Abstract
We consider black hole solutions with electric and magnetic sources in the four-dimensional Einstein-Born-Infeld-AdS theory with spherical, planar and hyperbolic horizon geometries. Exact analytical solutions for the metric function, electric and magnetic fields were obtained and they recover the RN-AdS black hole in the limit \(\beta \rightarrow +\infty \) for spherical horizon in the absence of the magnetic charge. Expressions for temperature, electric and magnetic potential were obtained and they satisfy the first law of the extended black hole thermodynamics, where a negative cosmological constant is associated with thermodynamic pressure. Also, the Born-Infeld vacuum polarization term \(Bd\beta \) was included into the first law in order to satisfy the Smarr relation. Critical behavior of the black hole was examined and condition on electric and magnetic charges were obtained when phase transition appears. Also, the critical ratio and capacity at constant pressure were calculated. Electric and magnetic charges enter into the metric function and thermodynamic quantities symmetrically and thus the presence of the magnetic charge does not bring very significant new features. Finally, we examine the Joule-Thomson expansion if the black hole mass is fixed. The inversion and isenthalpic curves were plotted and the cooling and heating regions were demonstrated. These results recover the Joule-Thomson expansion recently considered for the RN-AdS black hole in the corresponding limit.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kastor, D., Ray, S., Traschen, J.: Class. Quantum Grav. 26, 258 (2009)
Dolan, B.P.: Class. Quantum Grav. 28, 125020 (2011)
Dolan, B.P.: Class. Quantum Grav. 28, 235017 (2011)
Sekiwa, Y.: Phys. Rev. D 73, 084009 (2006)
Cvetič, M., Gibbons, G.W., Kubizňák, D., Pope, C.N.: Rhys. Rev. D 84, 024037 (2011)
Kubizňák, D., Mann, R.B., Teo, M.: Class. Quantum Grav. 34, 063001 (2017)
Kubizňák, D., Mann, R.B.: J. High Energ. Phys. 07, 033 (2012)
Altamirano, N., Kubizňák, D., Mann, R.B., Sherkatghanad, Z.: Galaxies 2, 89 (2014)
Aydıner, E., Okcu, O.: Eur. Phys. J. C 77, 24 (2017)
Jie-Xiong, M., Gu-Qiang, L., Shan-Quan, L., Xiao-Bao, X.: Phys. Rev. D 98, 124032 (2018)
Cisterna, A., Shi-Qian, H., Xiao-Mei, K.: Phys. Lett. B 797, 134883 (2019)
Bi, S., Du, M., Tao, J., Yao, F.: Chin. Phys. C 45, 025109 (2021)
Mazharimousavi, S.H., Halilsoy, M., Gurtug, O.: Eur. Phys. J. C 74, 2735 (2014)
Hassaïne, M., Martínez, C.: Phys. Rev. D 75, 027502 (2007)
Hassaïne, M., Martínez, C.: Class. Quantum Grav. 25, 195023 (2008)
Hendi, S.H.: Prog. Theor. Phys. 124, 493 (2010)
Panotopoulos, G., Rincón, Á.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 28, 1950016 (2019)
Tataryn, M.B., Stetsko, M.M.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 29, 2050111 (2020)
Gonzalez, H.A., Hassaïne, M., Martinez, C.: Phys. Rev. D 80, 104008 (2009)
Born, M., Infeld, L.: Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 144, 425 (1934)
Fernando, S., Krug, D.: Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 35, 129 (2003)
Banerjee, R., Roychowdhury, D.: Phys. Rev. D 85, 044040 (2012)
Banerjee, R., Roychowdhury, D.: Phys. Rev. D 85, 104043 (2012)
Li, S., Lü, H., Wei, H.: J. High Energ. Phys. 07, 004 (2016)
Myung, Y.S., Yong-Wan, K., Young-Jai, P.: Phys. Rev. D 78, 084002 (2008)
Dey, T.K.: Phys. Lett. B 595, 484 (2004)
Rong-Gen, C., Da-Wei, P., Wang, A.: Phys. Rev. D 70, 124034 (2004)
Mišković, O., Olea, R.: Phys Rev. D 77, 124048 (2008)
Yi-Huan, W.: Chin. Phys. B 19, 090404 (2010)
Gunasekaran, S., Kubizňák, D., Mann, R.B.: J. High Energ. Phys. 11, 110 (2012)
De-Cheng, Z., Shao-Jun, Z., Wang, B.: Phys. Rev. D 89, 044002 (2014)
Bretón, N., Clark, T., Fernando, S.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 26, 1750112 (2017)
Hendi, S.H., Allahverdizadeh, M.: Adv. High Energy Phys. 390101, 390101 (2014)
Sheykhi, A., Hajkhalili, S.: Phys. Rev. D 89, 104019 (2014)
Hendi, S.H., Panahiyan, S., Panah, B.E.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 25, 1650010 (2016)
Tataryn, M.B., Stetsko, M.M.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 28, 1950160 (2019)
Jiménez, J.B., Heisenberg, L., Olmo, G.J., Rubiera-Garcia, D.: Phys. Rep. 727, 1 (2018)
Gaete, P., Helayël-Neto, J.A.: Eur. Phys. Lett. 119, 51001 (2017)
Kruglov, S.I.: Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 12, 1550073 (2015)
Shapere, A.D., Trivedi, S., Wilczek, F.: Mod. Phys. Lett. A 6, 2677 (1991)
Sen, A.: Nucl. Phys. B 404, 109 (1993)
Chamseddine, A.H., Sabra, W.A.: Phys. Lett. B 485, 301 (2000)
Hartnoll, S.A., Kovtun, P.K.: Phys. Rev. D 76, 066001 (2007)
Hartnoll, S.A., Kovtun, P.K., Muller, M., Sachdev, S.: Phys. Rev. B 76, 144502 (2007)
Albash, T., Johnson, C.V.: J. High Energ. Phys. 09, 121 (2008)
Wirschins, M., Sood, A., Kunz, J.: Phys. Rev. D 63, 084002 (2001)
Lü, H., Pang, Y., Pope, C.N.: J. High Energ. Phys. 11, 033 (2013)
Dutta, S., Jain, A., Soni, R.: J. High Energ. Phys. 12, 060 (2013)
Eiroa, E.F.: Phys. Rev. D 73, 043002 (2006)
Gibbons, G.W., Rasheed, D.A.: Nucl. Phys. B 454, 185 (1995)
Stefanov, IZh, Yazadjiev, S.S., Todorov, M.D.: Phys. Rev. D 75, 084036 (2007)
Chemissany, W.A., Mees de Roo, S.: Class Quantum Grav. 25, 225009 (2008)
Kruglov, S.I.: Ann. Phys. 383, 550 (2017)
Kruglov, S.I.: Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 51, 121 (2019)
Meng, K., Cao, L., Zhao, J., Zhou, T., Qin, F., Deng, M.: Phys. Lett. B 819, 136420 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
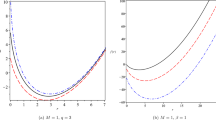
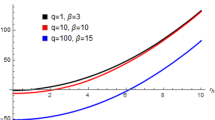
Graphs on the Fig. 5 illustrate solutions of the first equation of the system (24) and also Eq. (35) depending on parameter \(\beta \) for various other parameters. Graphs on the Fig. 6 demonstrate the dependence of the critical ratio (29) on parameters \(\beta \) and charges \(q_e\), \(q_m\).
Here q stands for \(\sqrt{q_e^2+q_m^2}\). These two identical graphs demonstrate, that the critical ratio (29) depends only on the combination \(\beta q\). On the graph a solid curves correspond to \(q_1=0.5\), \(q_2=1\), \(q_3=2\) from bottom to top. The horizontal dashed line denotes the RN-AdS limit, namely 3/8. Vertical lines correspond to \(\beta _1=4\), \(\beta _2=2\), \(\beta _3=1\) from right to left. The horizontal dotted line crosses the solid curves in points where \(\beta _1q_1=\beta _2q_2=\beta _3q_3=2\). Parameters on the graph (b) correspond to the ones on the graph (a) by replacing \(\beta \rightarrow q\), \(q\rightarrow \beta \)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tataryn, M.B., Stetsko, M.M. Thermodynamics of a static electric-magnetic black hole in Einstein-Born-Infeld-AdS theory with different horizon geometries. Gen Relativ Gravit 53, 72 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-021-02842-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10714-021-02842-y