ab and anti-actin Ab. One control of MCF10A cells without treatment with EVs was included (Basal). Graphs represent the mean ± SD and indicate the fold of E-cadherin and N-cadherin above basal value. ns: not significant. (TIF 498 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leal-Orta, E., Ramirez-Ricardo, J., Garcia-Hernandez, A. et al. Extracellular vesicles from MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells stimulated with insulin-like growth factor 1 mediate an epithelial–mesenchymal transition process in MCF10A mammary epithelial cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 16, 531–546 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-021-00638-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-021-00638-y